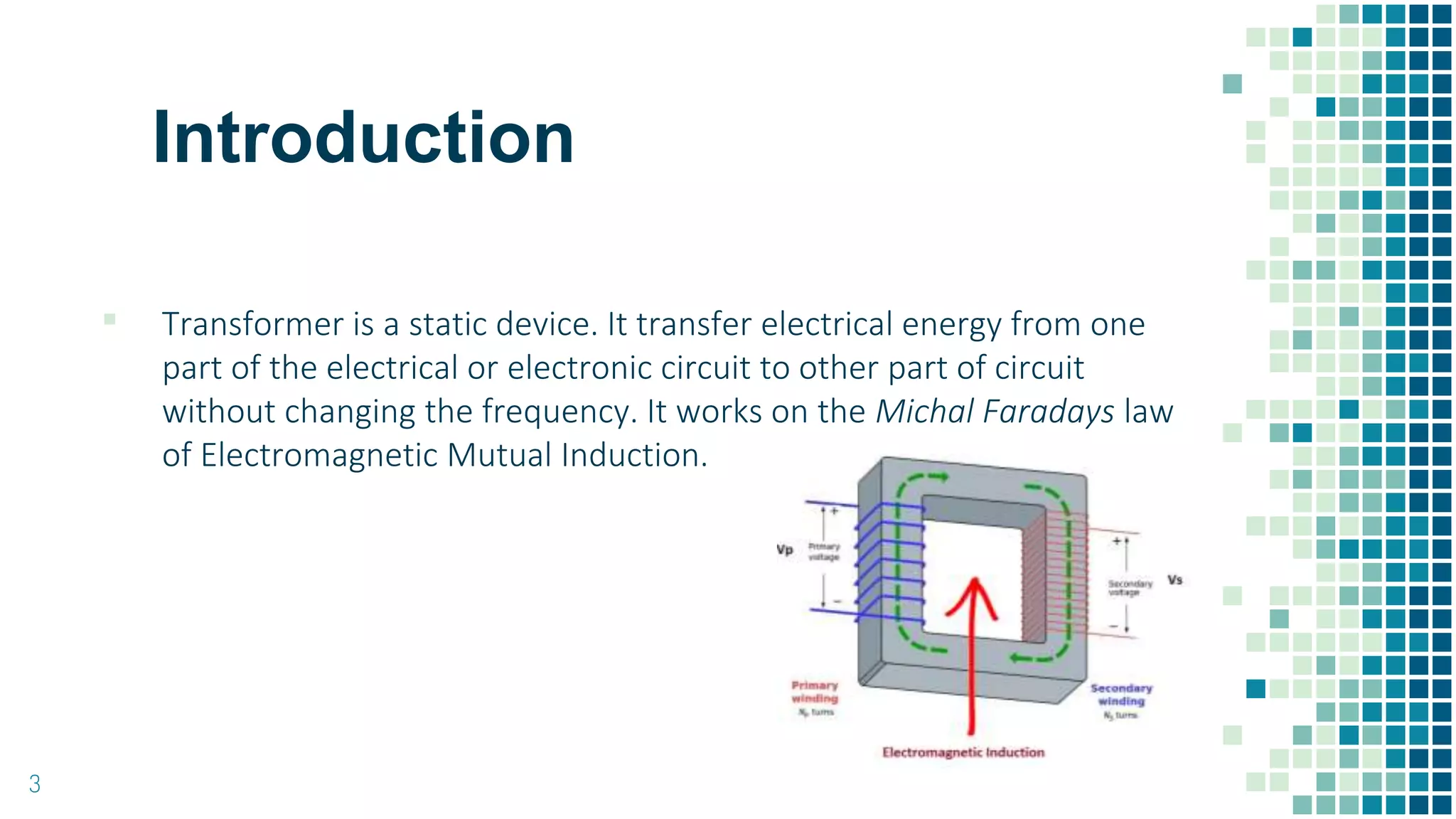
This document discusses transformers, including their history, principles of operation, construction, types, applications, and need. Transformers transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction without changing frequency. The first transformer was developed in 1885 by Z.B.D. It works by inducing an electromotive force in a secondary winding through a changing magnetic field generated by a primary winding. Transformers can be classified based on their construction, windings, and coolant material. They are used for impedance matching, voltage transformation in power applications, and adjusting voltages for appliances and transmission.