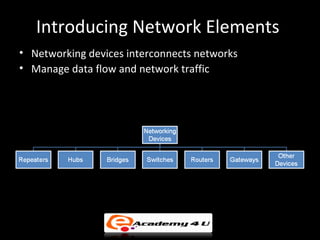
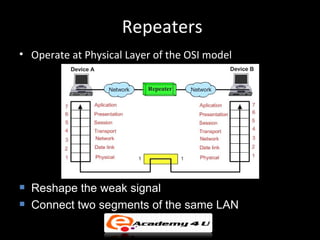
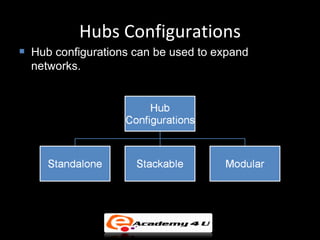
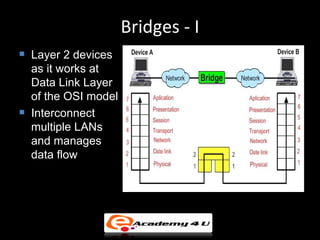
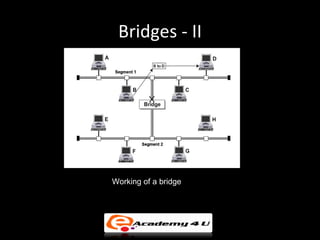
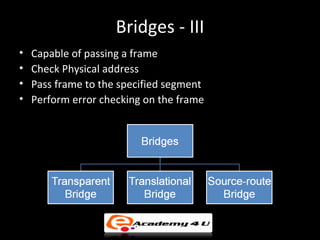
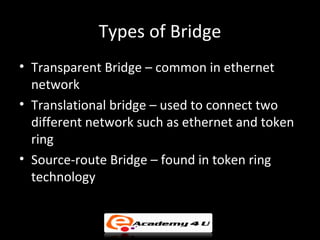
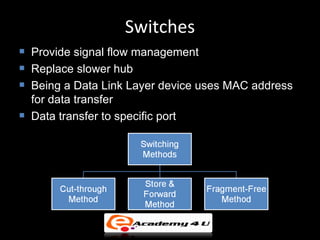
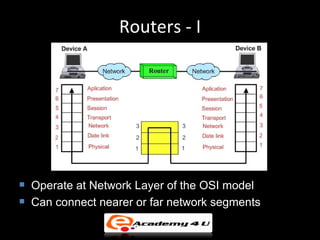
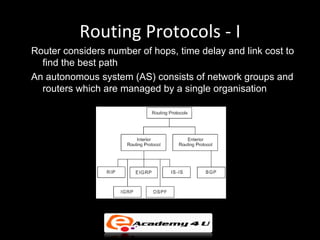
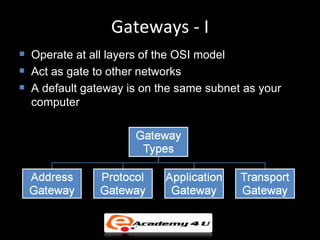
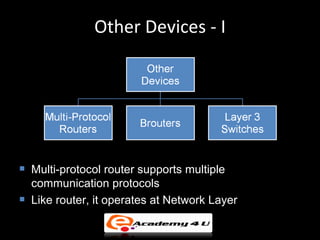
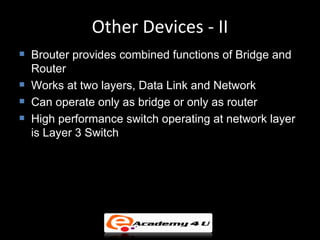
Networking devices like hubs, switches, routers, and gateways interconnect networks and manage data flow. Hubs operate at the physical layer and connect segments but do not filter traffic. Switches operate at the data link layer and can direct traffic to specific ports for better performance than hubs. Routers operate at the network layer and can connect networks across LANs, MANs, and WANs using IP addressing to route packets. Gateways can operate at multiple layers and act as connections between different network protocols or applications.