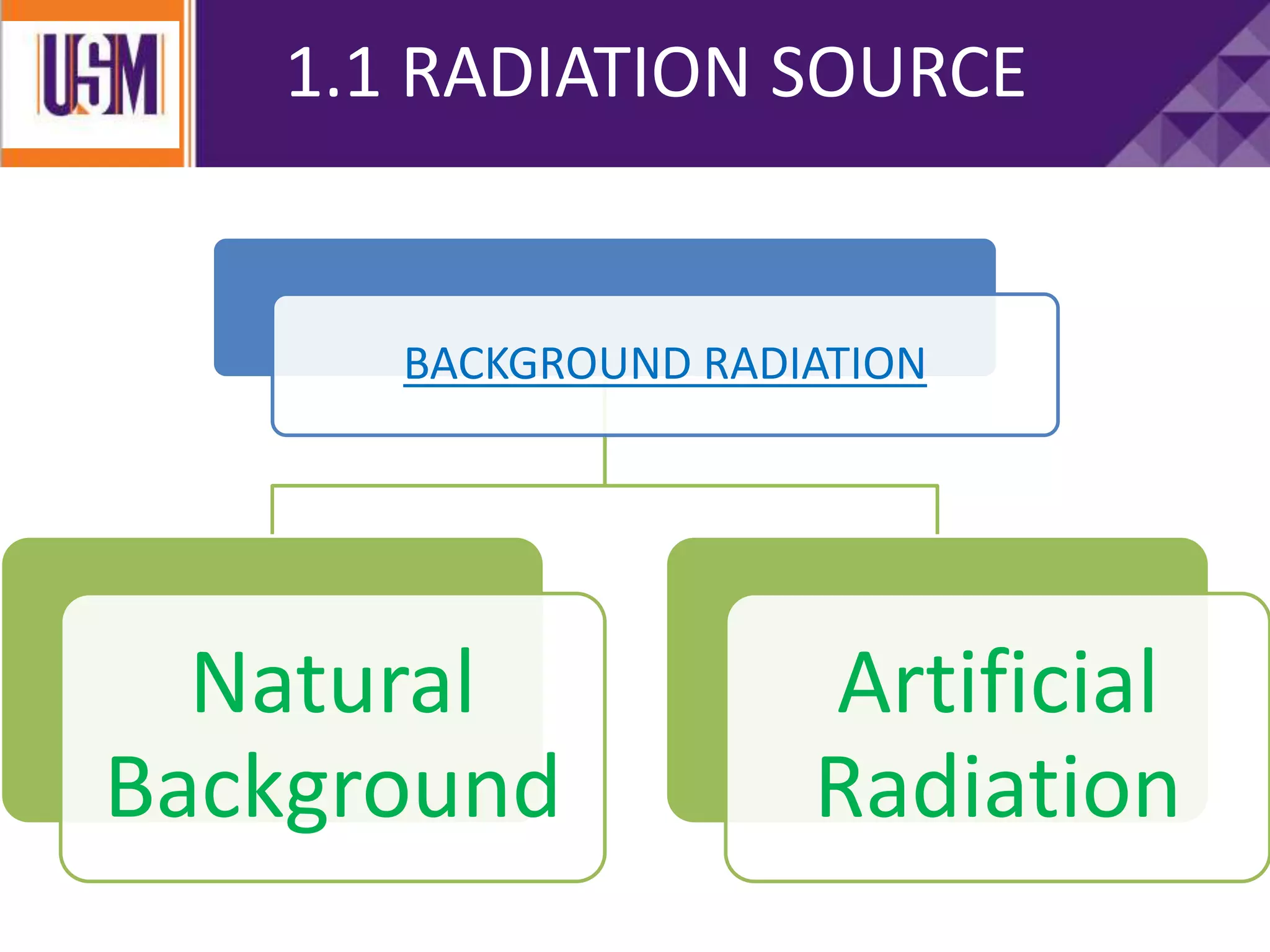
