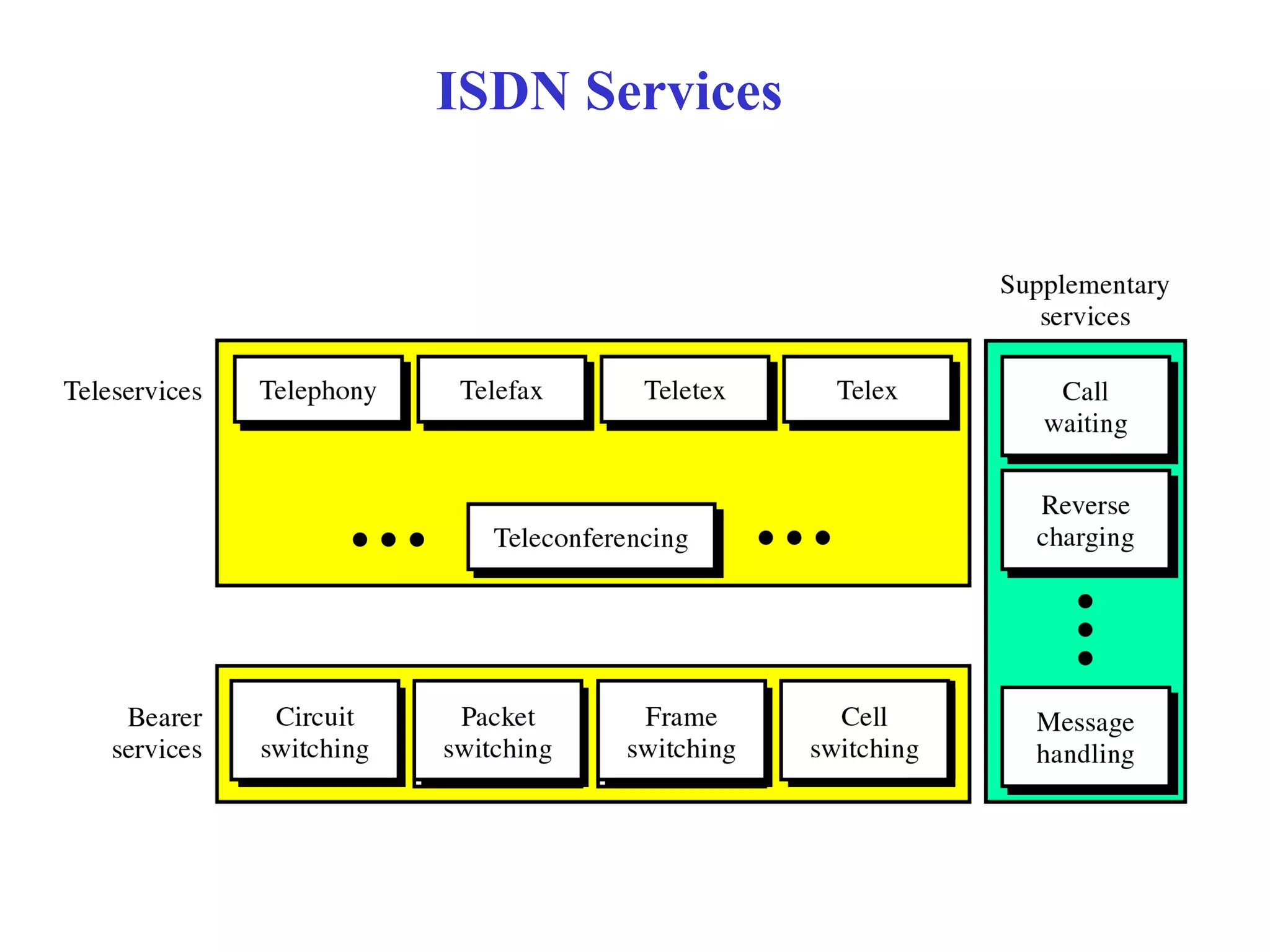
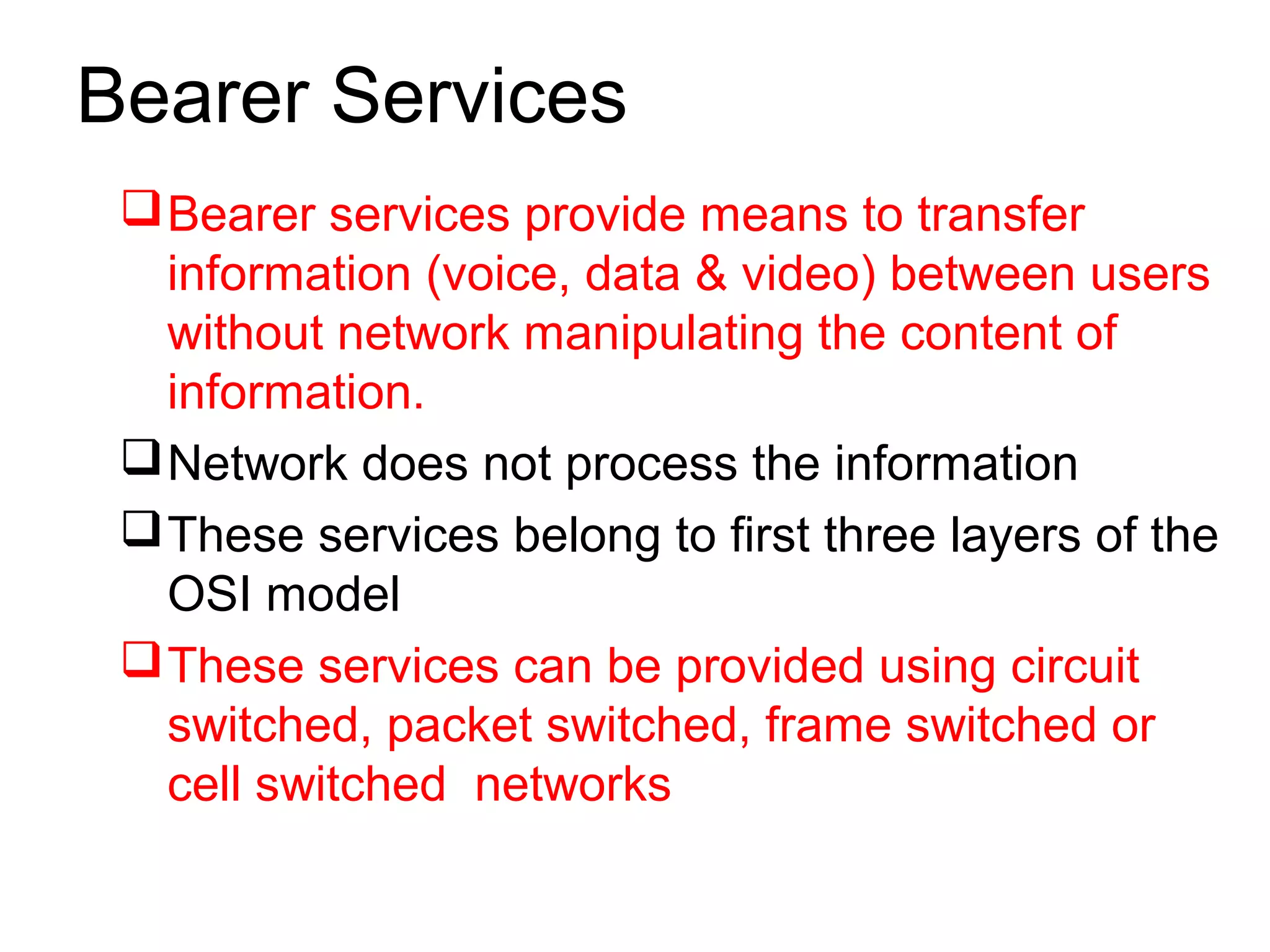
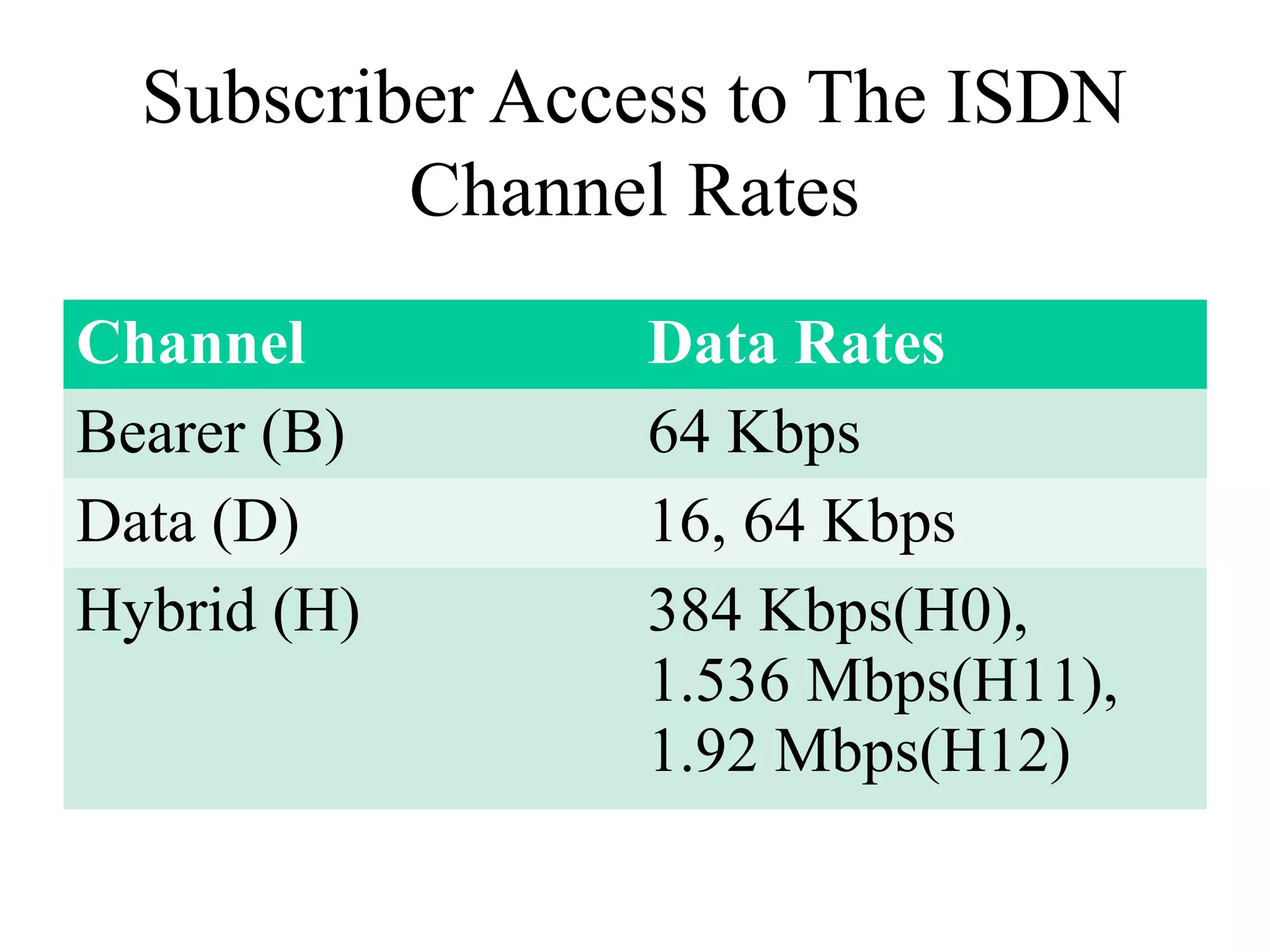
