Embed presentation
Downloaded 576 times











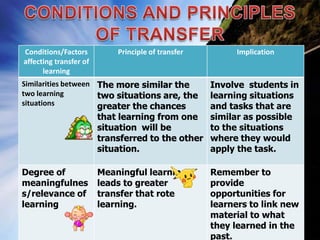
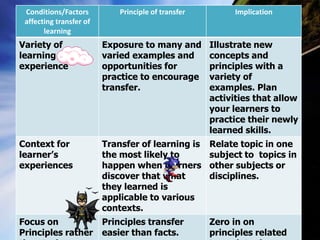


Transfer of learning occurs when learning in one context impacts performance in another context. There are different types of transfer, including positive transfer where performance is improved, and negative transfer where performance is negatively impacted. Far transfer involves applying skills and knowledge in changing situations, while near transfer applies skills the same way each time. Conditions and principles of transfer must be considered for effective learning transfer.













