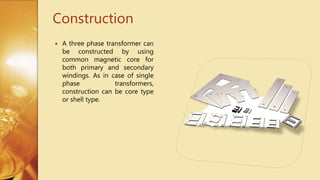
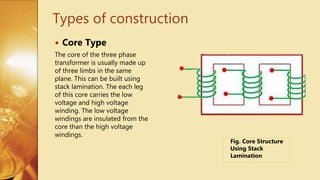
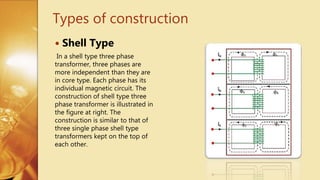
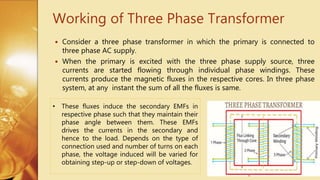
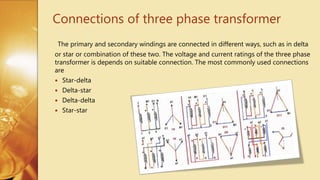
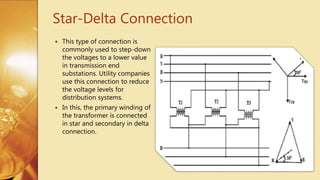
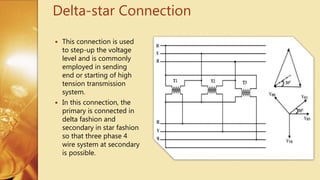
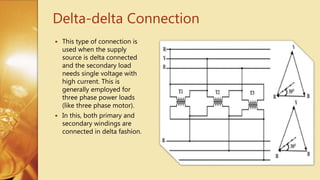
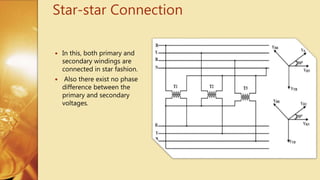
Three Phase Transformer
Presented by:
Rizwan Yaseen 2017-EE-432
Zeeshan Saeed 2017-EE-414
Muhammad Hamad 2017-EE-404
Muhammad Zeeshan 2017-EE-402
A three phase transformer is made of three sets of primary and secondary windings wound around the legs of a common iron core. It allows for higher transmission voltages using lower amperage wiring. The core can be constructed as either a core type or shell type configuration. A three phase transformer works by inducing secondary voltages from the three phase primary voltages to maintain the proper phase relationships for power distribution.