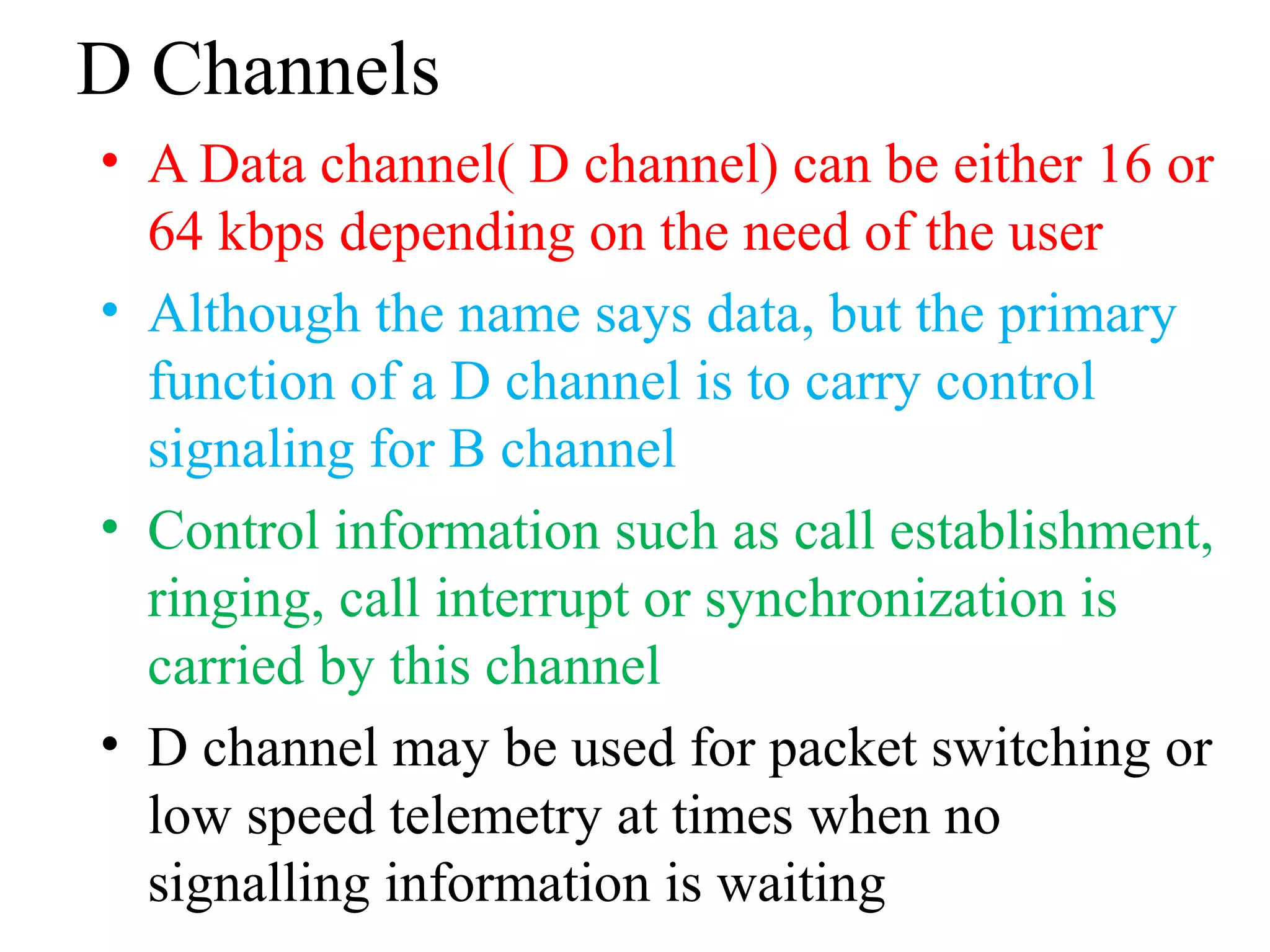
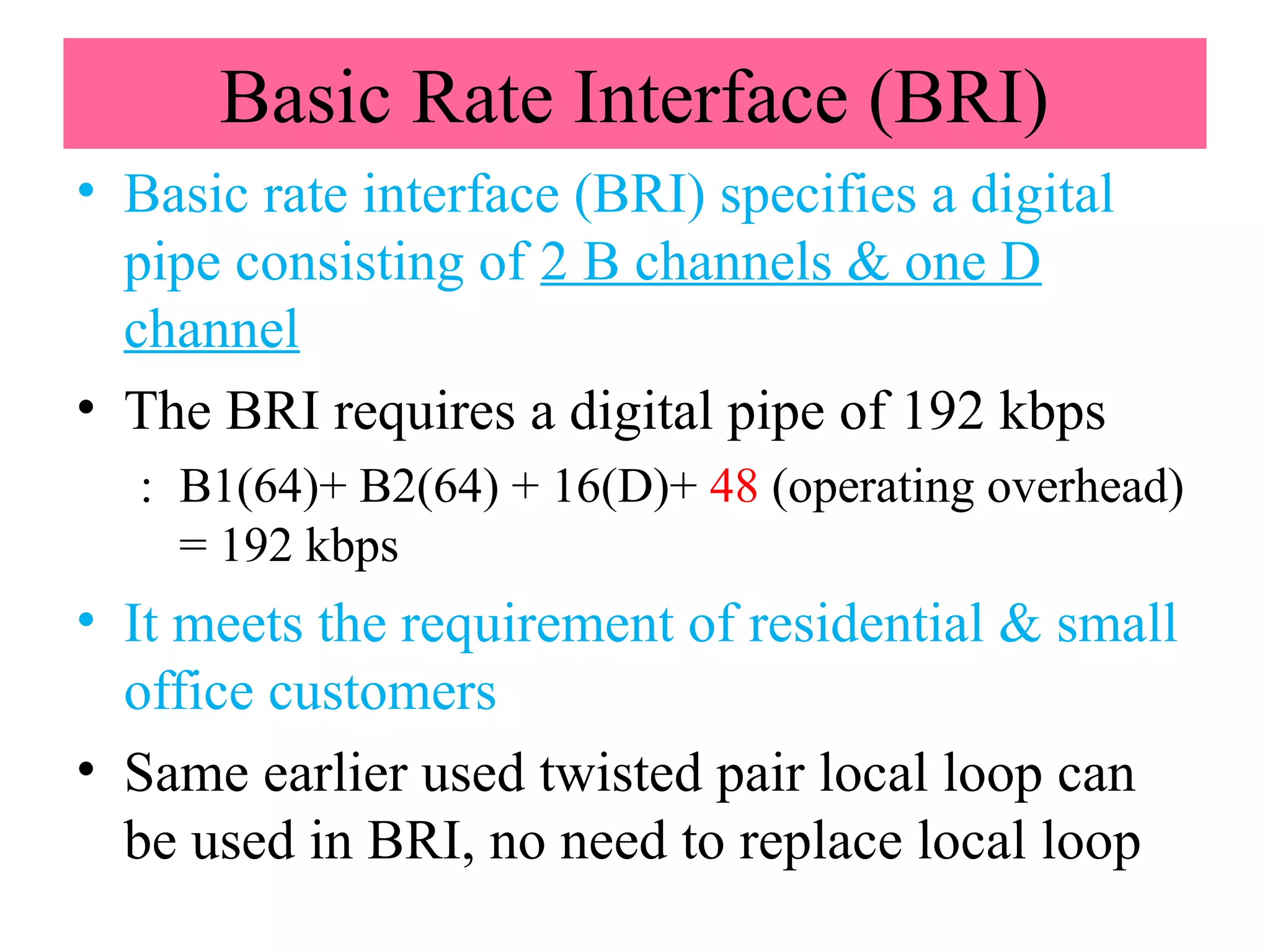
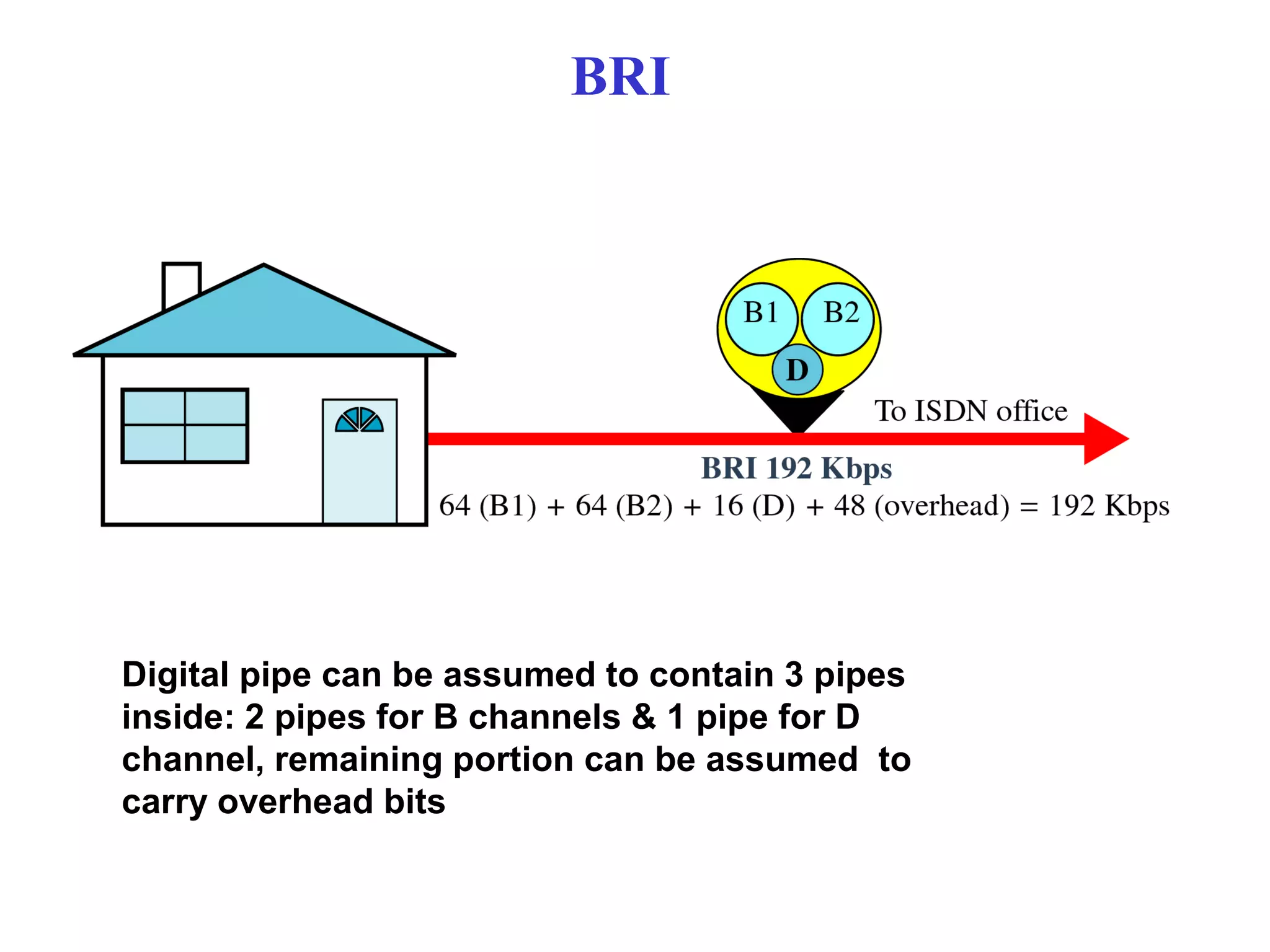
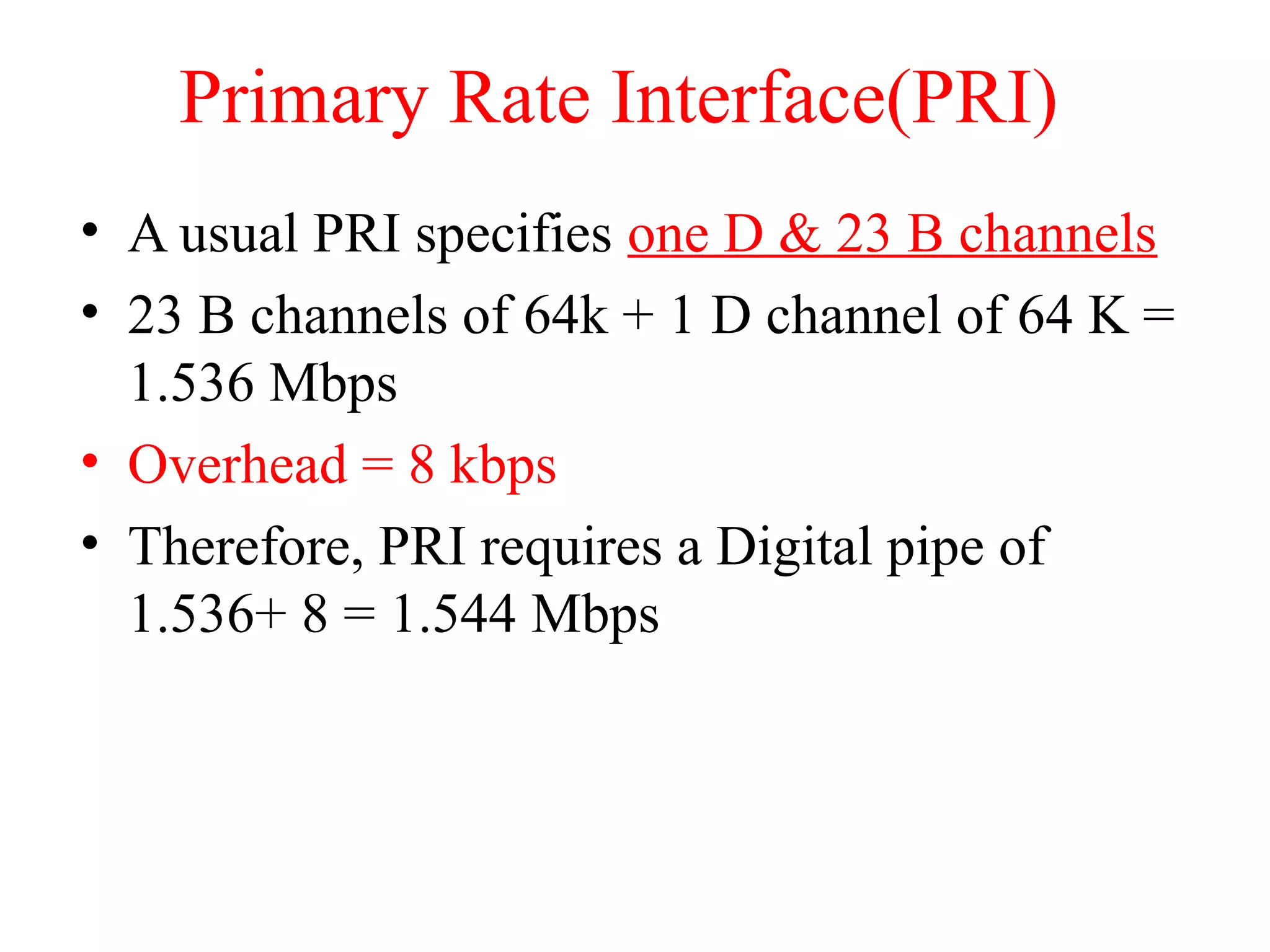
