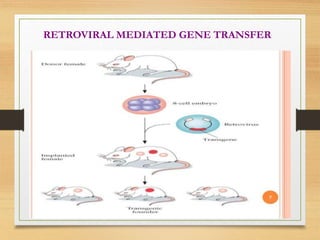
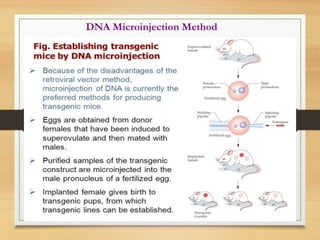
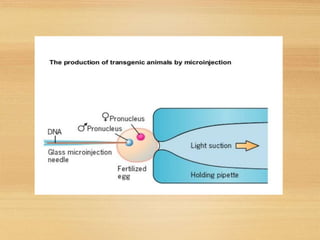
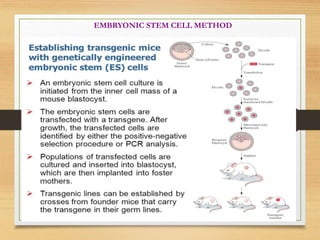
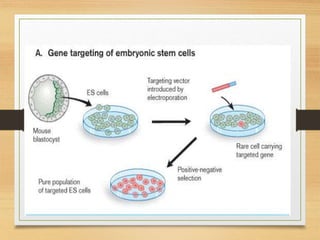
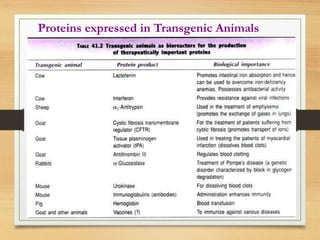
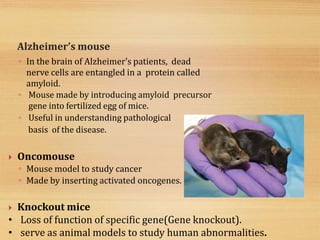
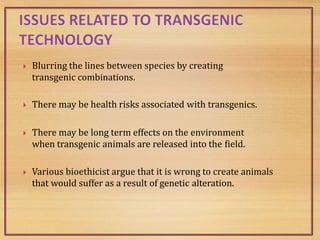
This document discusses transgenic animals. It defines transgenic animals as those with foreign genes deliberately inserted into their genomes. It describes the three main methods for creating transgenic animals: retrovirus-mediated gene transfer, DNA microinjection, and embryonic stem cell-mediated gene transfer. Examples are given of transgenic animals created for medical, agricultural, and industrial purposes, such as disease-resistant livestock, bioreactors that produce useful proteins, and fish engineered for rapid growth. Both the promises and ethical concerns of transgenic technology are acknowledged.