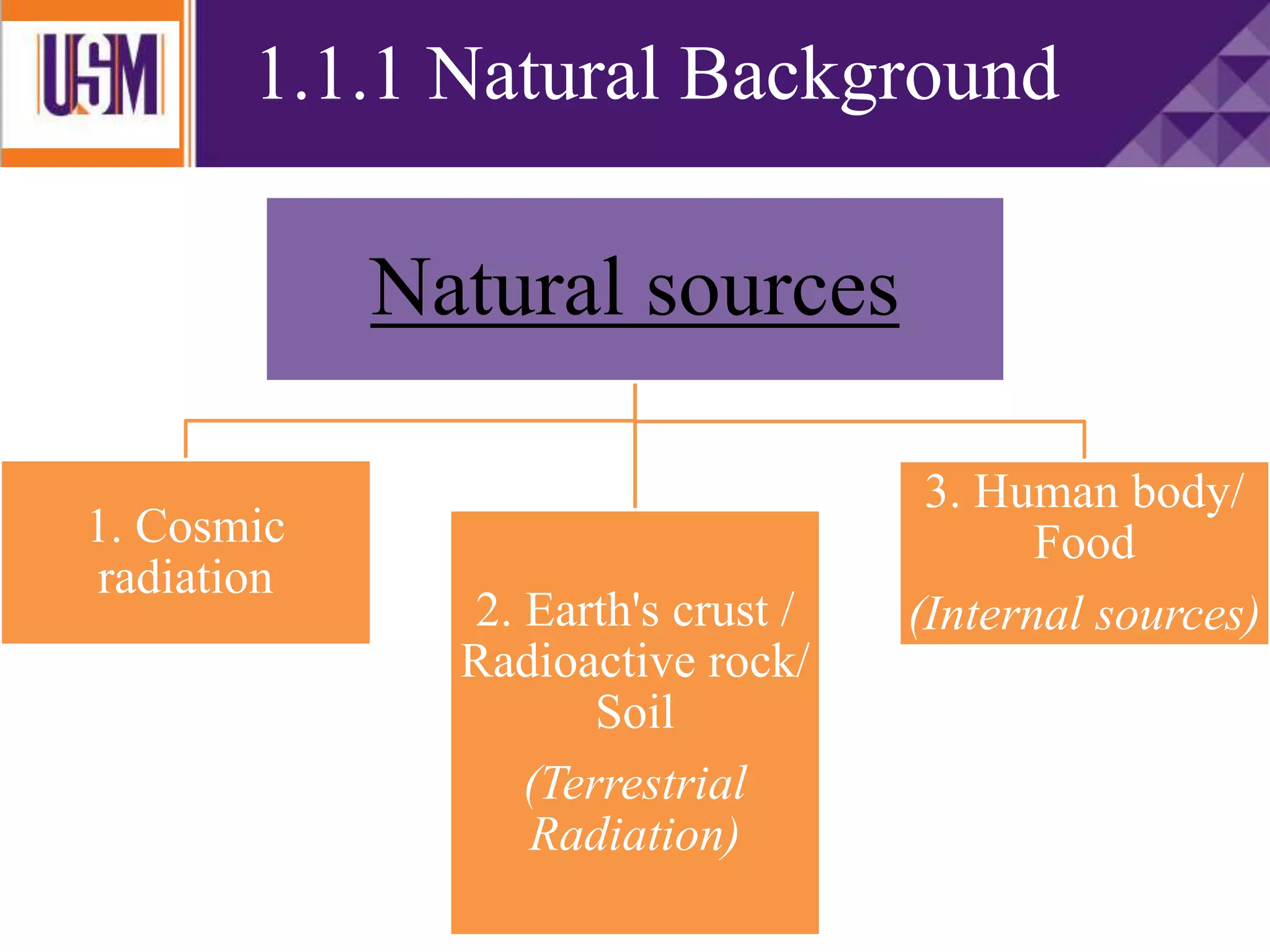
