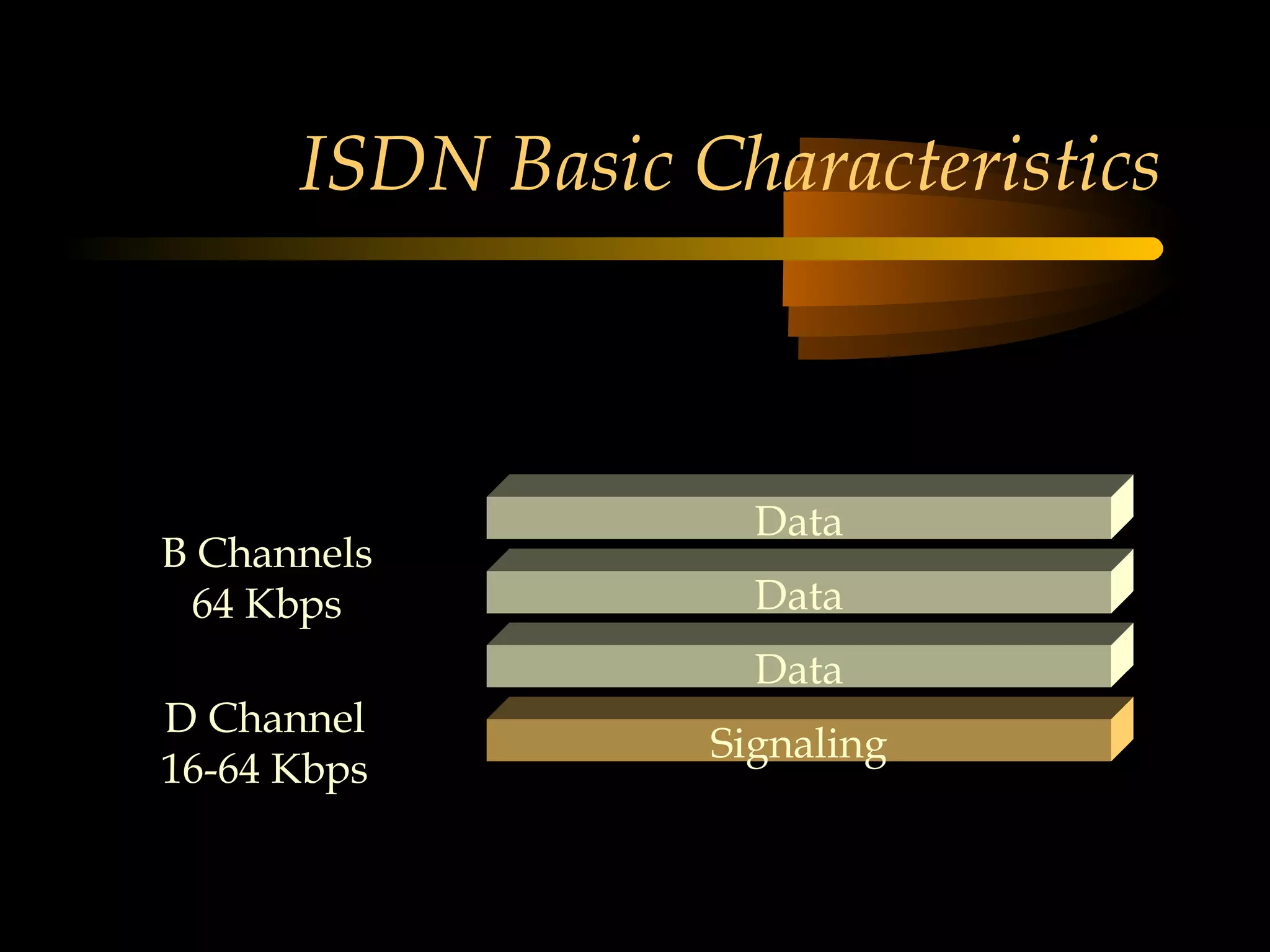
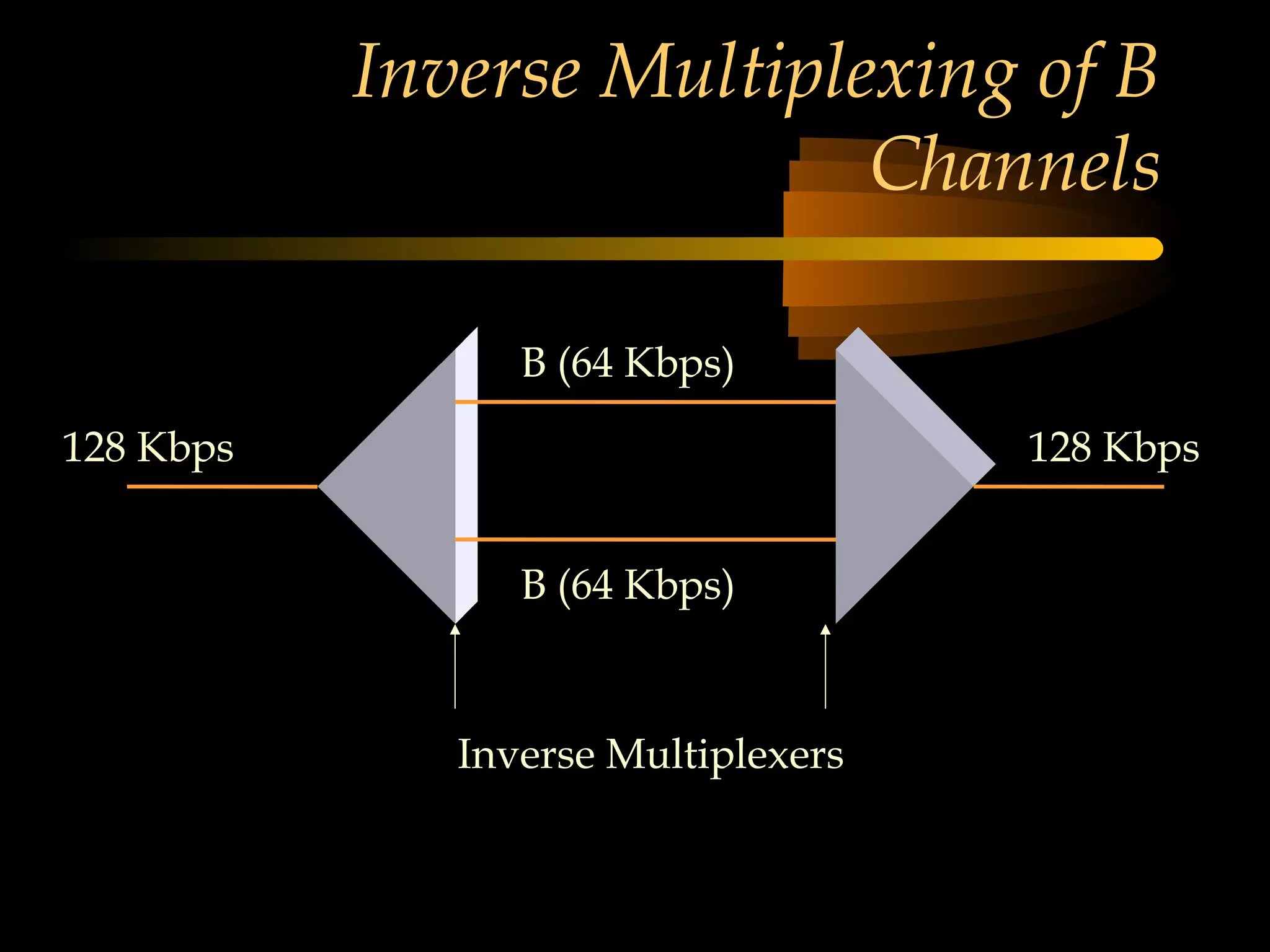
