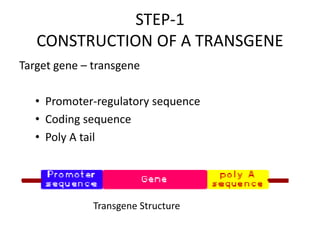
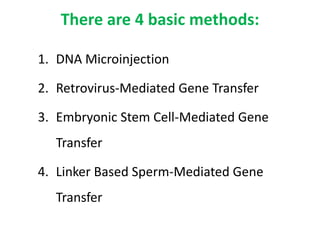
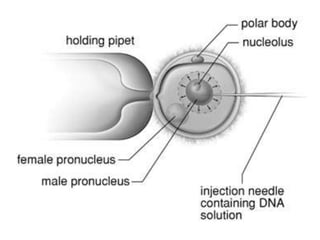
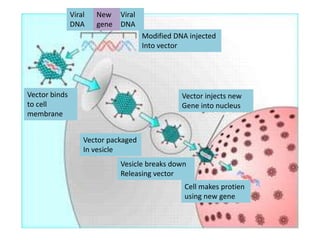
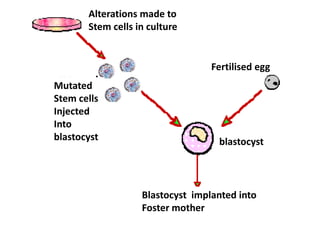
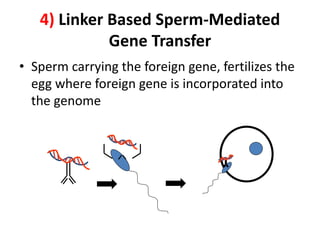
Transgenic animals are created through recombinant DNA technology by inserting foreign genes into the animal's genome. This is done to improve livestock, use animals as bioreactors for pharmaceutical production, and for research purposes. The main methods of creating transgenic animals are DNA microinjection, retrovirus-mediated gene transfer, embryonic stem cell transfer, and sperm-mediated gene transfer. Examples include transgenic cows that produce more nutritious milk, pigs with genes to reduce environmental pollution, and mice used widely as model organisms. While transgenic animals have benefits, there are also ethical concerns regarding animal welfare and unintended environmental impacts.