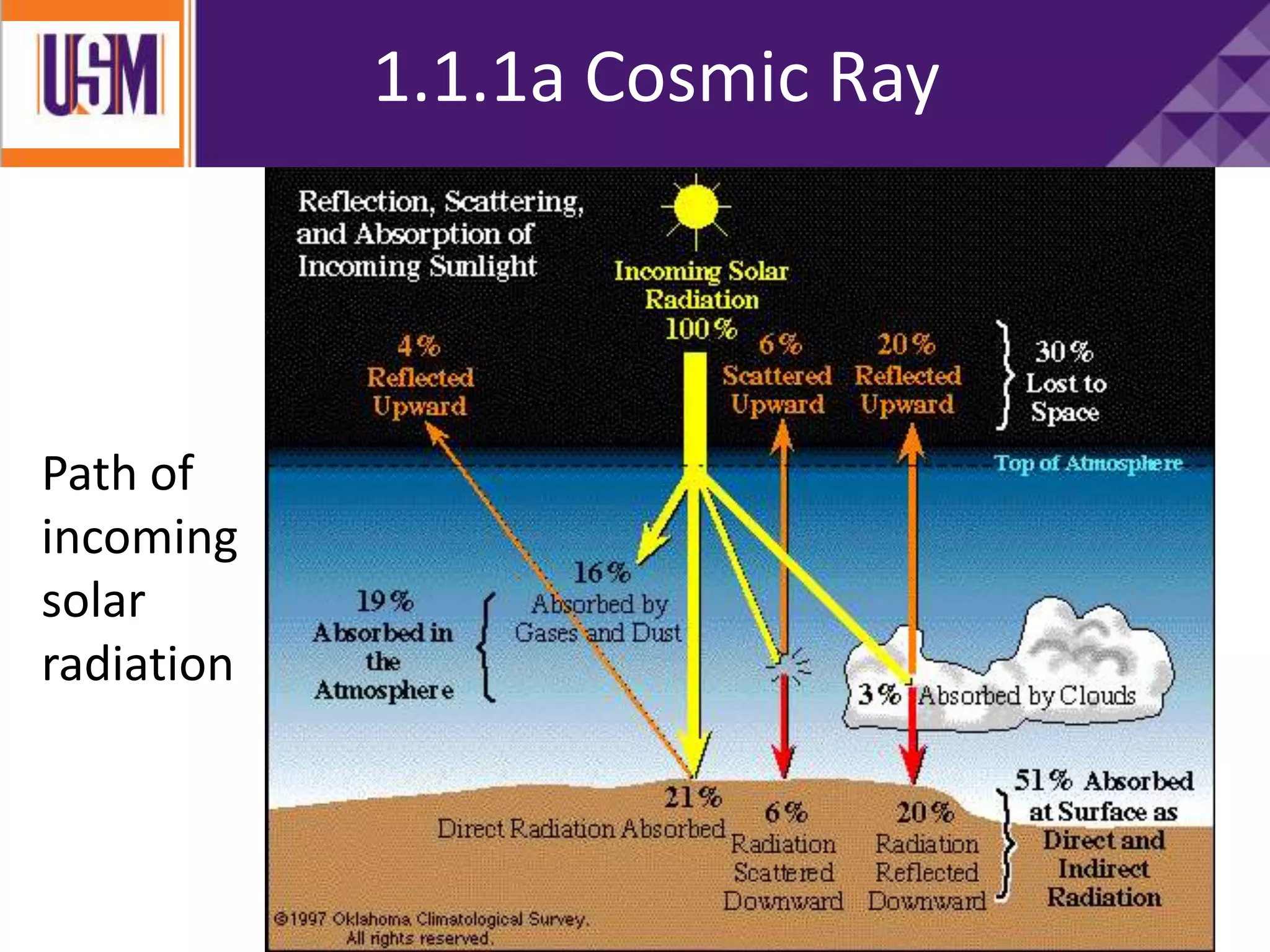
