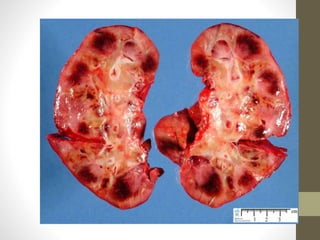
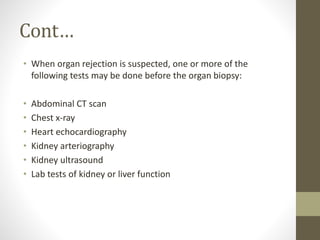
Transplant rejection occurs when a transplant recipient's immune system attacks a transplanted organ, recognizing it as foreign. It can occur quickly due to an antigen mismatch or develop over years. Symptoms depend on the organ but may include decreased function. Tests may include biopsies and imaging. Treatment aims to suppress the immune system with medications for life to prevent rejection, while regular monitoring for signs of rejection is important.