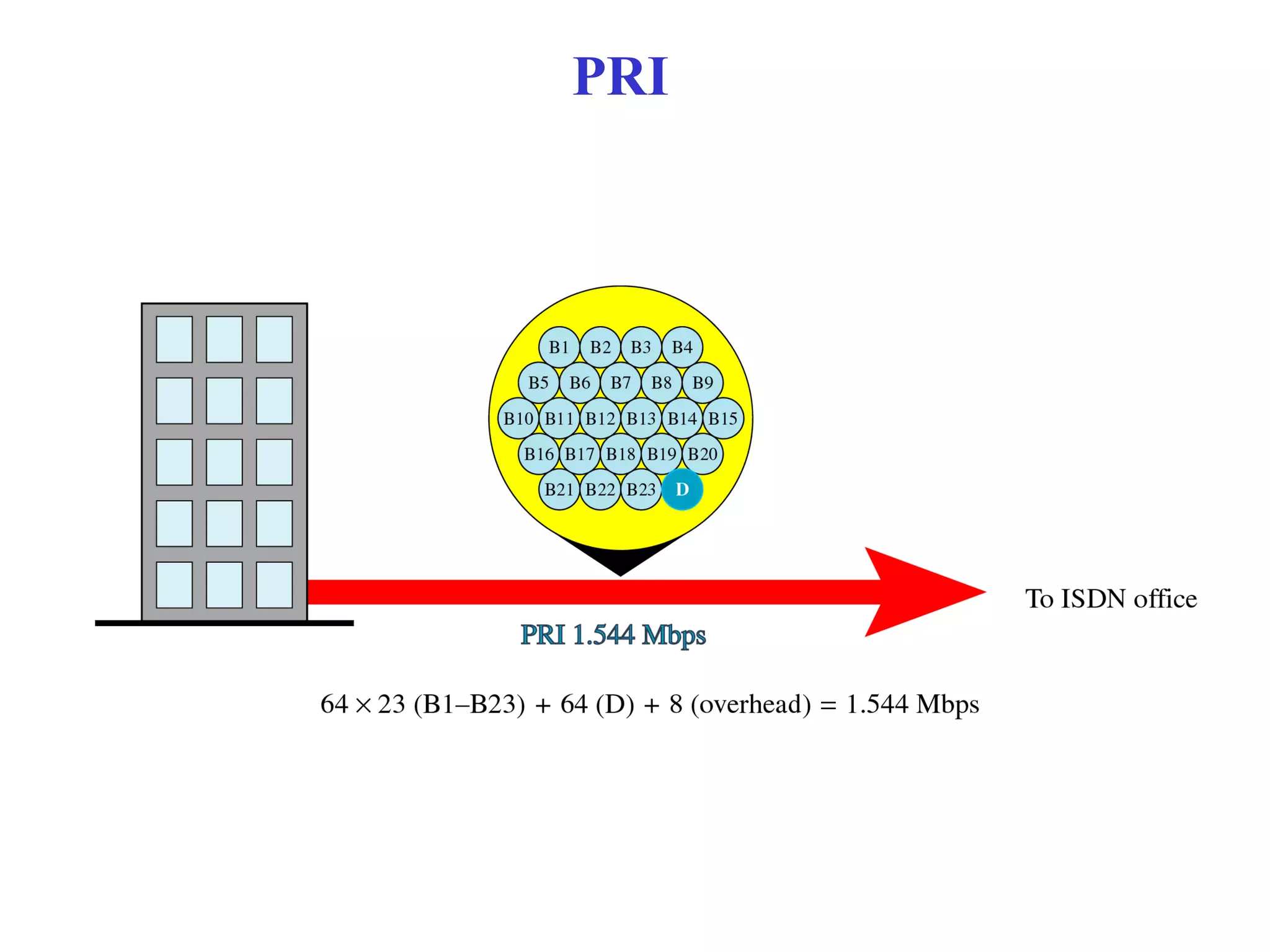
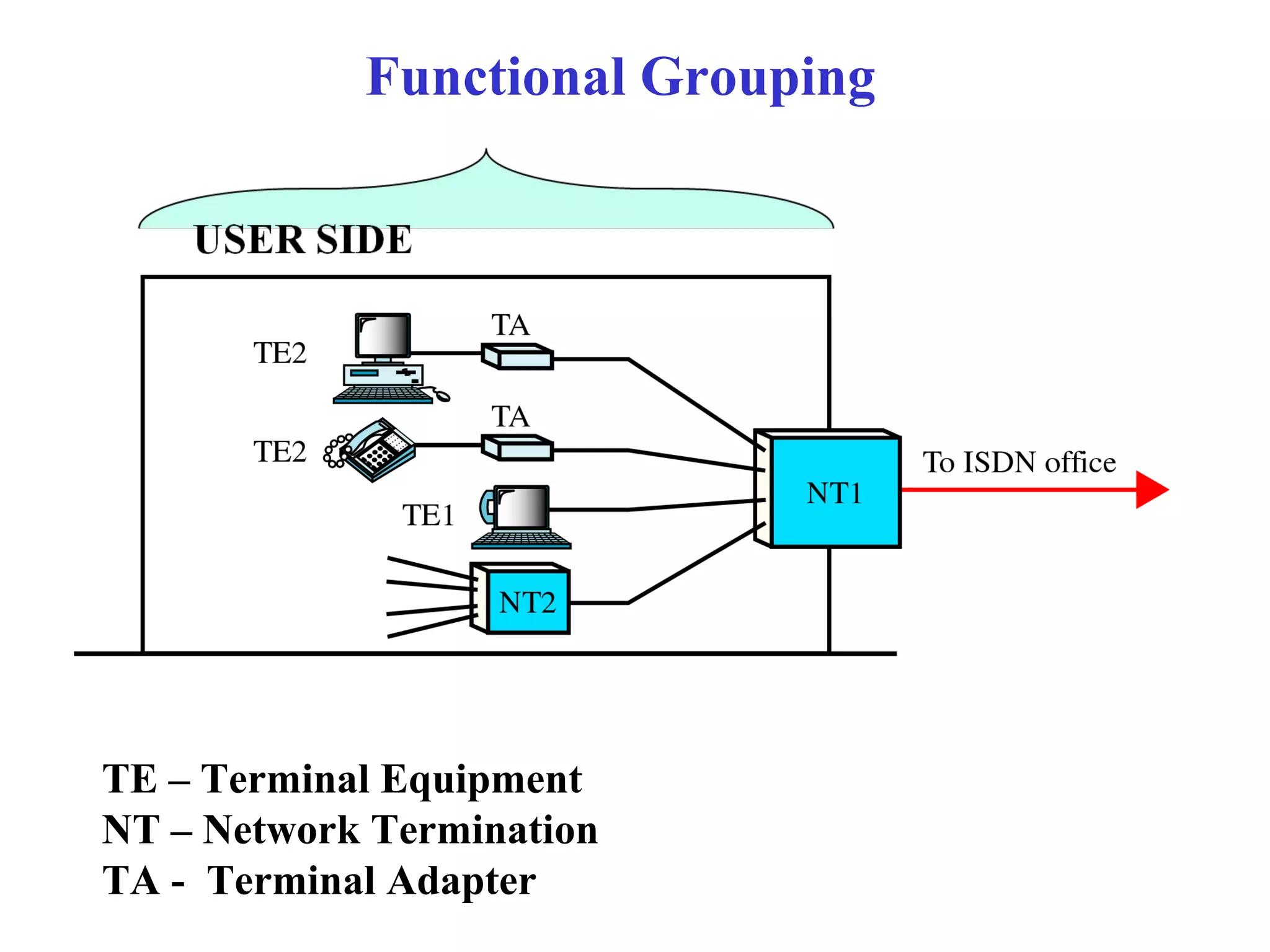
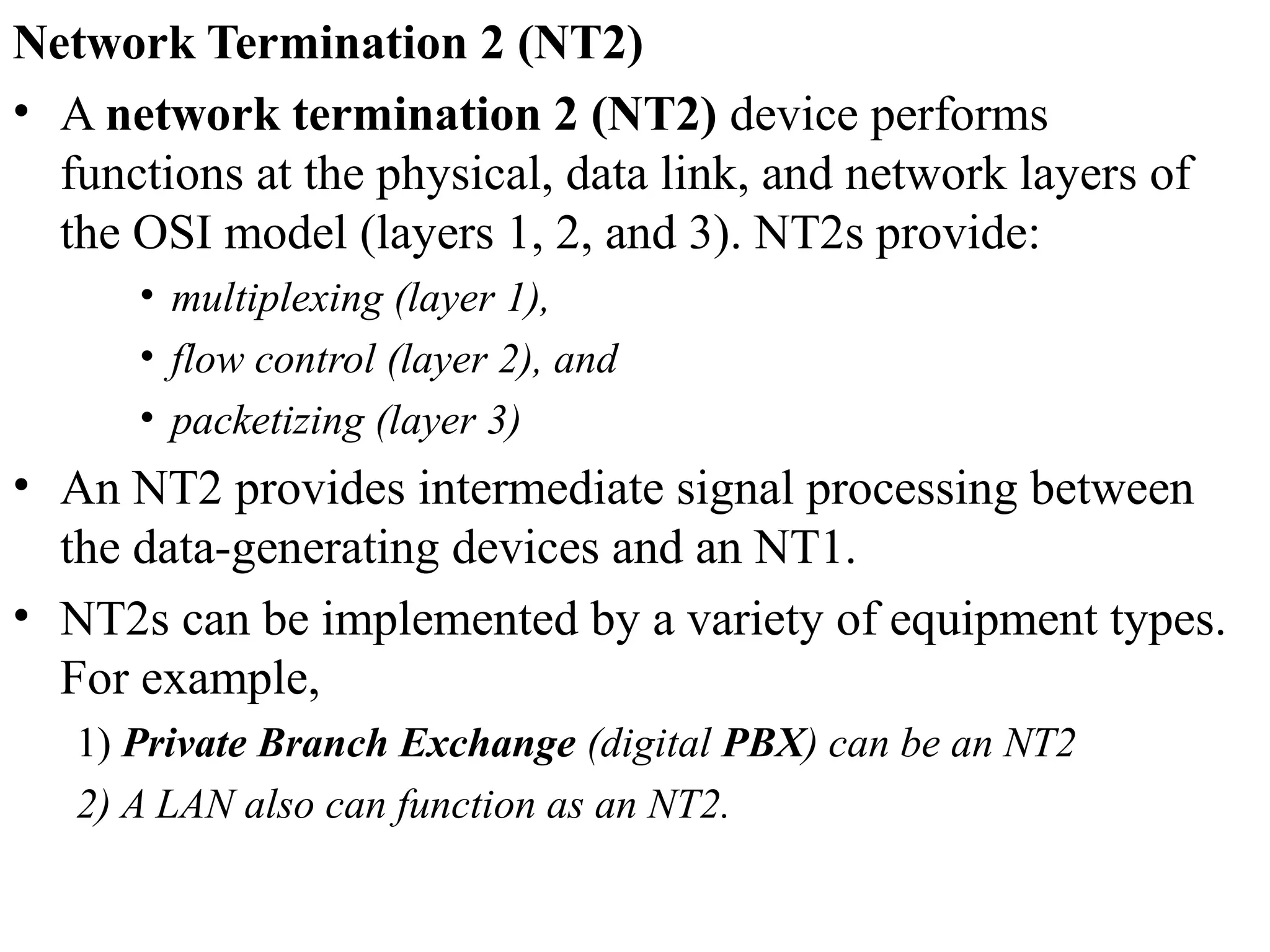