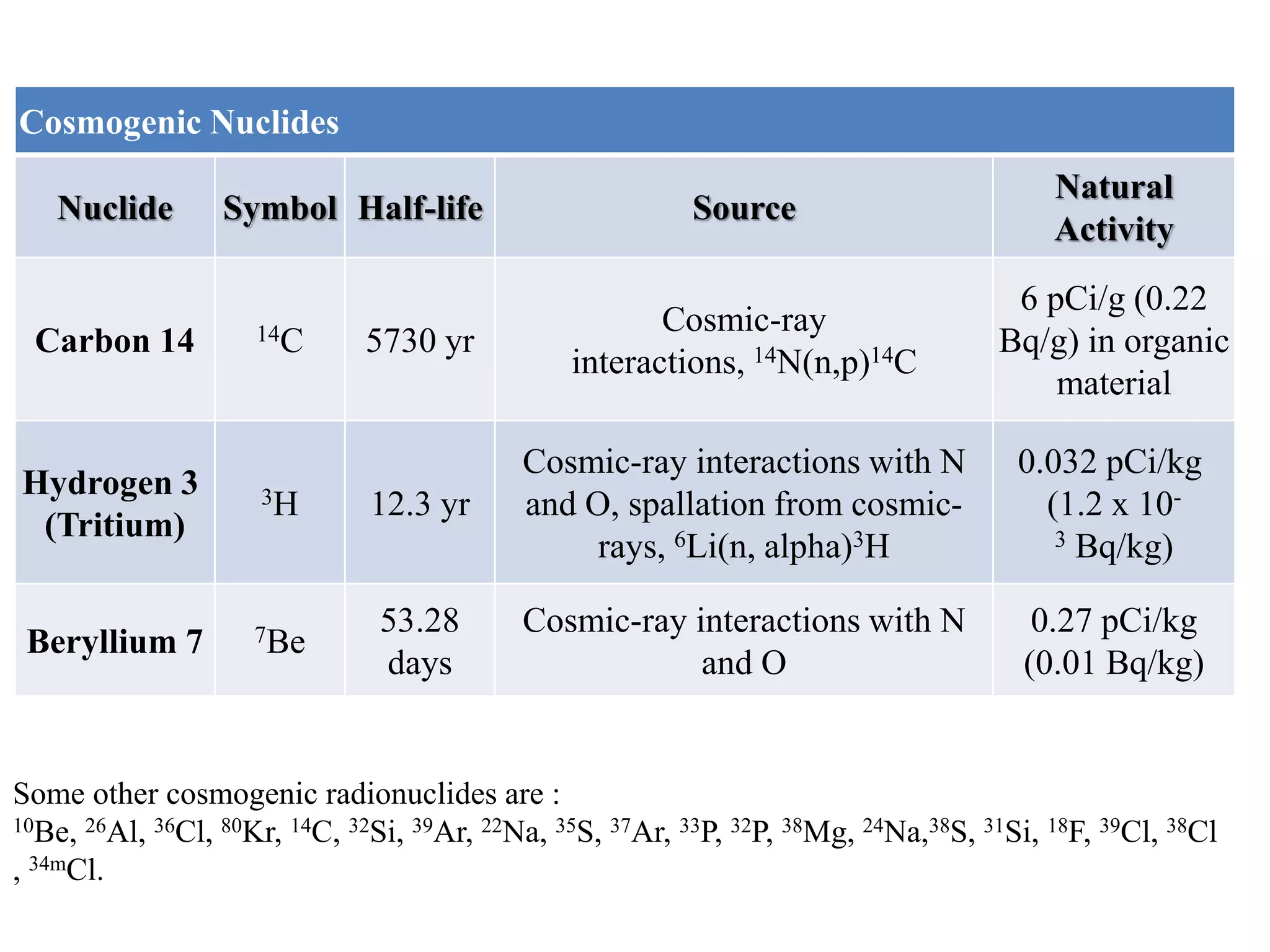