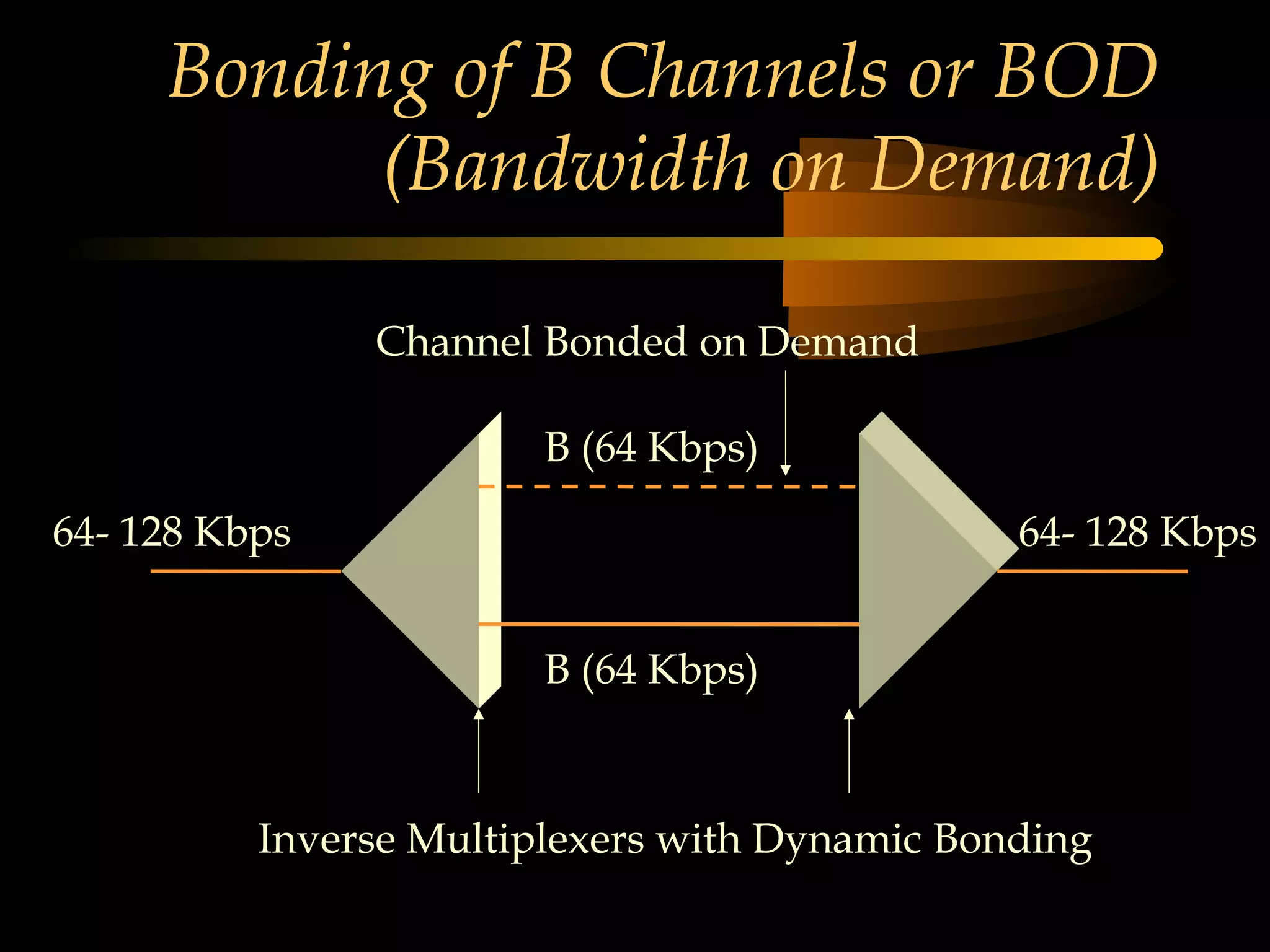
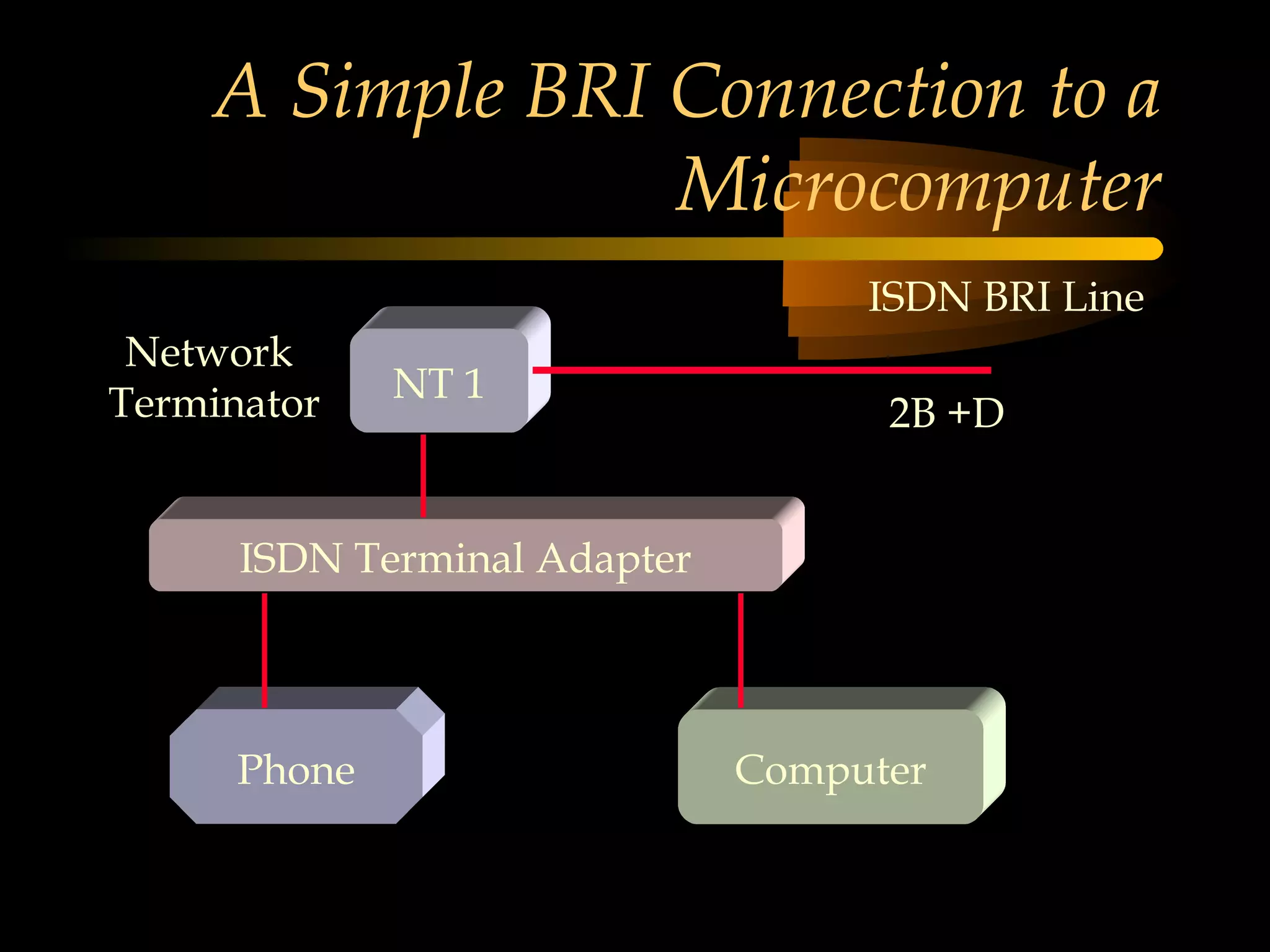
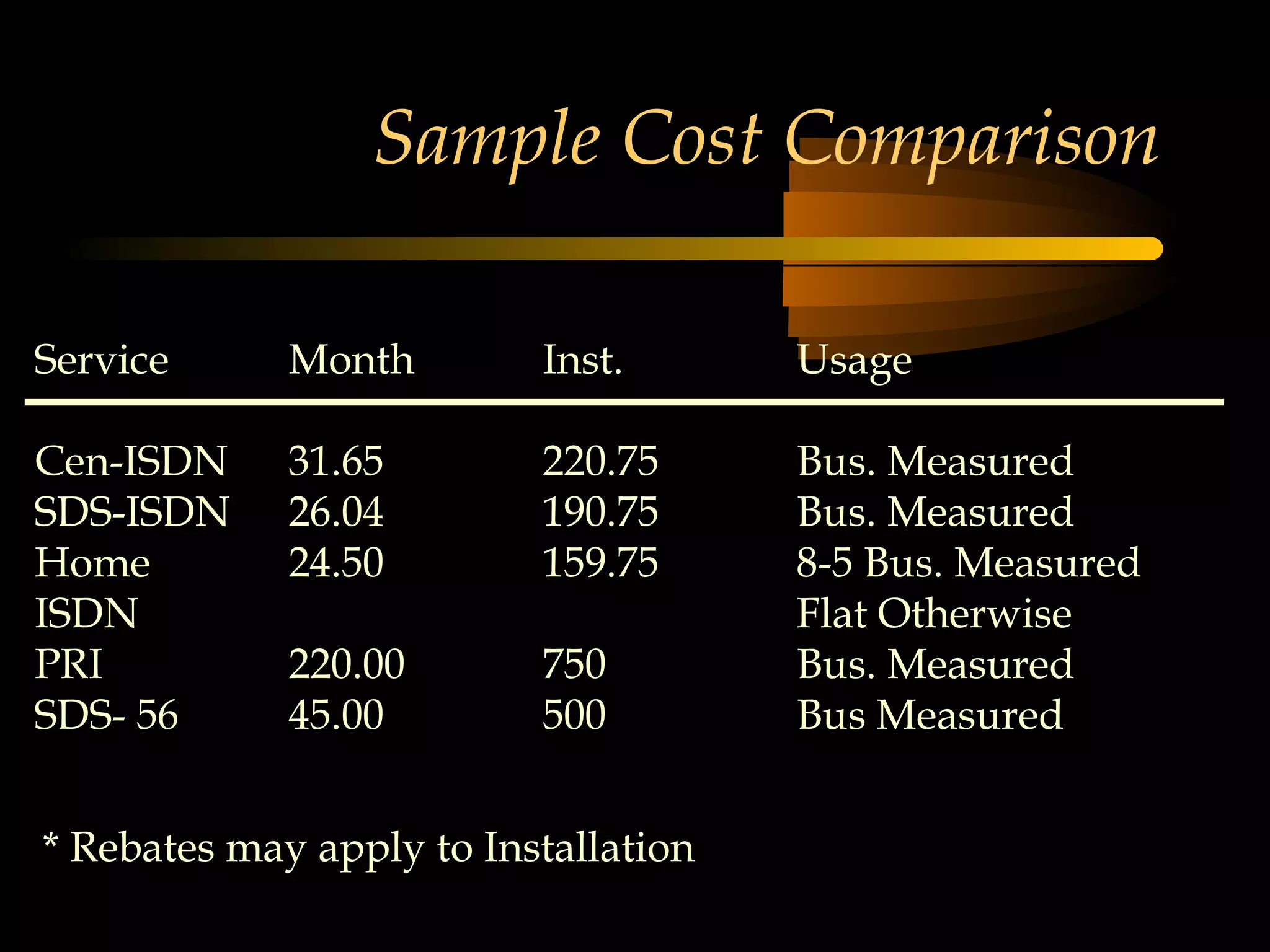
