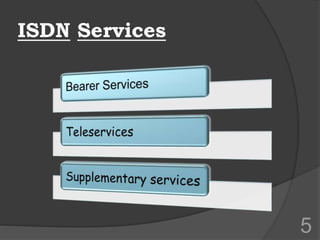
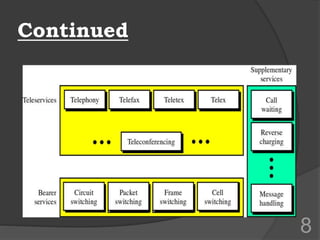
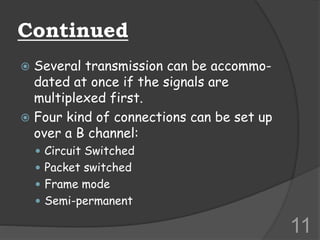
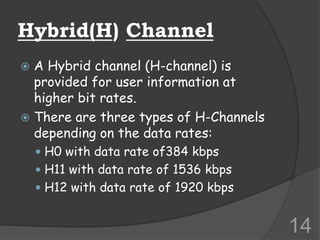
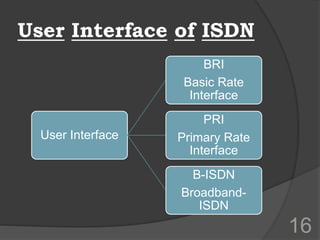
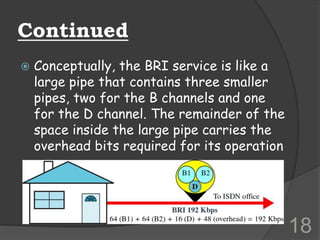
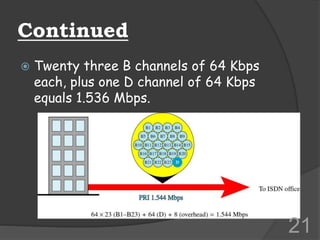
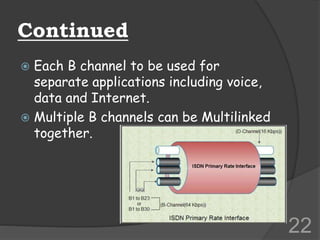
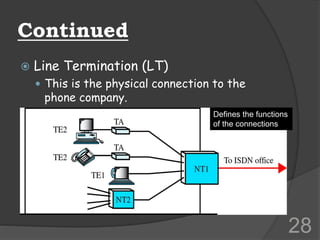
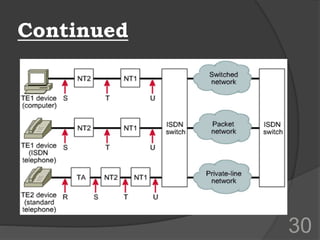
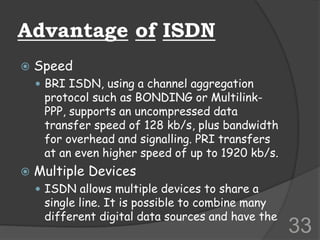
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) is a set of communication protocols that allows digital transmission of voice, video, and data over existing telephone lines. It was developed to digitize and integrate telephone networks to allow transmission of different data types. ISDN provides bearer, tele, and supplementary services through basic rate interface (BRI) with 2 B channels of 64 kbps each and 1 D channel of 16 kbps, or primary rate interface (PRI) with 23 B channels of 64 kbps and 1 D channel of 64 kbps. While ISDN provided faster speeds than analog networks, it has been surpassed by newer technologies like DSL and cable that provide even higher speeds at lower costs.