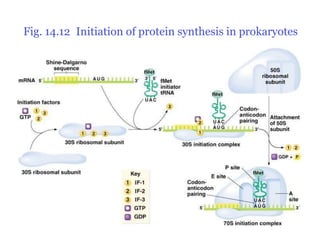
Ribosomes translate mRNA into polypeptides. They consist of two subunits containing rRNA and proteins. tRNAs carry specific amino acids and recognize mRNA codons through complementary base pairing between their anticodons. Translation involves initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the small ribosomal subunit binds the 5' end of mRNA. Elongation adds amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain through peptide bond formation. Termination releases the polypeptide when a stop codon is reached. Accurate protein synthesis depends on specific interactions between mRNA codons, tRNA anticodons, and the ribosomal subunits.