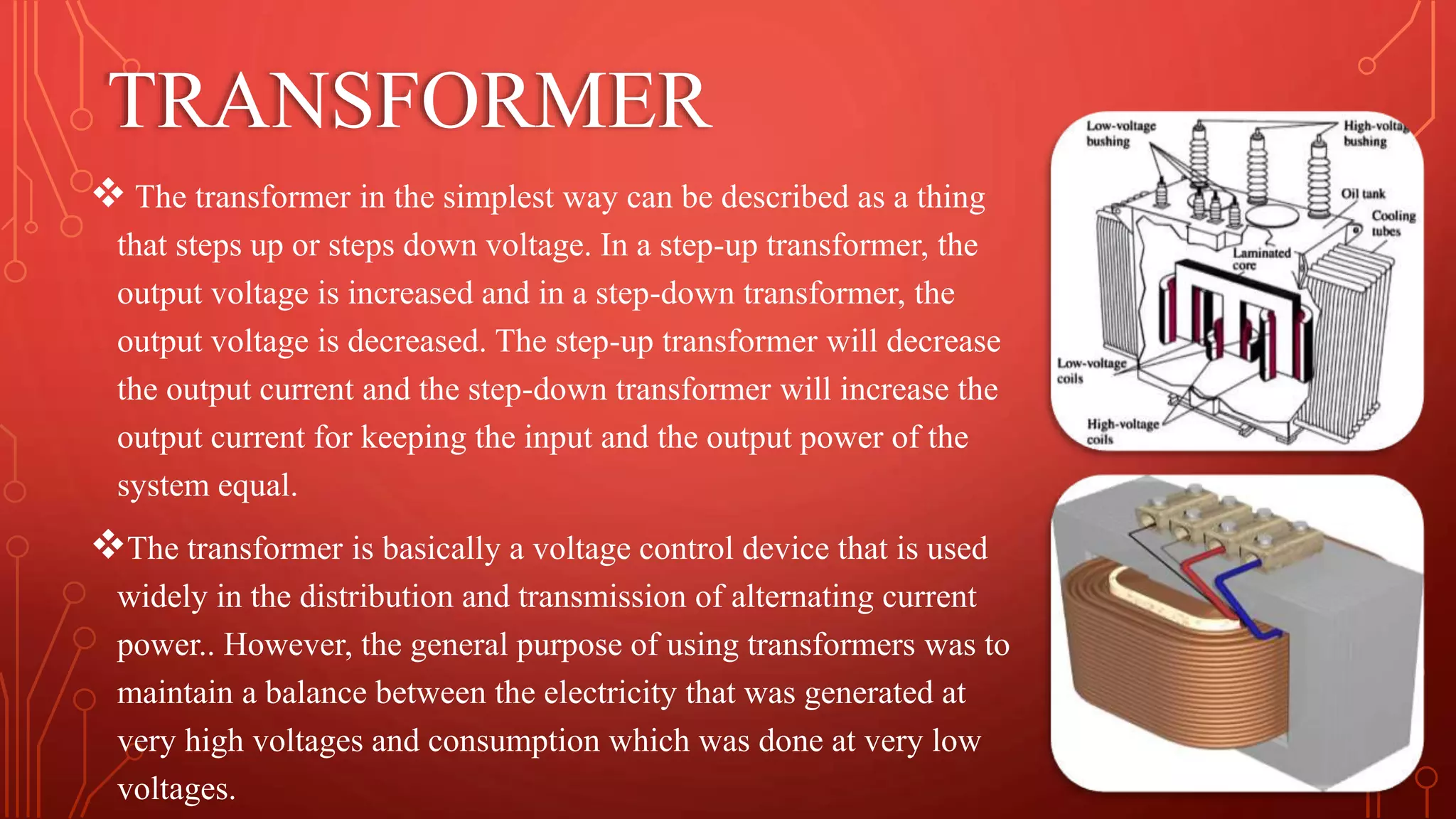
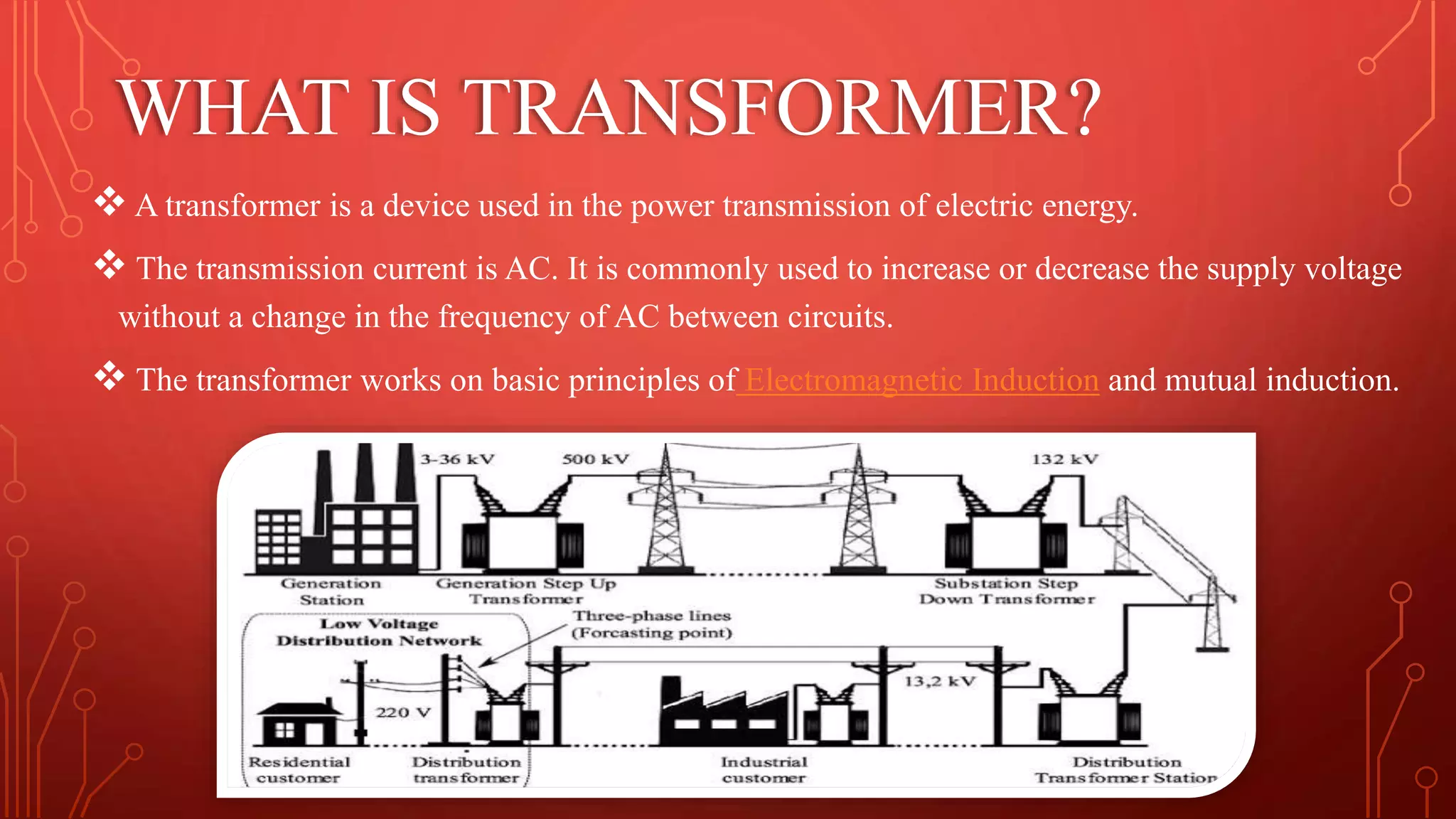
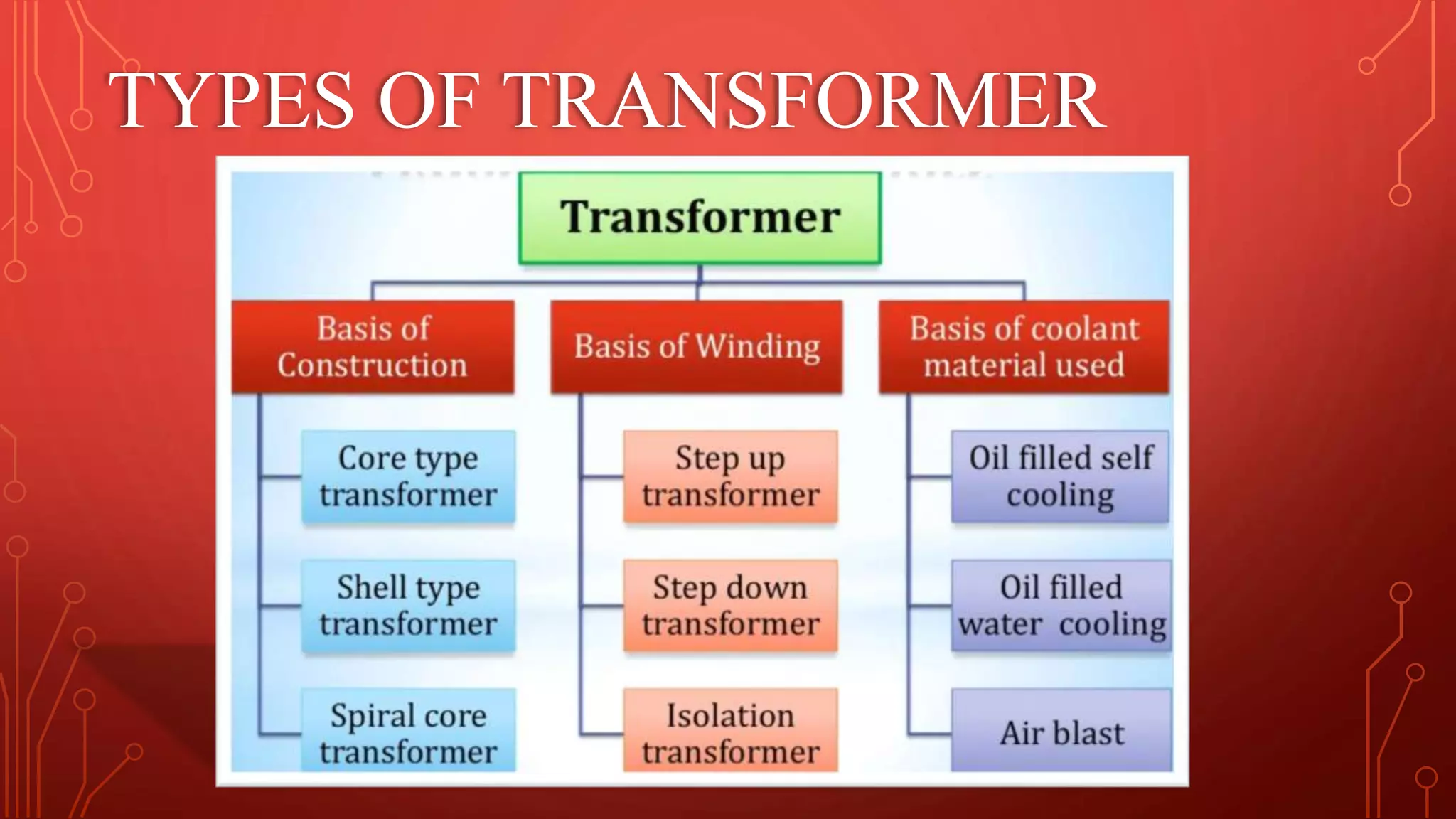
