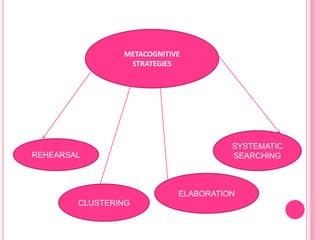
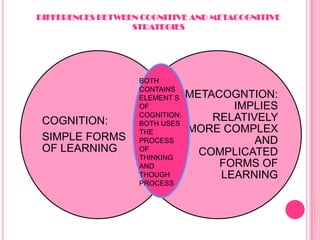
Metacognition refers to thinking about one's own thinking. It involves awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes. There are two main components - knowledge about cognition and regulation of cognition. Knowledge of cognition includes knowledge about strategies that can be used for different learning situations. Regulation of cognition refers to skills such as planning, monitoring, and evaluating one's comprehension. Metacognitive skills are essential for effective learning as they allow students to consciously monitor and manage their learning.