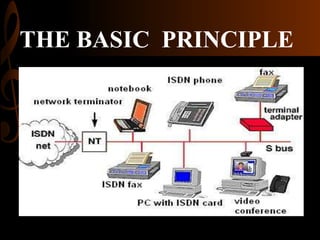
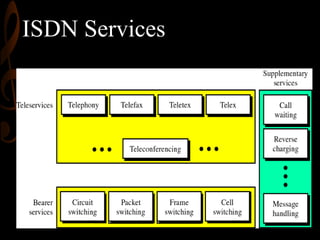
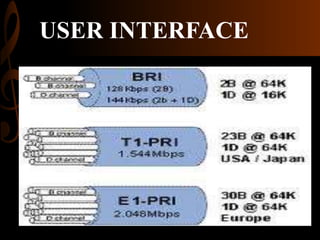
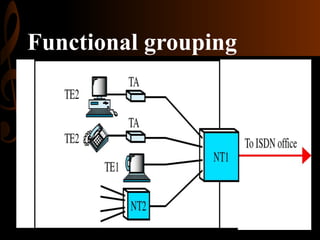
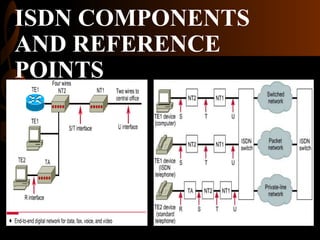
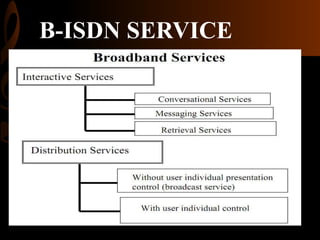
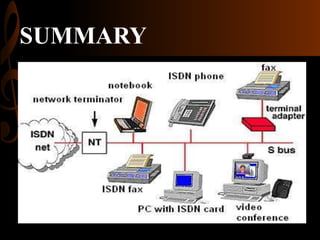
ISDN, developed by ITU-T in 1976, is a set of protocols designed to digitize the telephone network for audio, video, and text transmission, enhancing connectivity and service integration. It features bearer services for direct information transfer, teleservices for processed data, and supplementary services, with key interfaces including Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI). ISDN aims to support both narrowband and broadband communications, facilitating diverse applications and ensuring improved voice quality over traditional analog systems.