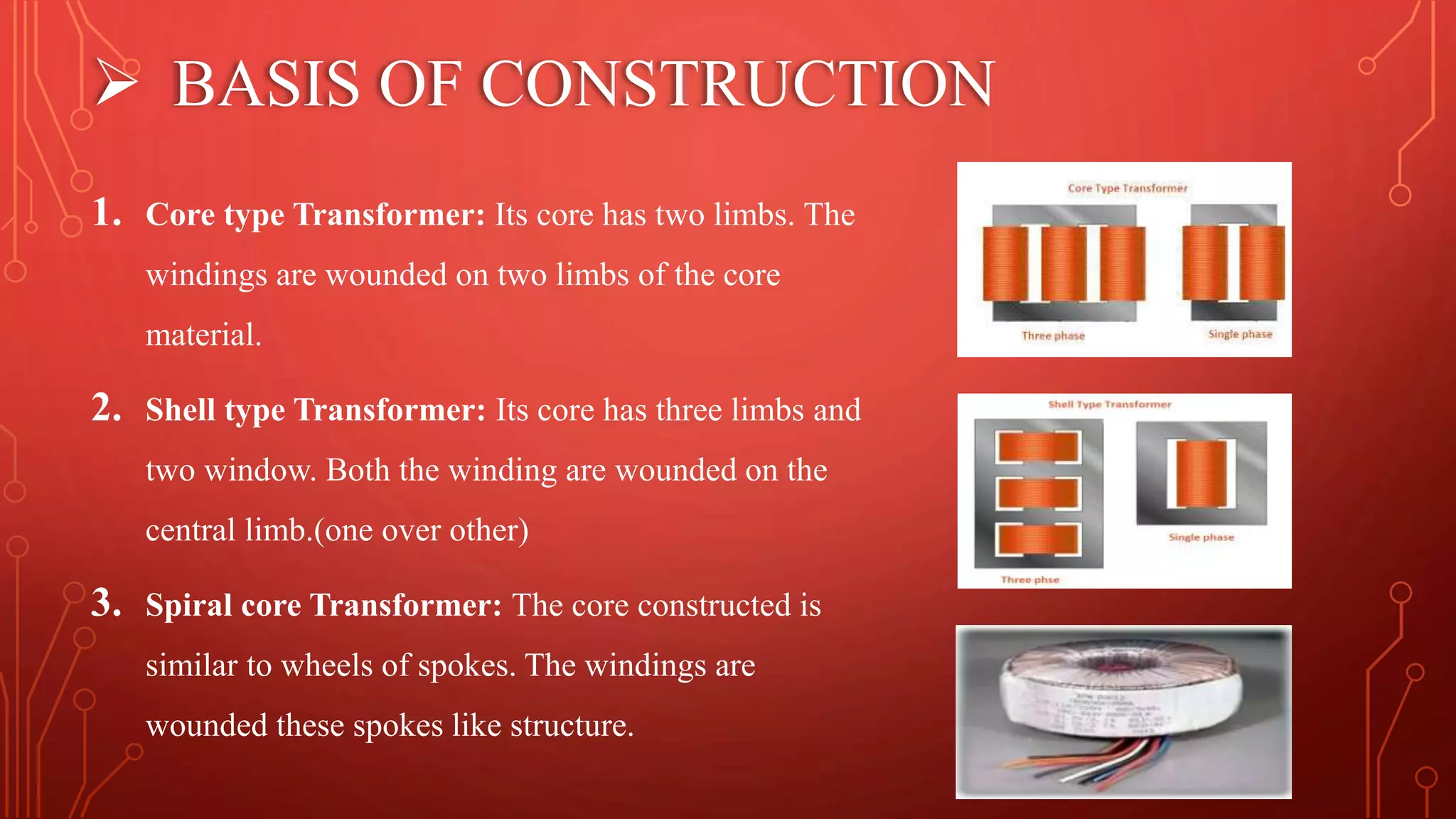
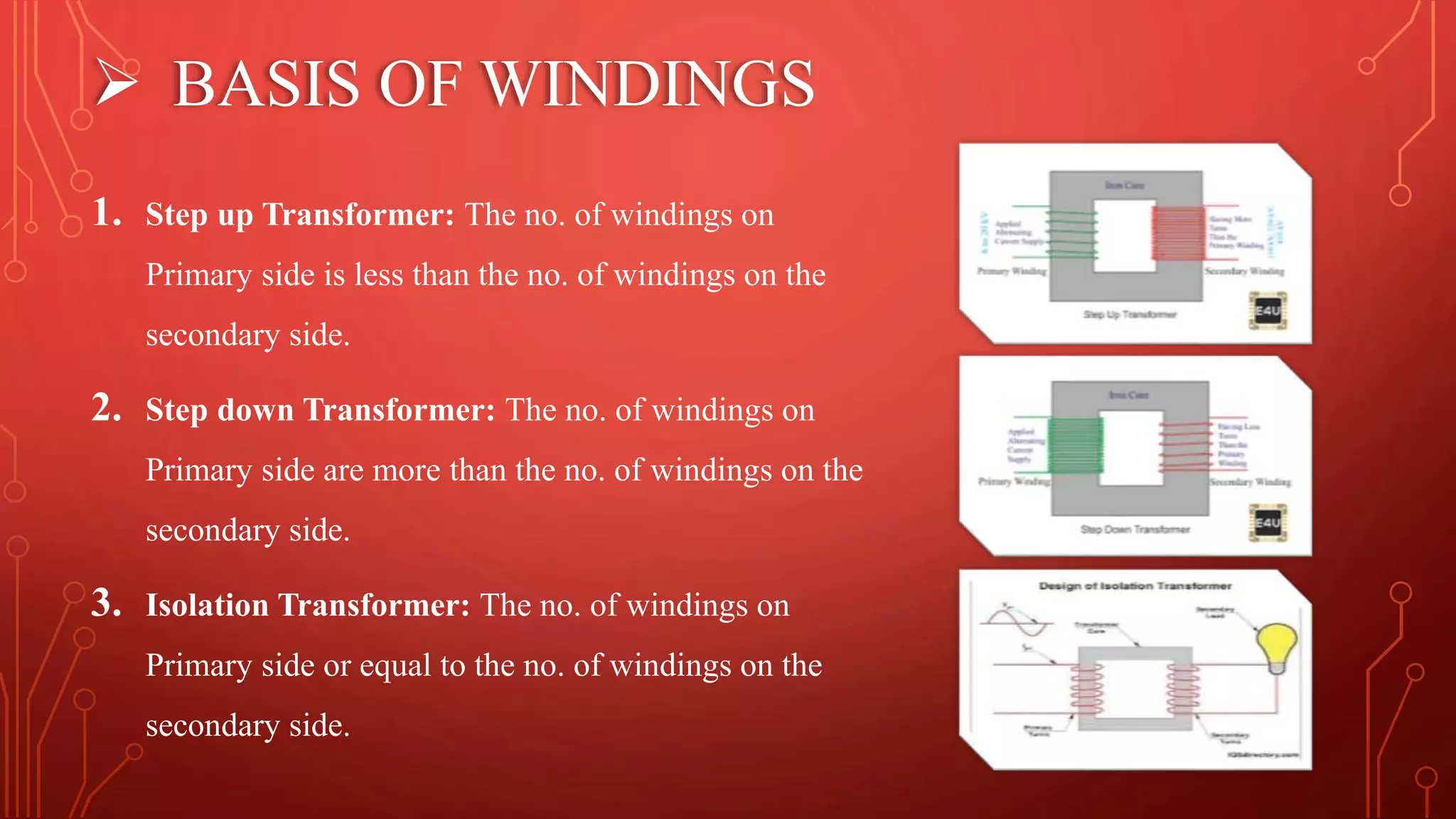