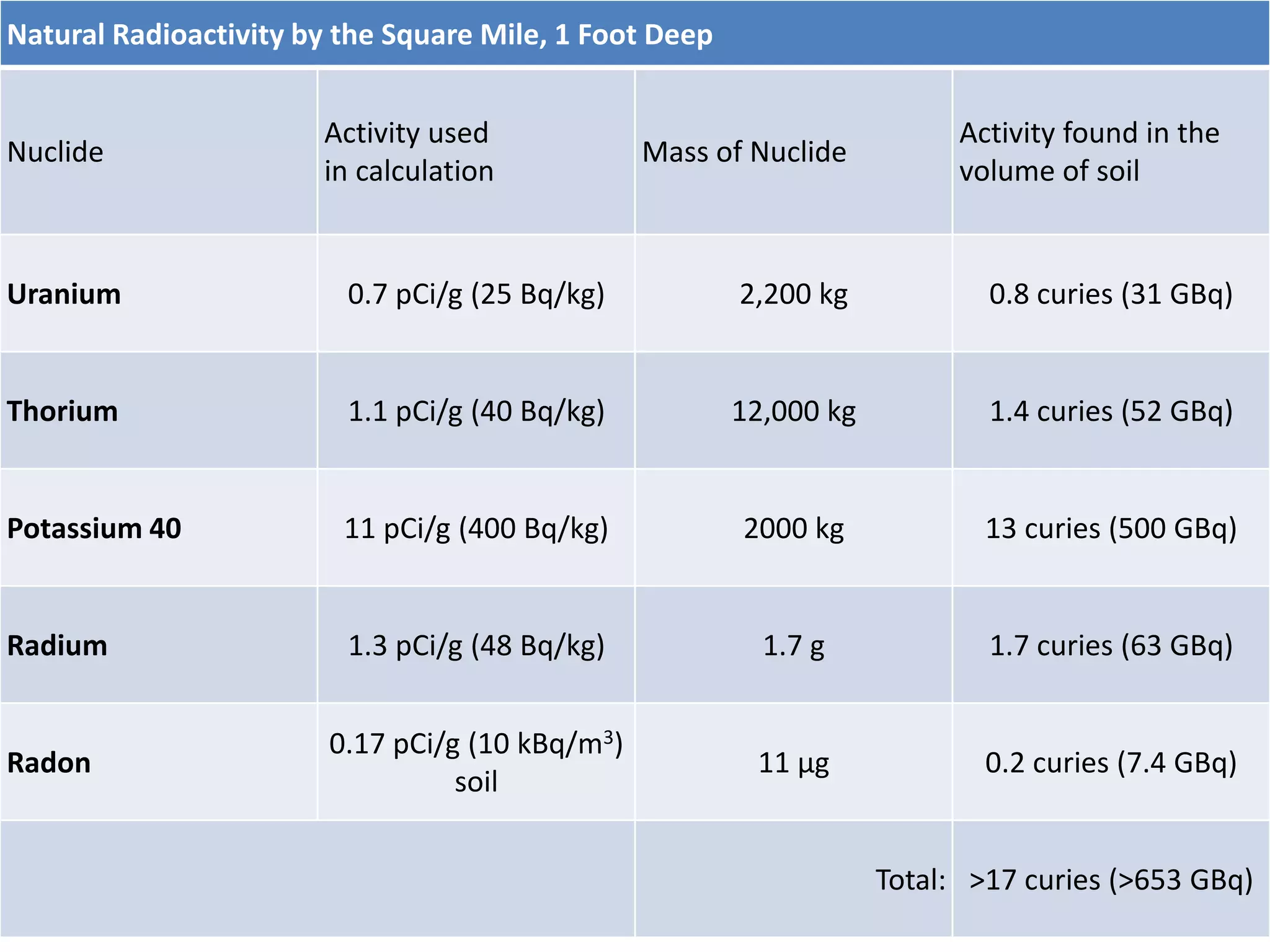