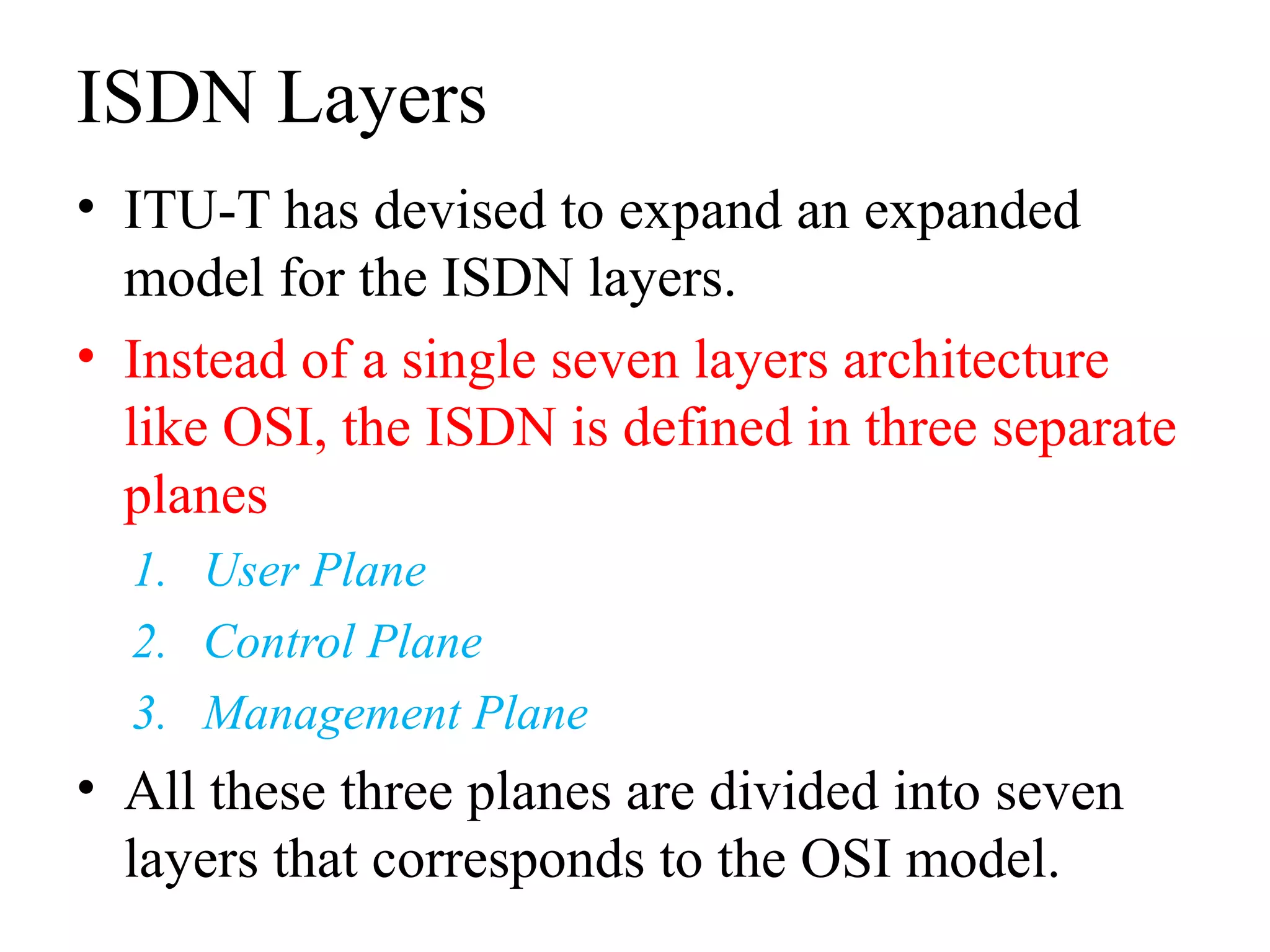
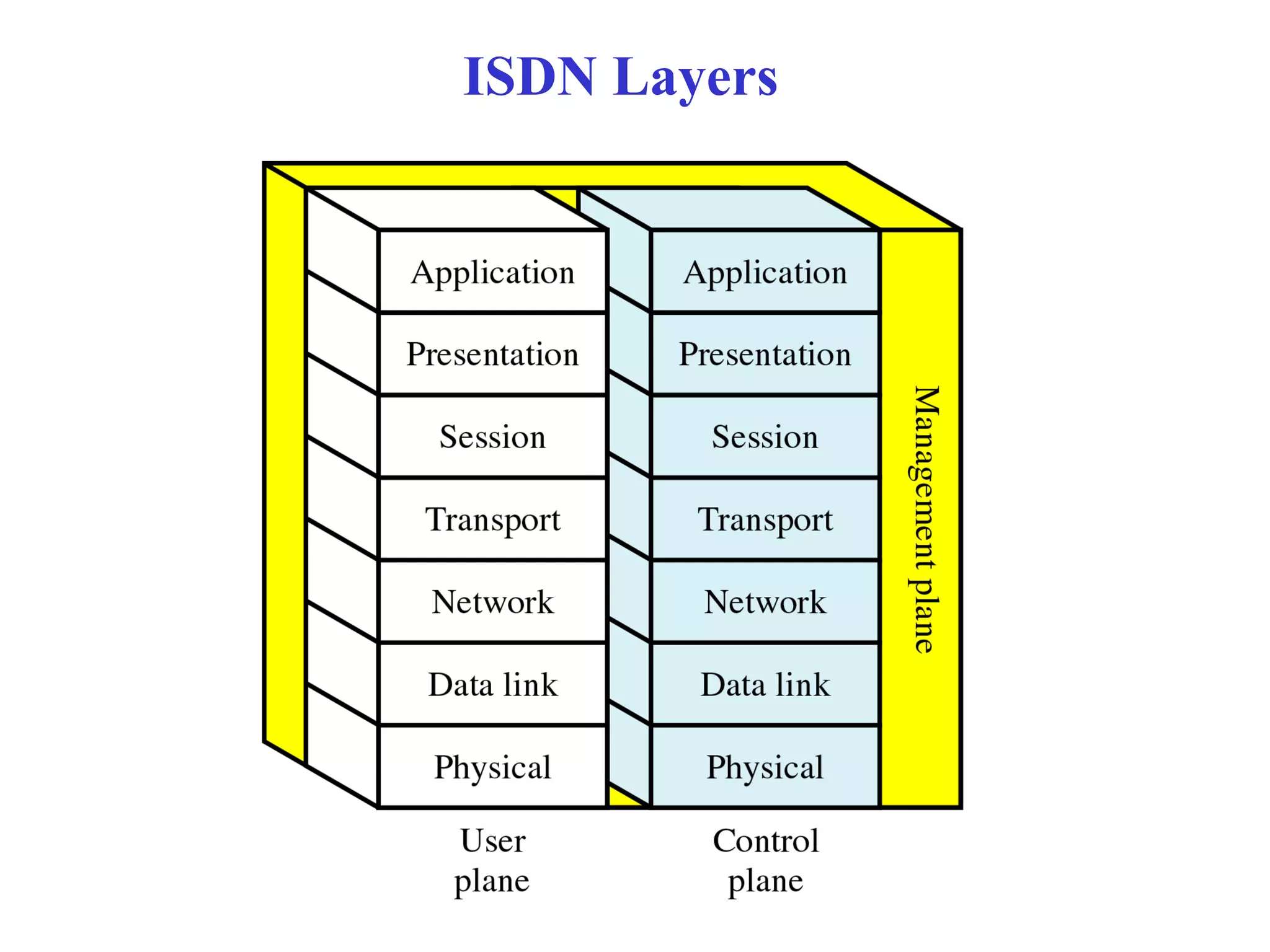
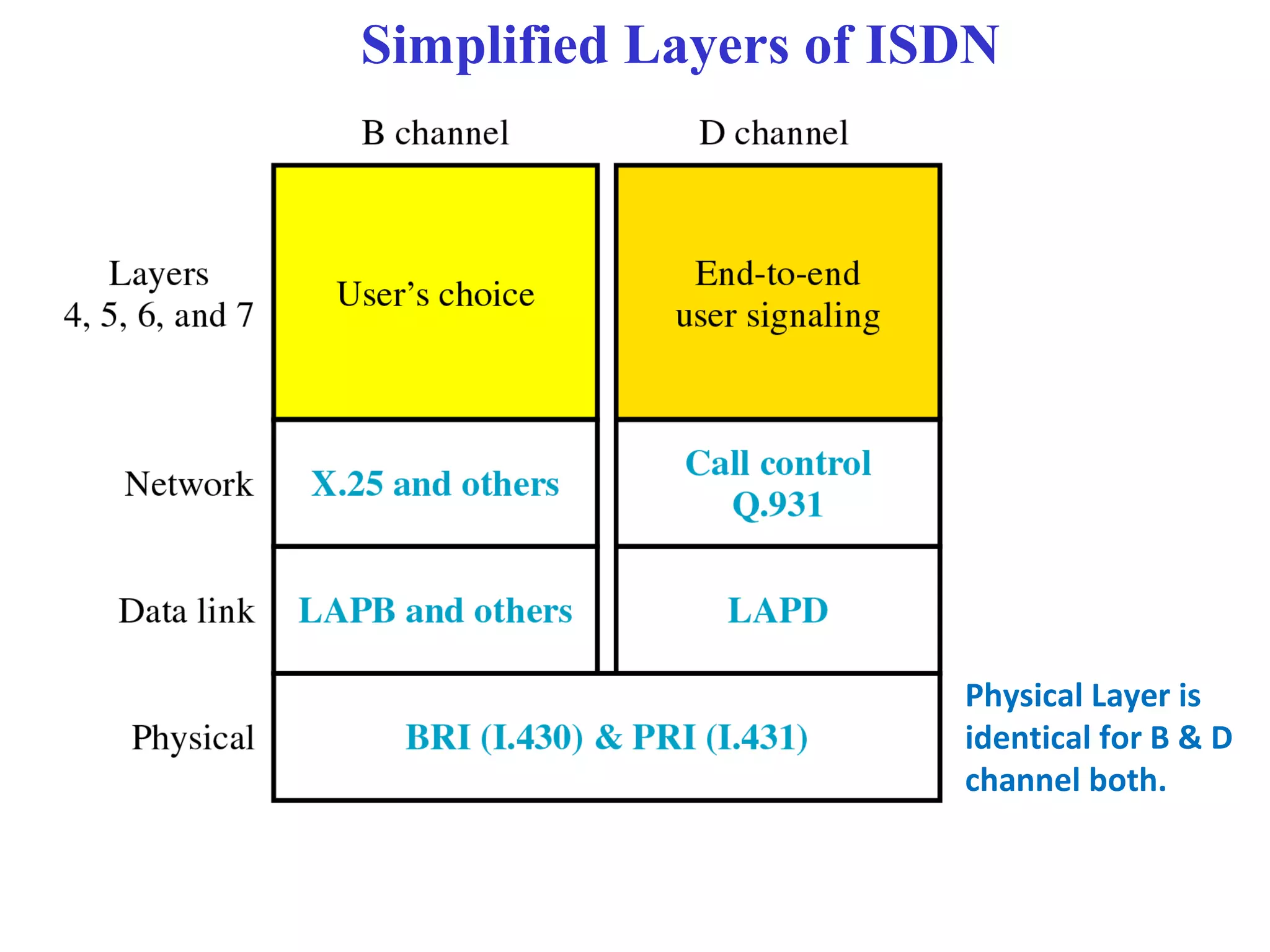
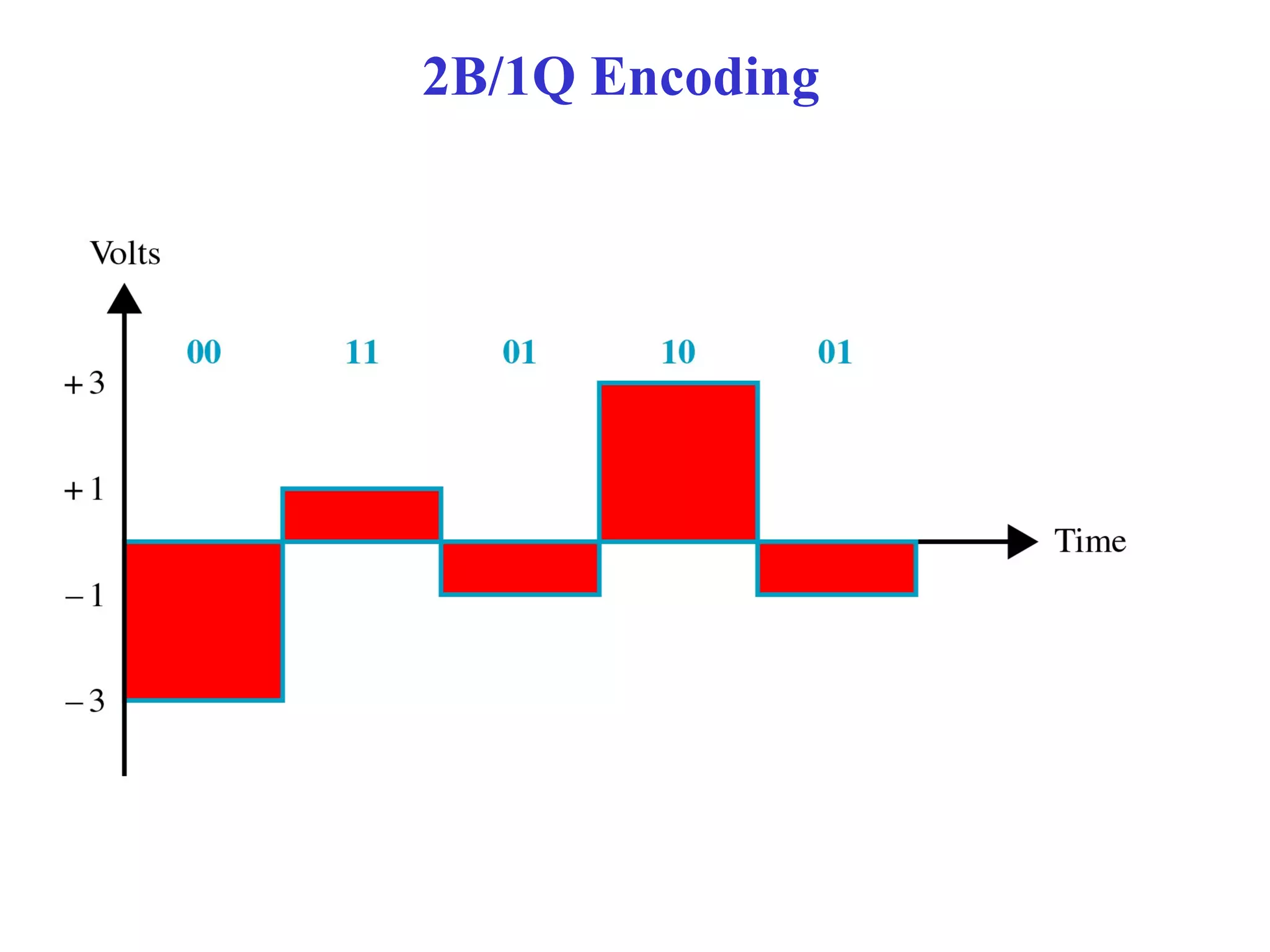
