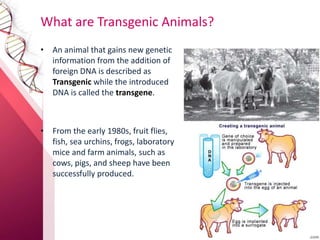
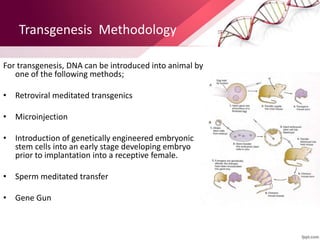
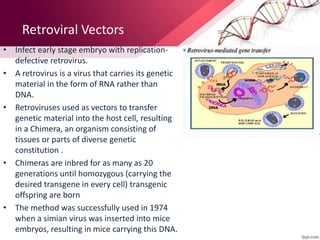
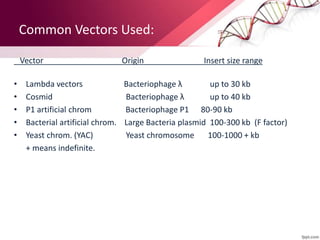
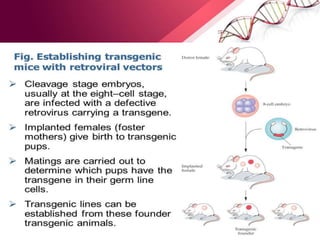
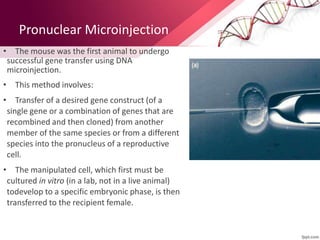
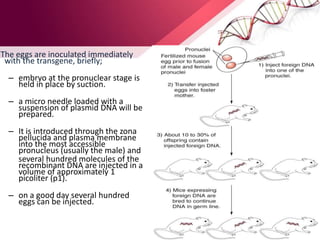
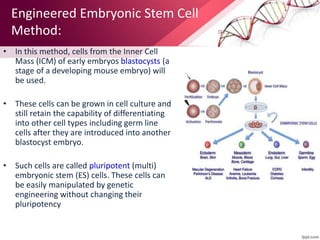
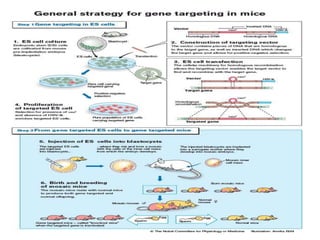
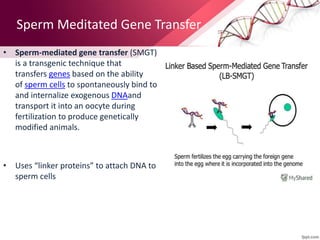
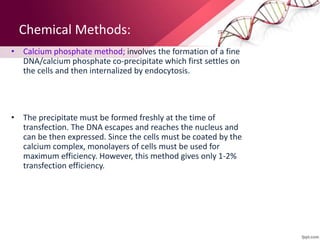
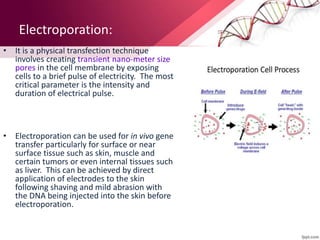
Transgenic animals are produced by introducing foreign DNA into an animal's genome. The first transgenic animal was a mouse created in 1974. Since then, various methods have been used to generate transgenic fish, livestock, and other species. Transgenic animals have applications in biomedical research, agriculture, and industry. They can serve as models for human disease or help produce pharmaceuticals in their milk. However, transgenesis also carries risks if the inserted gene has unintended effects on the animal's development or physiology.