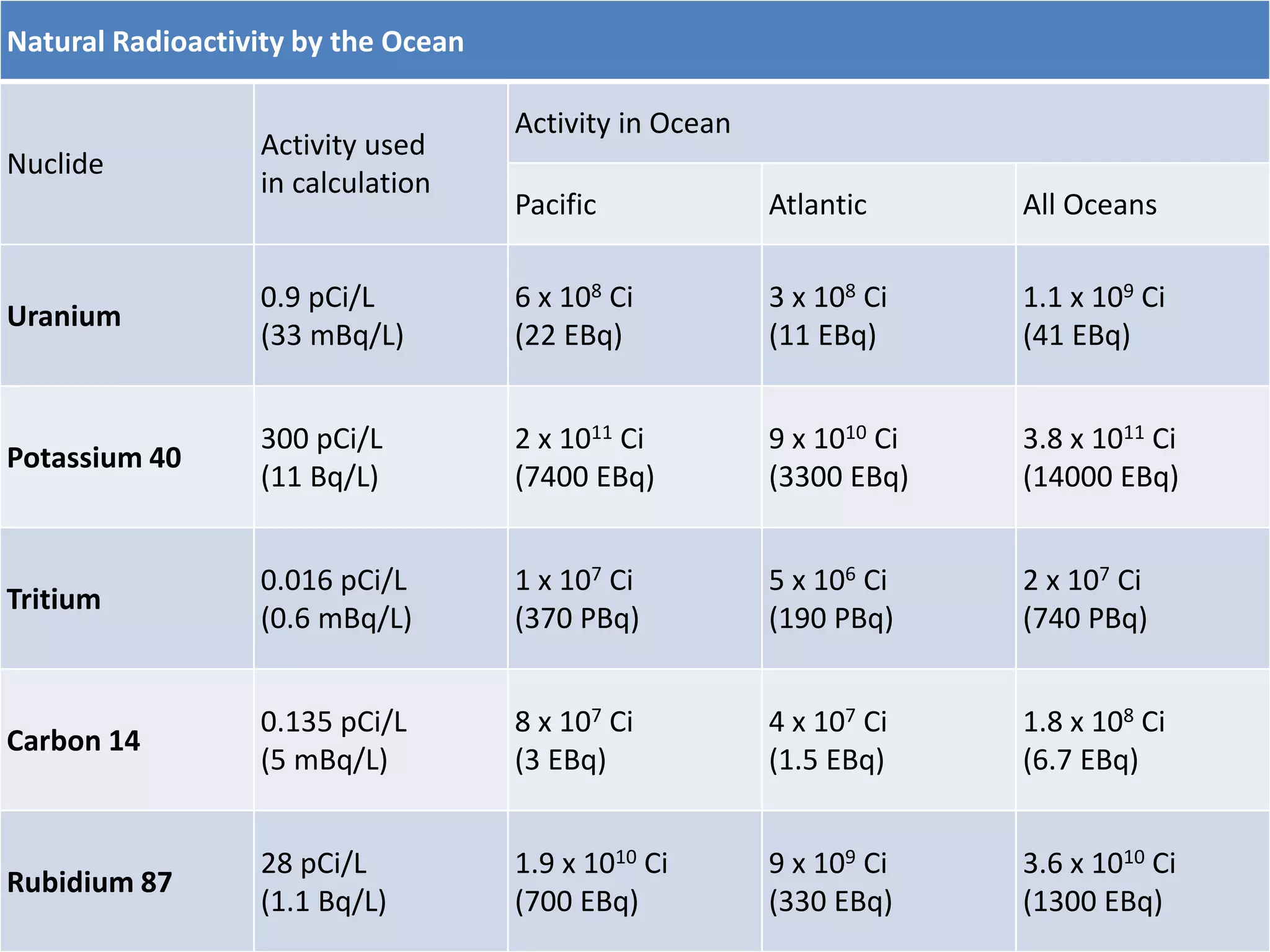