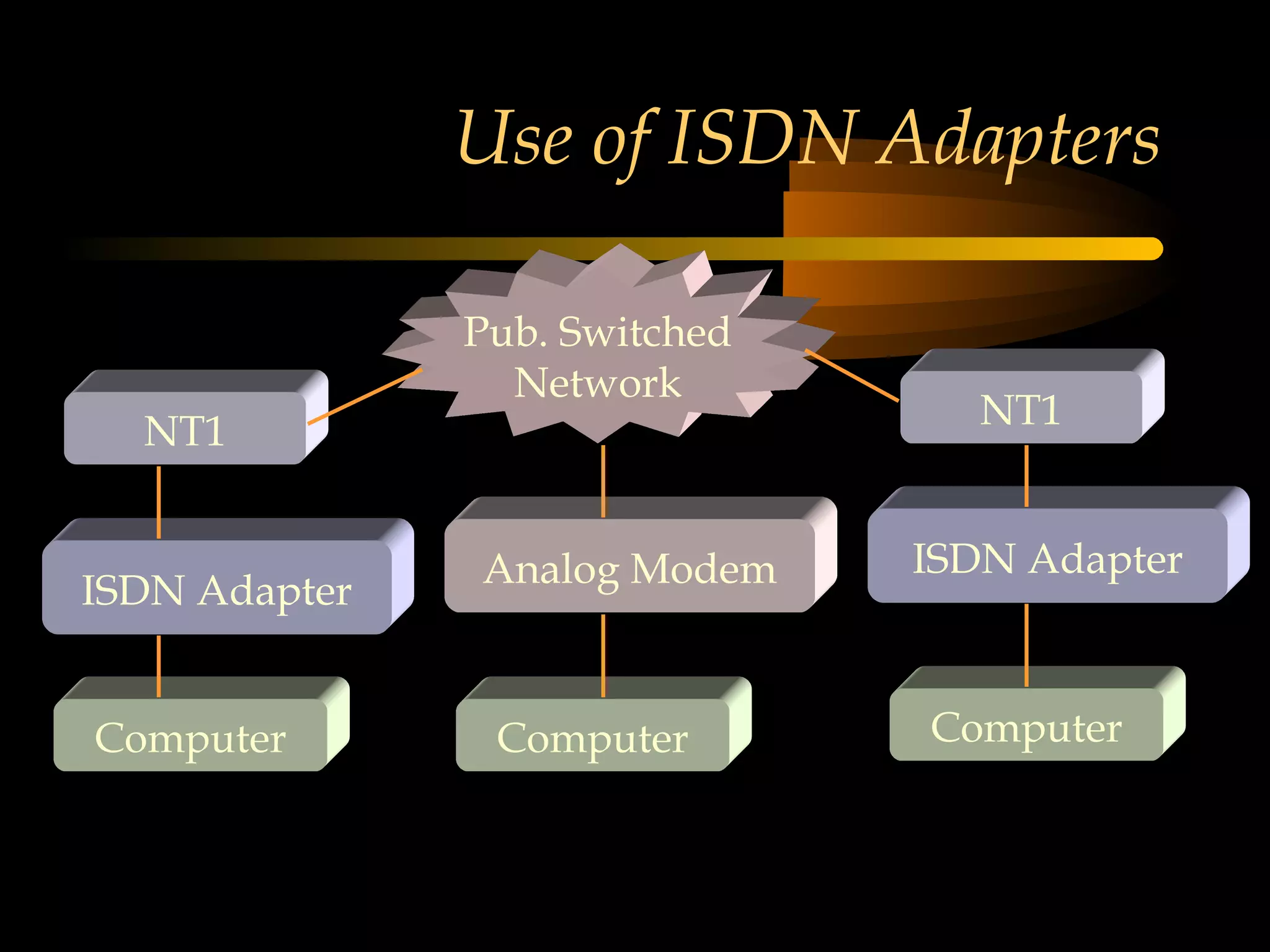
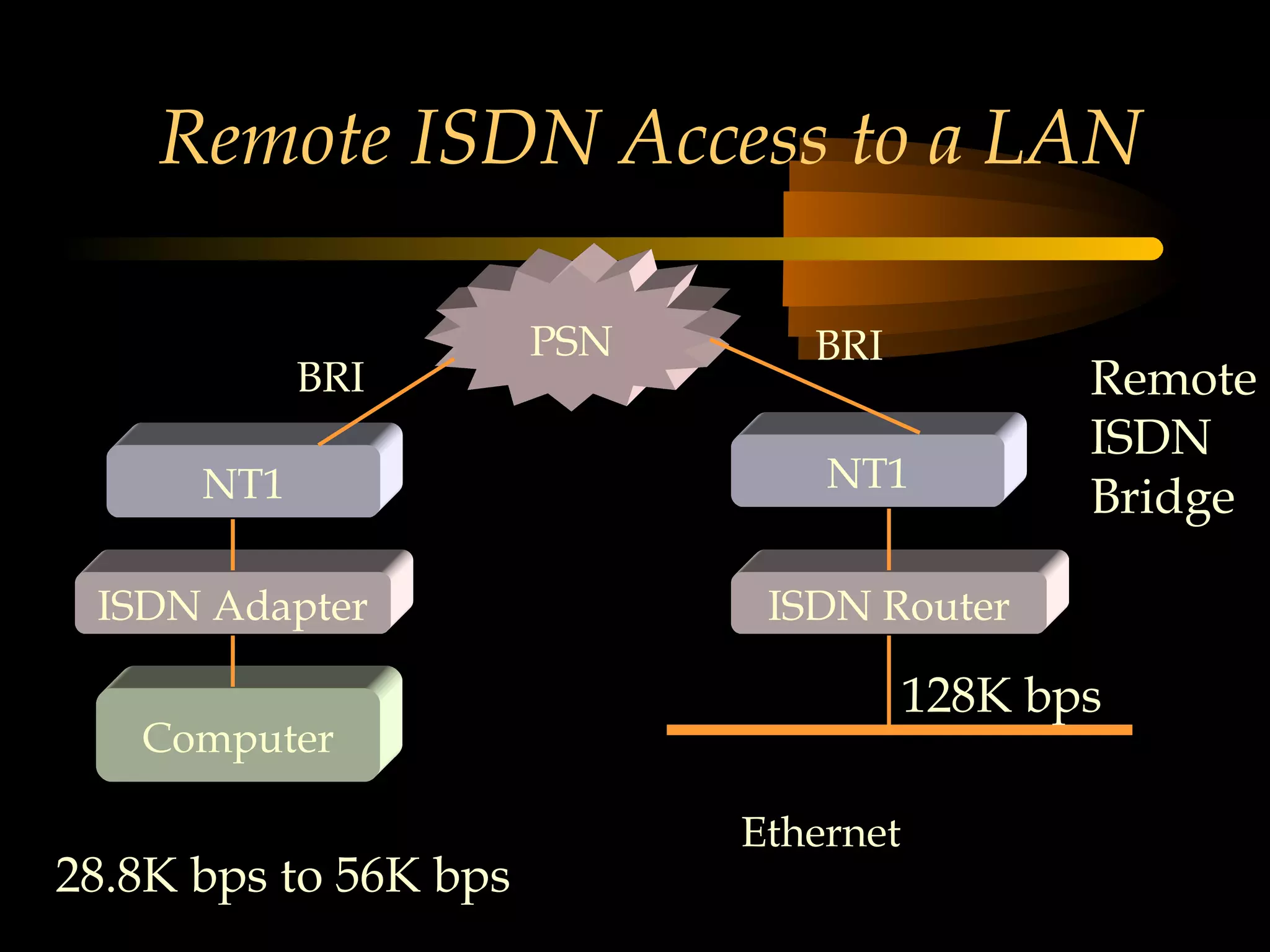