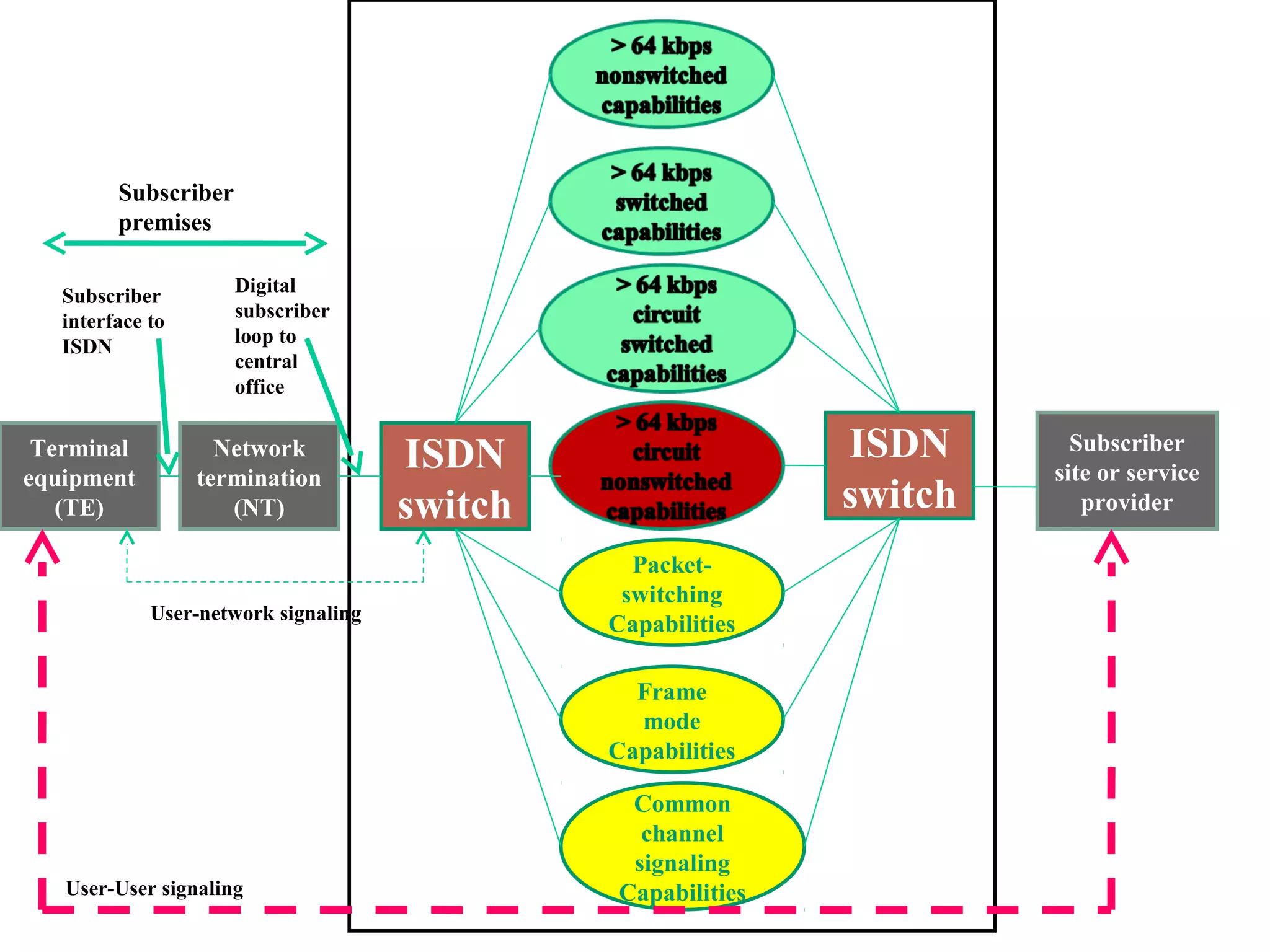
The document is a lecture on ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) services, detailing its three types: bearer services, teleservices, and supplementary services. It describes the access channels (B, D, and H channels) for data transmission and outlines the Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI) for different user needs. Additionally, it discusses the ISDN architecture, including network termination devices, terminal equipment, and the governing standards for ISDN.