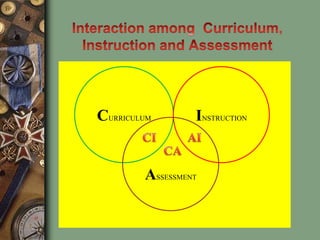
The document discusses the relationships between curriculum, instruction, and assessment. It defines curriculum as the structured set of learning outcomes and objectives that make up the "what" of teaching. Several criteria for selecting curriculum content are described, including significance, utility, validity, learnability, and feasibility. Assessment is defined as collecting information on student achievement related to curriculum expectations. Instruction refers to teaching methods and styles used to deliver the curriculum. The quality of instruction depends on several factors, and a close link is needed between curriculum, instruction, and assessment for effective teaching and learning.