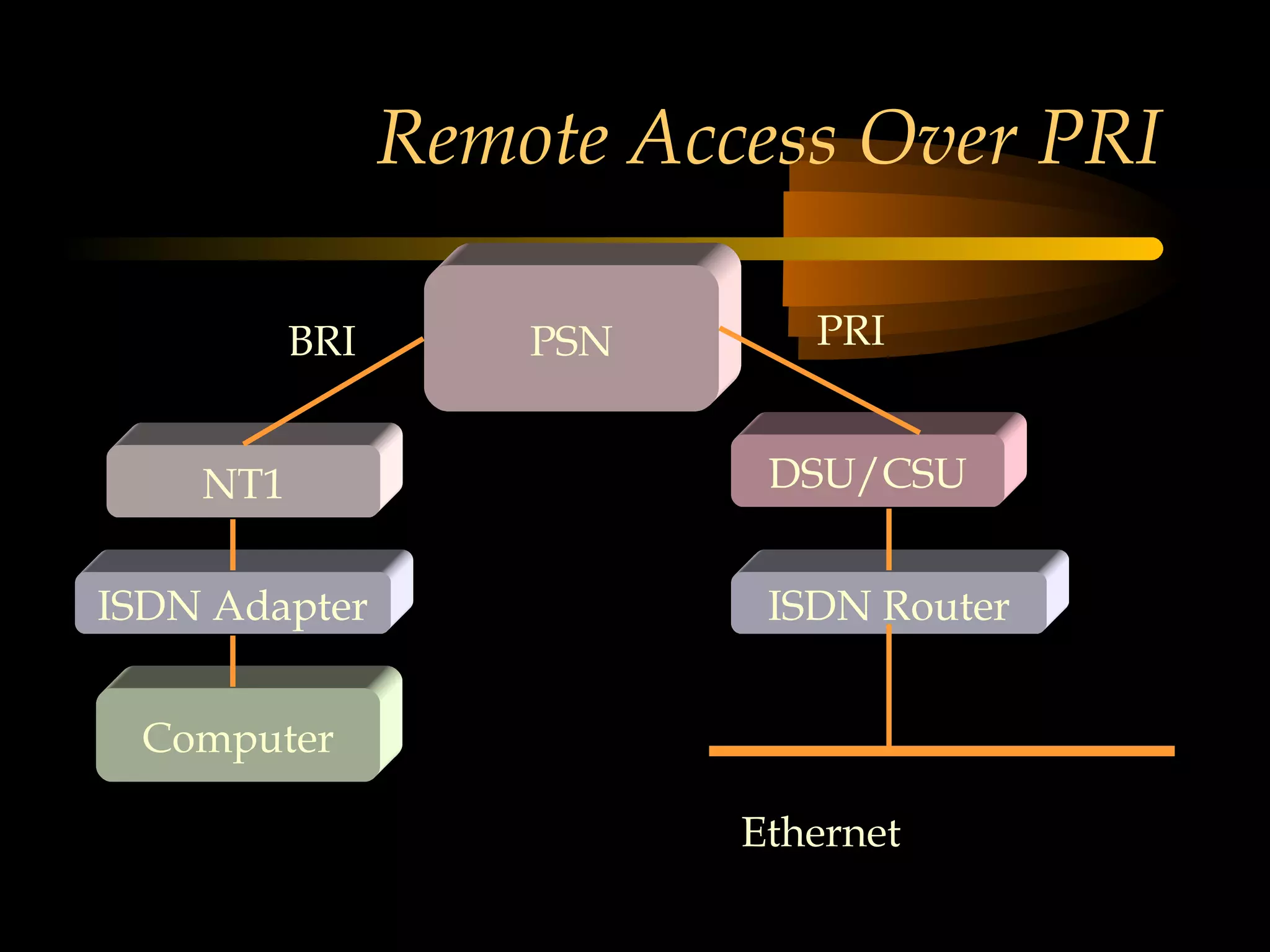
This document provides an overview of the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) in 3 chapters. It defines ISDN and describes its two main types of services: Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI). BRI uses 2 B channels and 1 D channel, while PRI uses 23 B channels and 1 D channel. Examples of using each for remote access to local area networks are provided. The document aims to explain ISDN standards, services, and example applications.