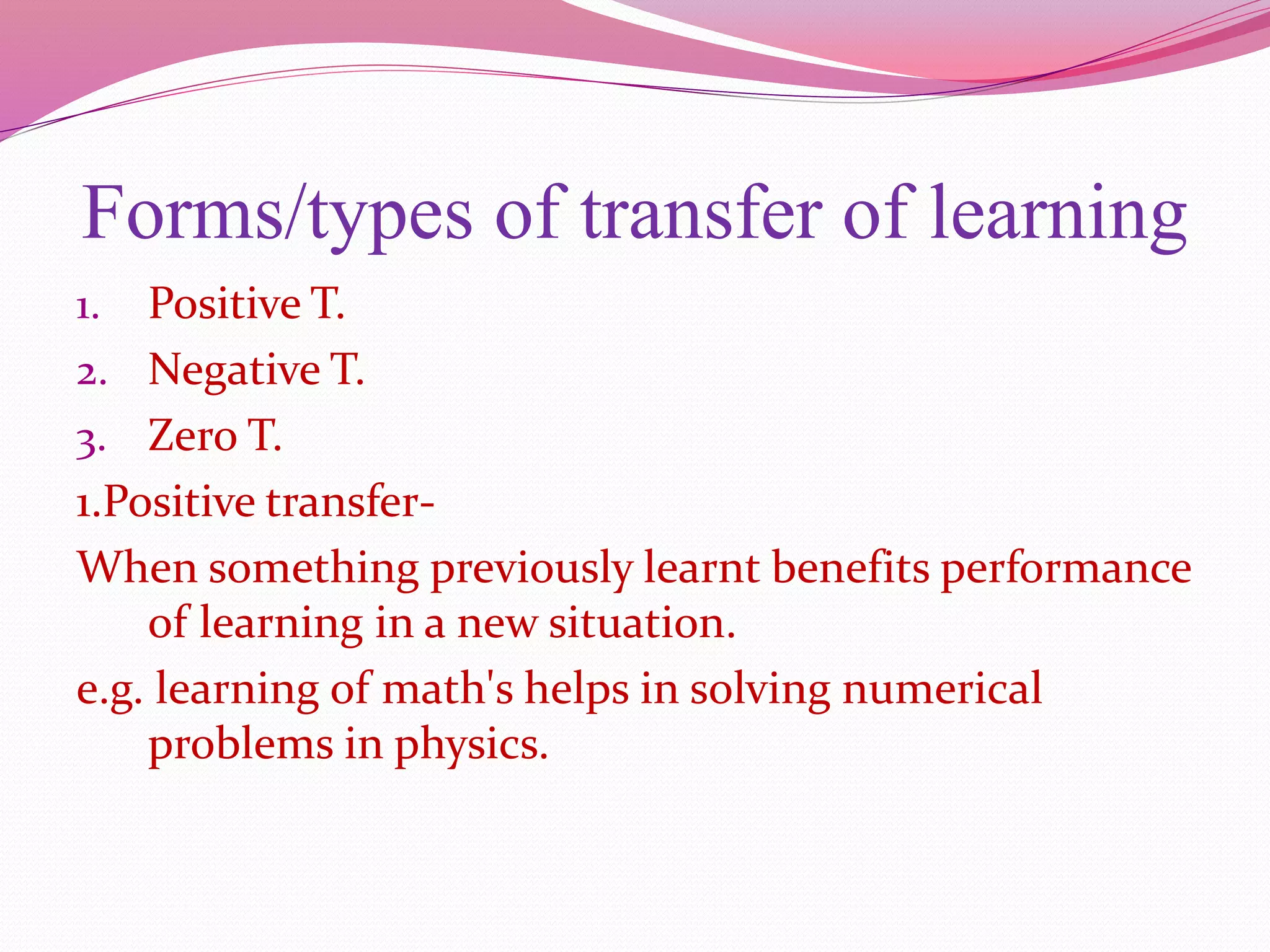
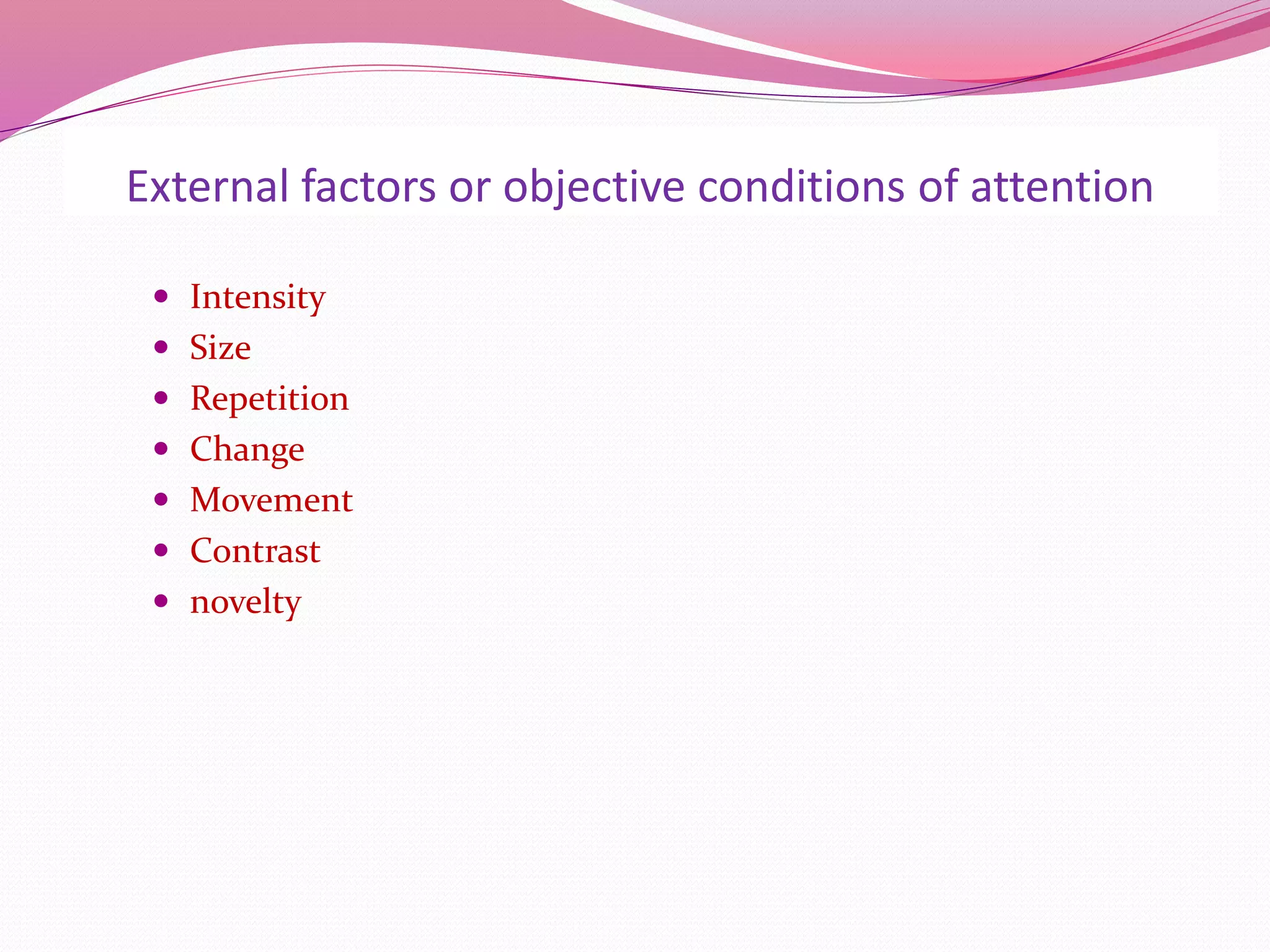
This document discusses imitation and transfer of learning. It defines imitation as copying another's actions, which is observed in animals. Imitation with purpose utilizes imitation to accomplish something significant. Transfer of learning is defined as applying learning from one situation to another. There are three types of transfer: positive, where previous learning benefits new learning; negative, where it hinders new learning; and zero, where there is no effect. Factors like intelligence, attitudes, meaningful learning experiences, and teaching methods can influence transfer. Teachers should aim to develop understanding of principles rather than rote learning to promote effective transfer.