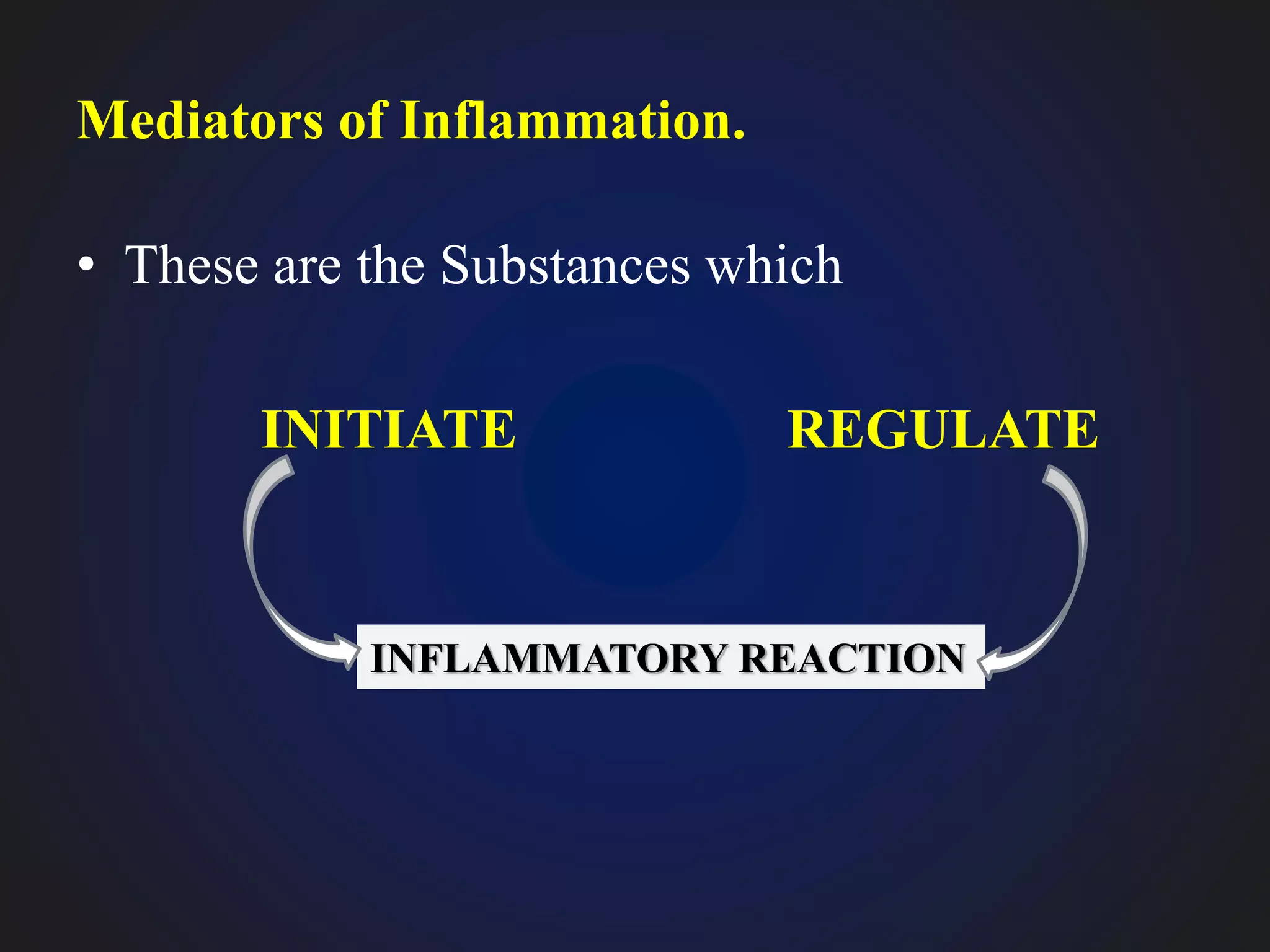
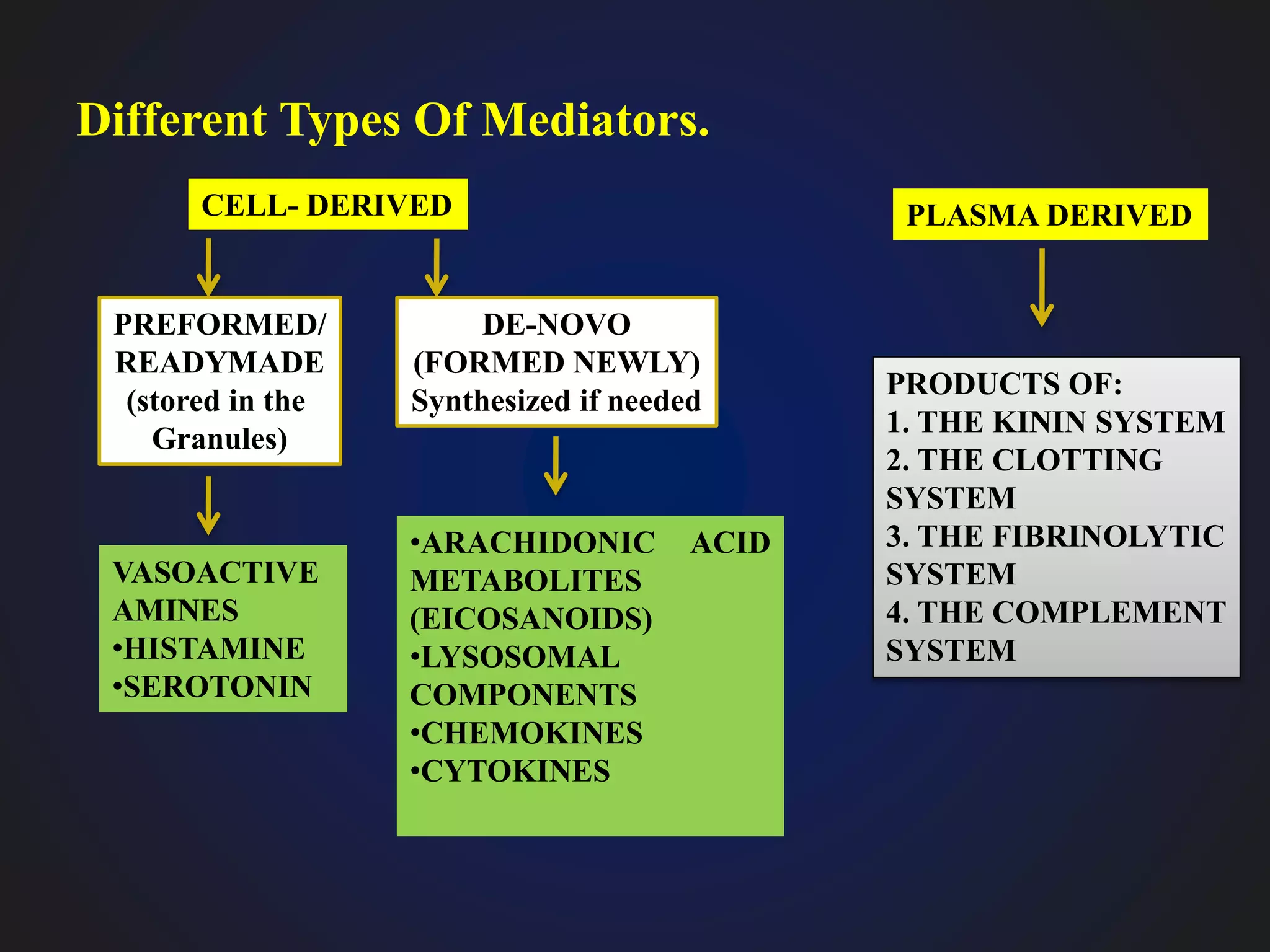
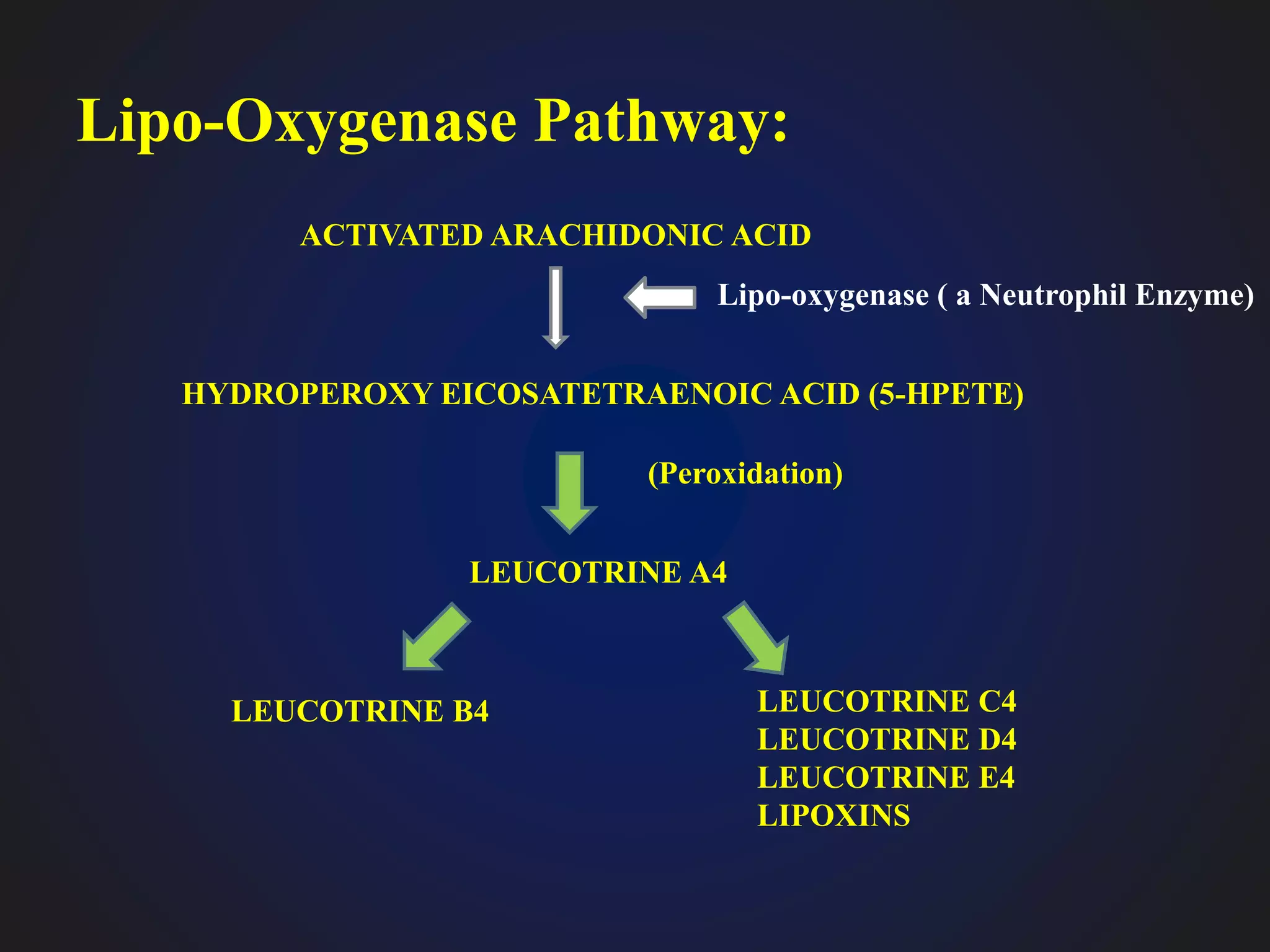
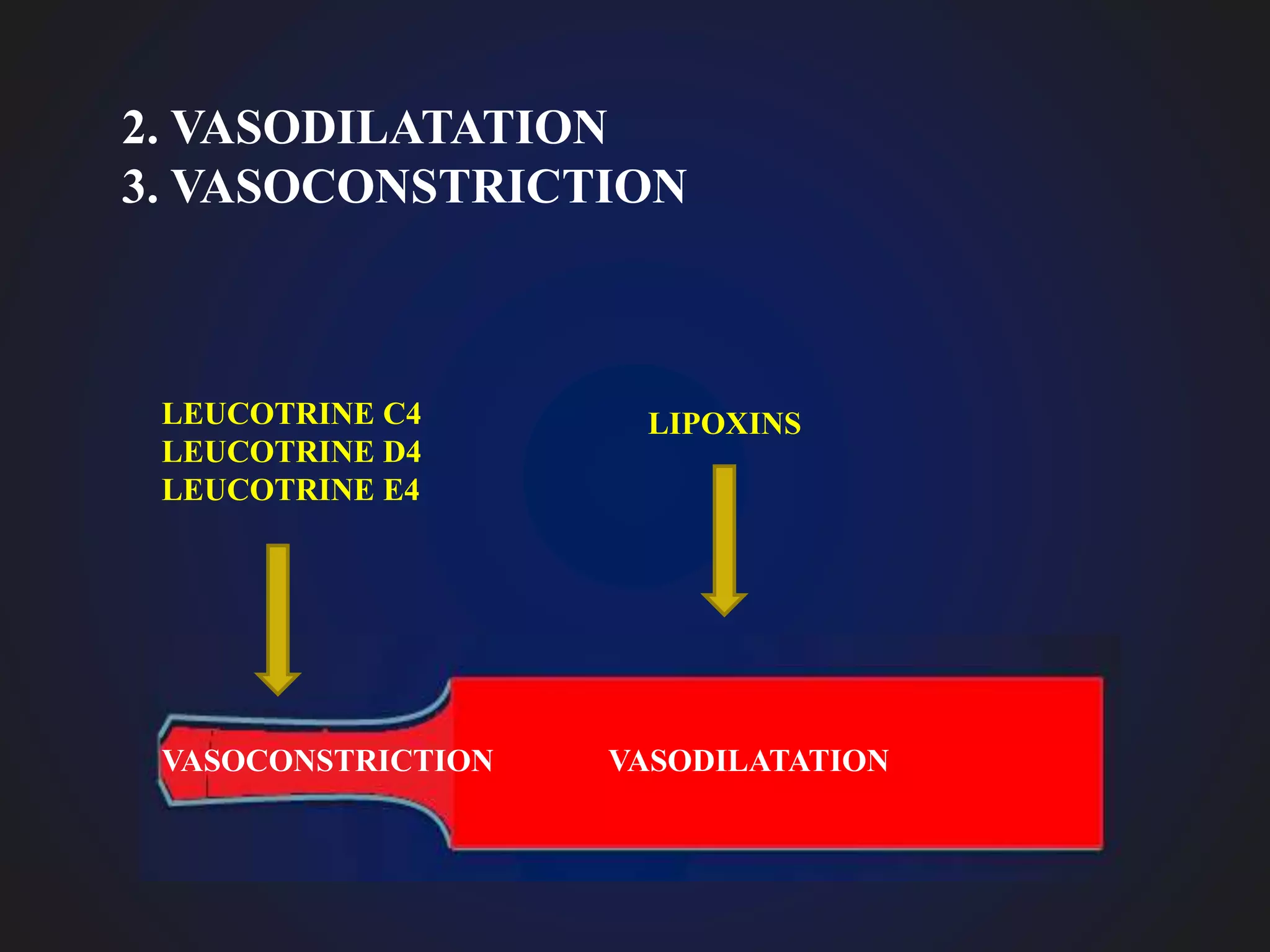
This document discusses mediators of inflammation, which are substances that initiate and regulate the inflammatory reaction. There are several types of mediators, including vasoactive amines like histamine and serotonin, arachidonic acid metabolites called eicosanoids, and cytokines. Eicosanoids are potent mediators that are derived from arachidonic acid through either the cyclooxygenase pathway, producing prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and prostacyclin, or the lipoxygenase pathway, producing leukotrienes. These mediators have various effects like vasodilation, vasoconstriction, and bronchodilation or bronchonconstriction.