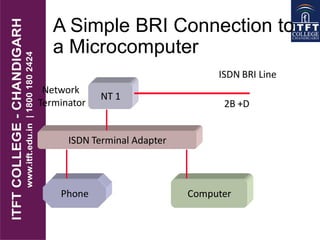
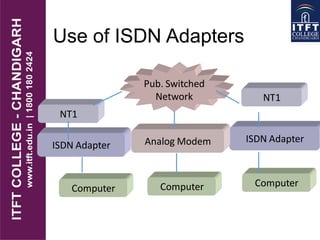
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) is a digital telecommunication line that can deliver data, audio, video, and images over copper telephone wires. It allows for end-to-end digital communication at speeds of up to 128 Kbps for a single ISDN line or higher speeds when multiple lines are combined. There are two main types of ISDN connections: Basic Rate Interface (BRI) with 2 bearer (B) channels and 1 data (D) channel, and Primary Rate Interface (PRI) with 23 B channels and 1 D channel. ISDN transformed telecommunications by providing digital connectivity for homes and businesses worldwide.