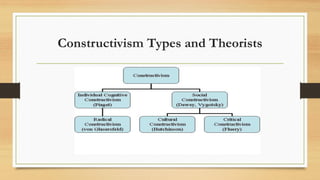
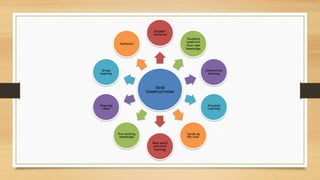
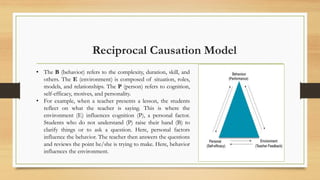
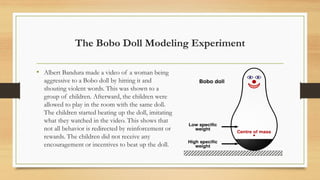
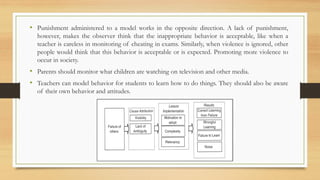
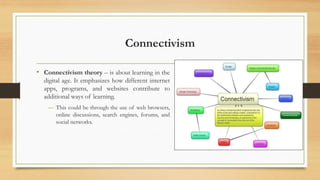
The document explores constructivism, a learning theory positing that knowledge is actively constructed by learners through experiences rather than passively received. It details guiding principles, types of constructivism (cognitive and social), and key theorists like Dewey, Piaget, and Vygotsky, emphasizing the importance of social interactions and real-world contexts in the learning process. Additionally, the document outlines the advantages and disadvantages of constructivist learning, advocating for learner-centered teaching approaches that encourage student ownership and engagement.