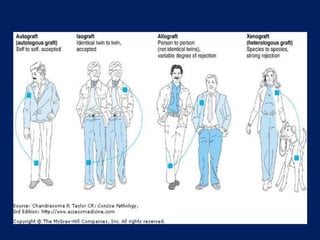
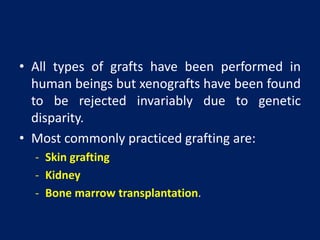
Transplant rejection occurs when the immune system of a transplant recipient attacks and rejects the donated organ or tissue. There are four types of grafts based on genetic relationship between donor and recipient: autografts, isografts, allografts, and xenografts. For successful transplantation without rejection, matching major histocompatibility locus antigens between donor and recipient is important. Rejection can be avoided by tissue typing to ensure donor and recipient tissues are as similar as possible.