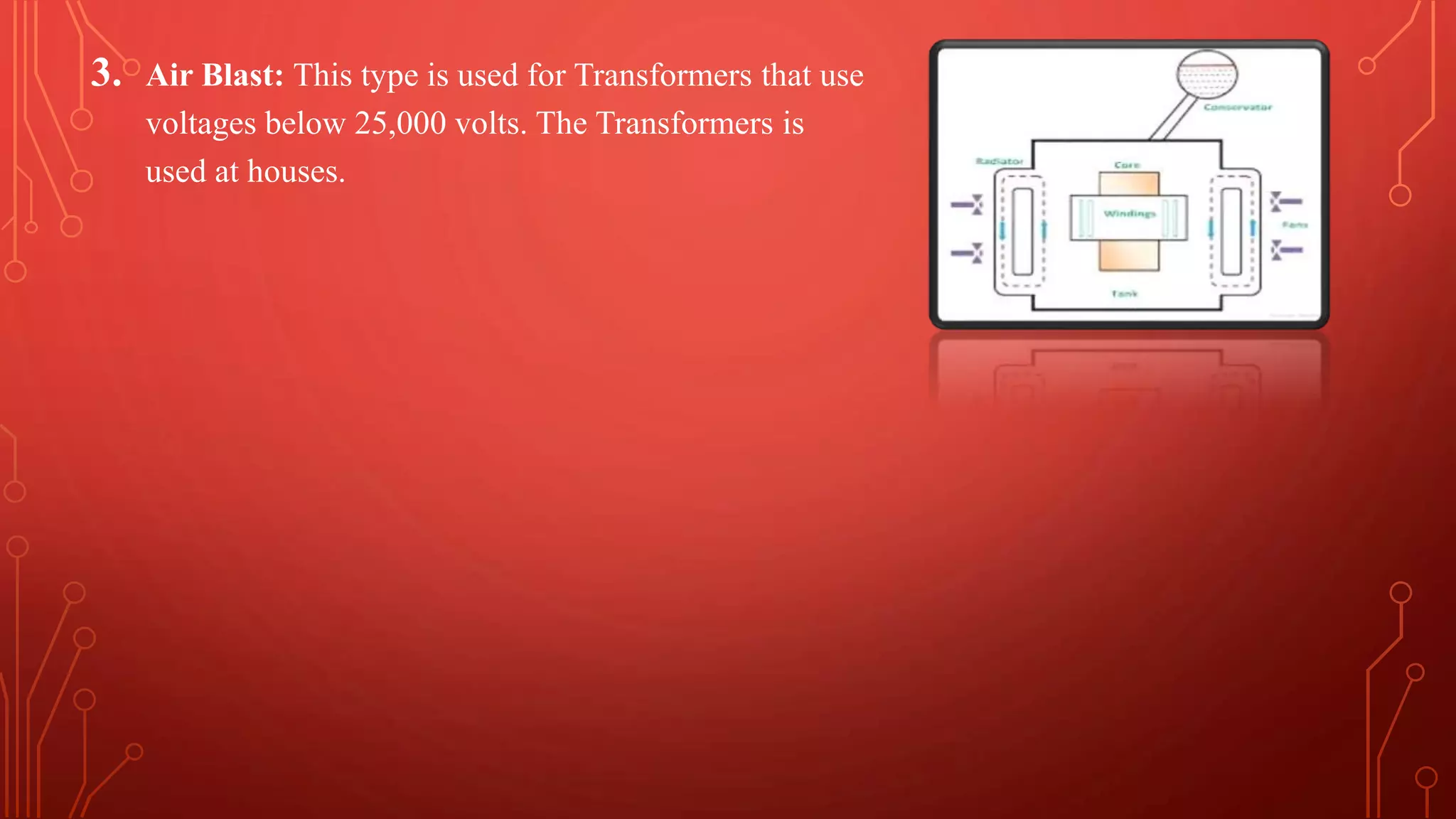
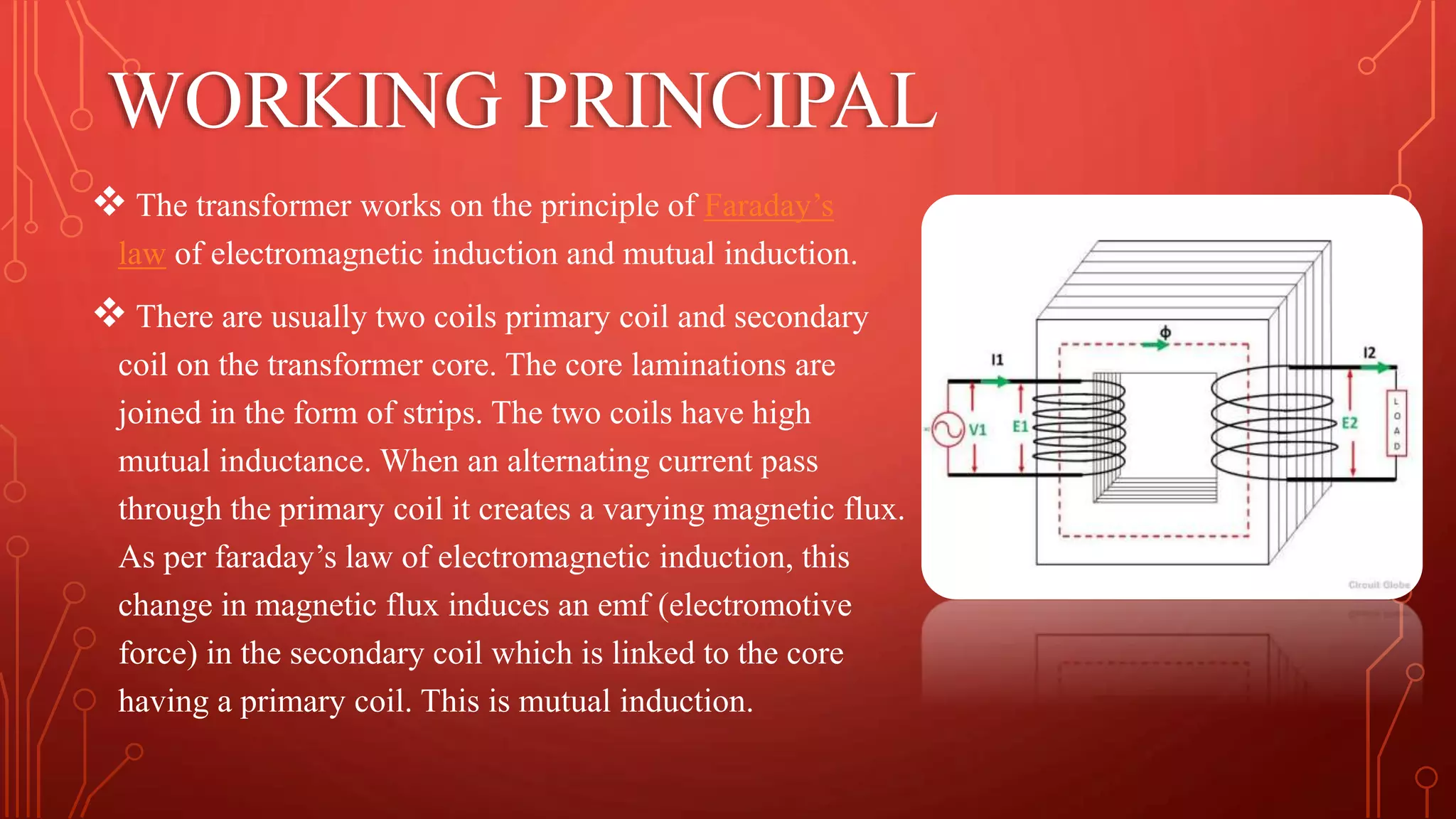
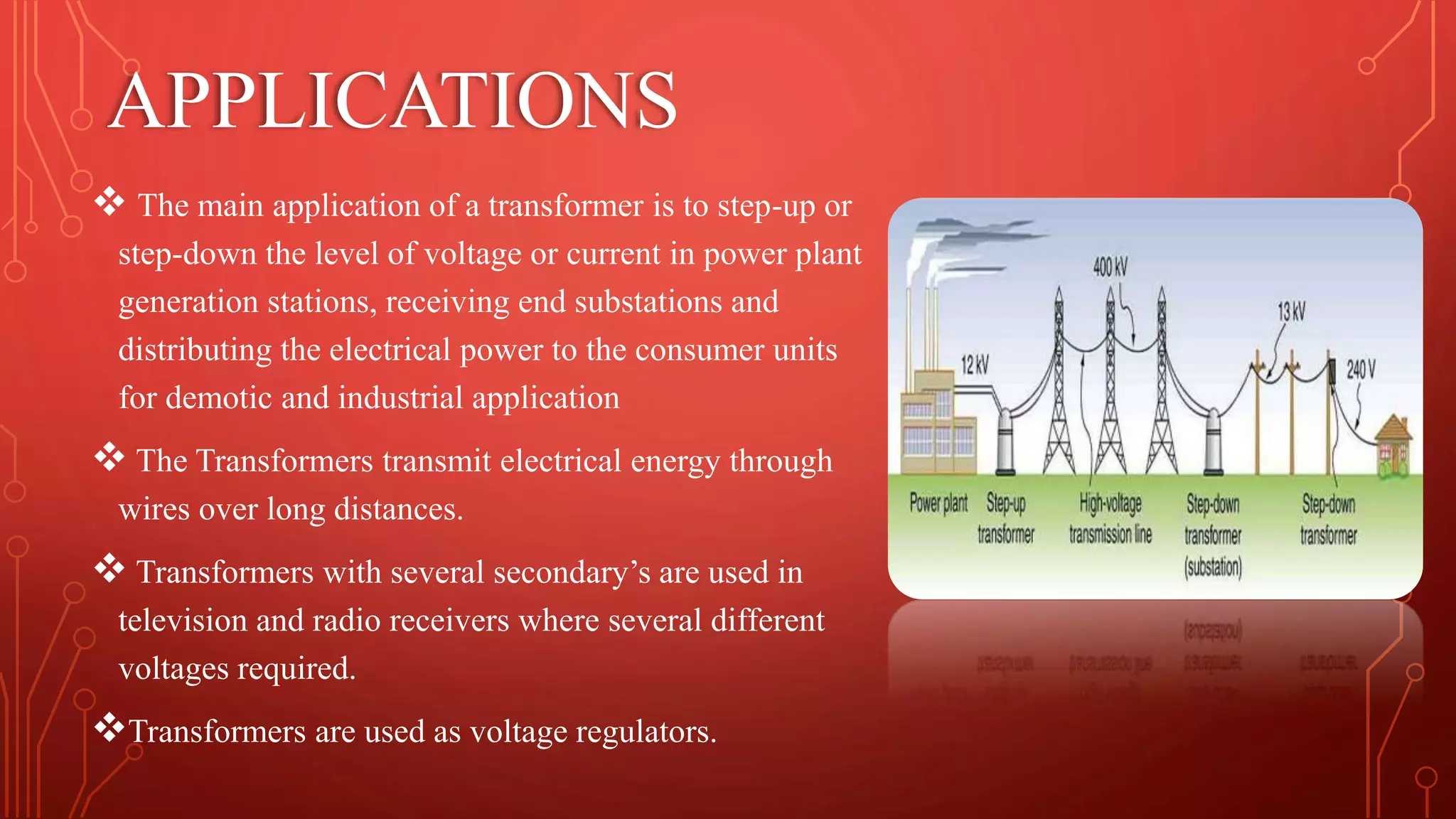
Transformers are used to increase or decrease voltages in power transmission and distribution systems. They work on the principle of electromagnetic induction and have two coils - a primary coil and secondary coil wound around an iron core. William Stanley helped make transformers more practical in 1885. Transformers allow efficient long distance transmission of power by stepping up voltage which reduces transmission losses, and stepping down voltage before delivery to consumers. They have various applications in power systems and electronics.