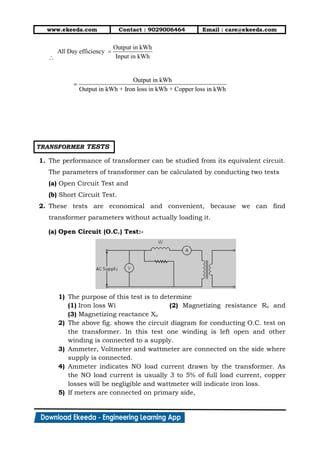
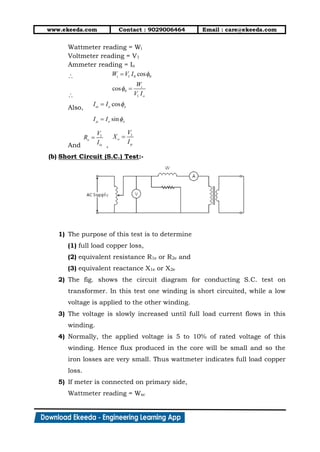
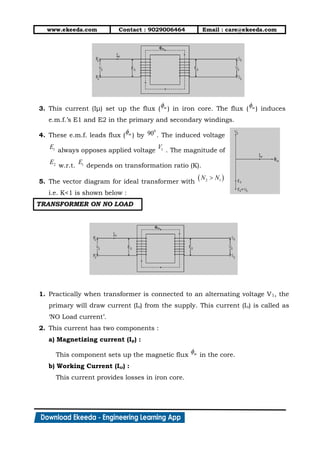
1) The document discusses the working principle, types, EMF equation, and equivalent circuit of transformers. It describes how transformers work by mutual induction between two inductively coupled coils.
2) Transformers can be classified by construction (shell, core, berry types) and by functioning (step-up, step-down, isolation transformers). The EMF equation defines the transformation ratio between primary and secondary voltages and currents.
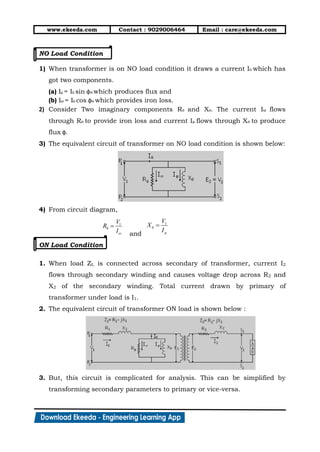
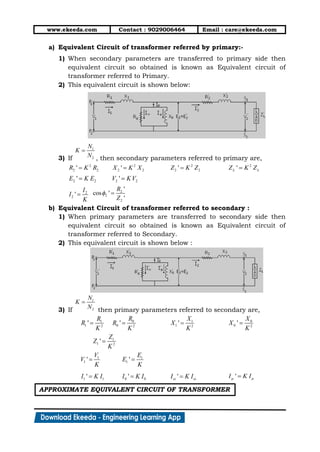
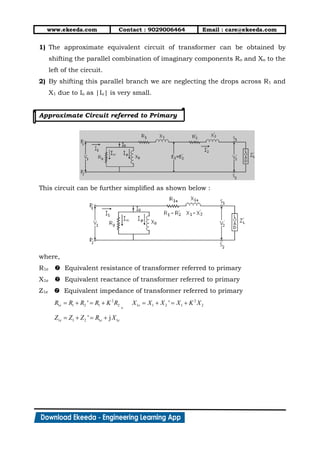
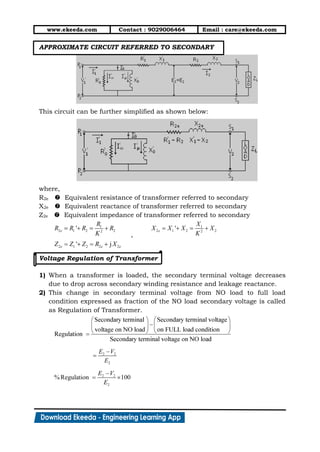
3) Equivalent circuits are used to model transformer behavior on no-load and load conditions. Losses are represented by resistances while the magnetizing current is modeled by a reactance. Secondary parameters can be referred to the primary for analysis.







![www.ekeeda.com Contact : 9029006464 Email : care@ekeeda.com
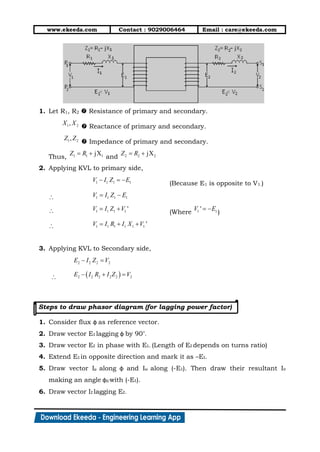
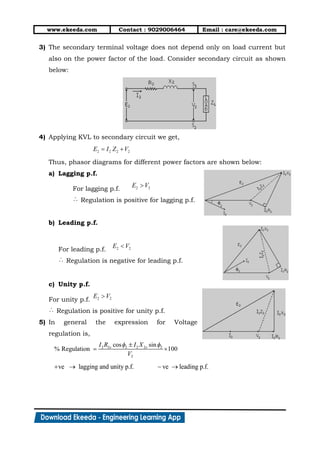
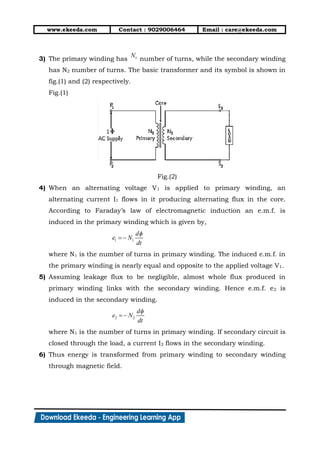
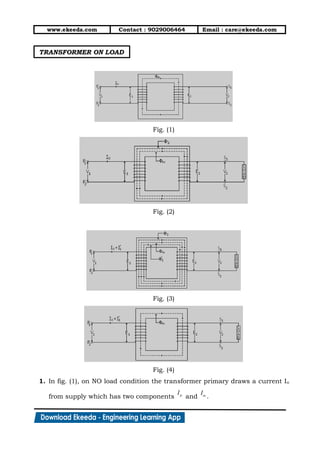
2. In fig.(2), when a load with lagging power factor is connected across the
secondary of transformer, secondary current (I2) starts flowing through the
load. This secondary current sets up flux in iron core which opposes
main flux .
3. Because of this net flux in the iron core decreases. Hence flux linking with
primary coil reduces and induced e.m.f. E1 decreases.
4. In fig.(3), Due to reduction in induced voltage across primary (E1), potential
difference is created. Thus primary will draw an extra amount of current
(I1) to overcome load connected across secondary. This current is always
out of phase with (I2).
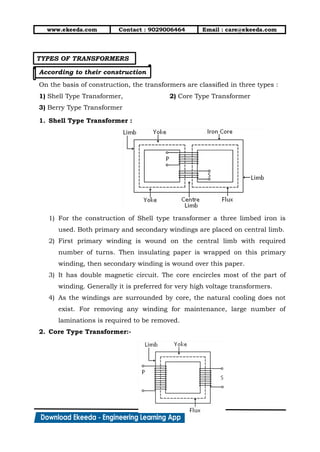
5. This current ( ) generates flux ( ) which opposes flux ( ). This action
cancels out flux ( ) and ( ).
6. In fig. (4), as flux ( ) and ( ) cancel out each other, the net flux in iron
core becomes . Hence, magnetic flux in iron core of transformer remains
same whether transformer is ON load or NO load condition.
7. As flux in iron core of transformer remains constant,
iron losses in transformer remains constant. Hence
iron losses are called constant losses.
8. Now net current in primary is I1 which is vector
addition of and i.e.
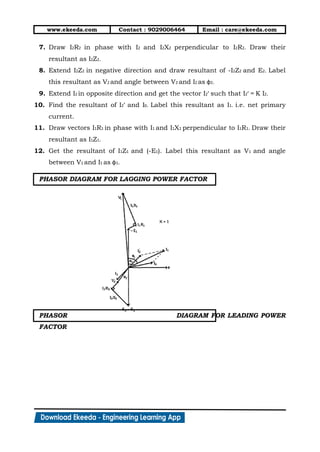
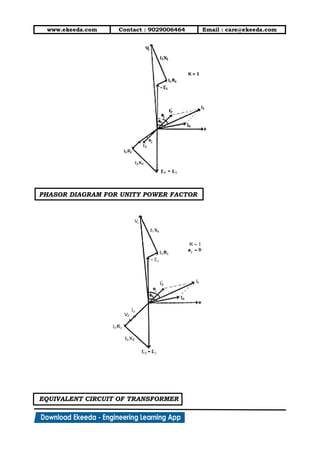
9. The complete phasor diagram of transformer ON load
is shown below.
PRACTICAL TRANSFORMER [TRANSFORMER WITH LEAKAGE IMPEDANCE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlephasetransformers-190121145455/85/Single-phase-transformers-12-320.jpg)