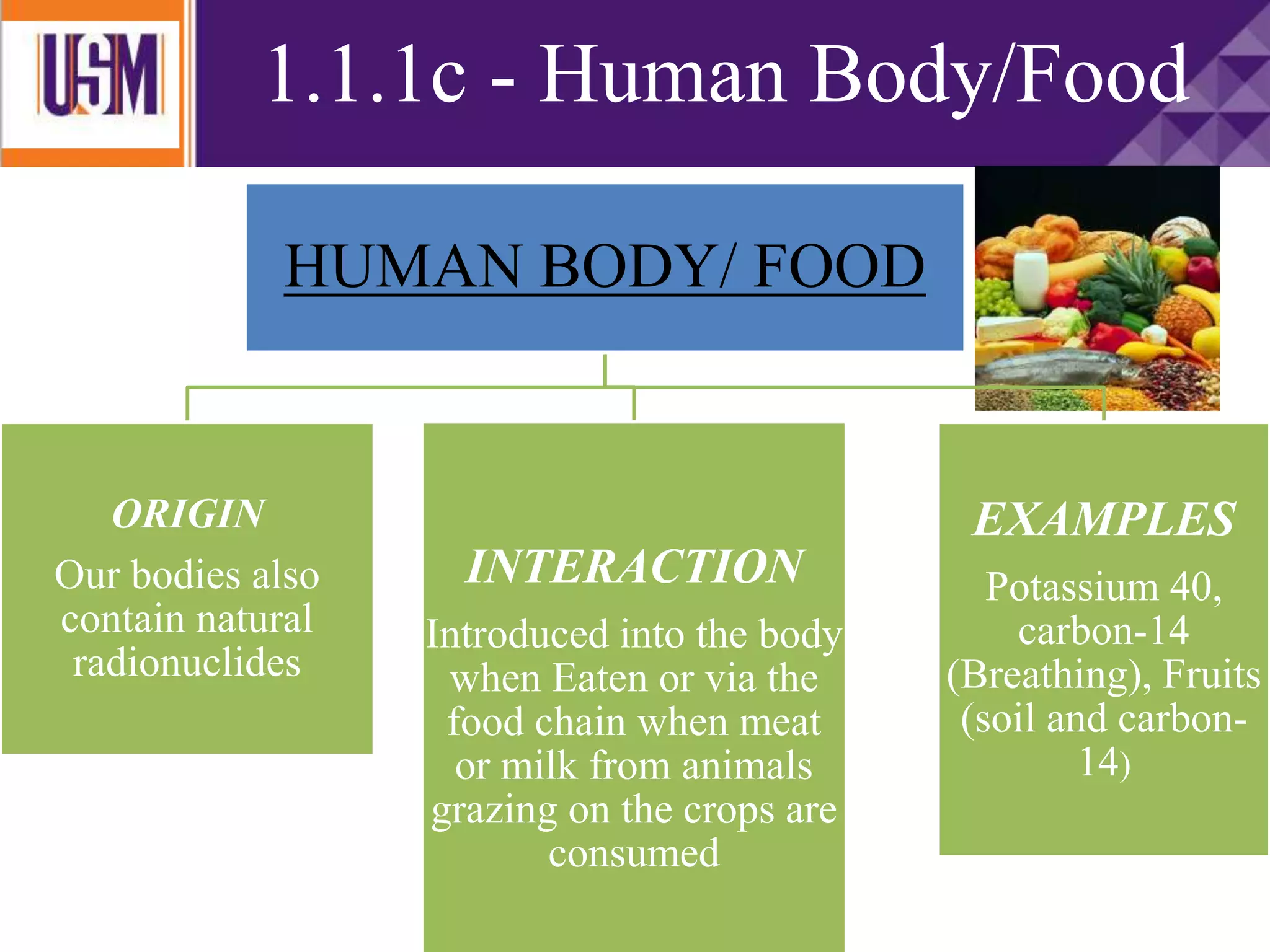
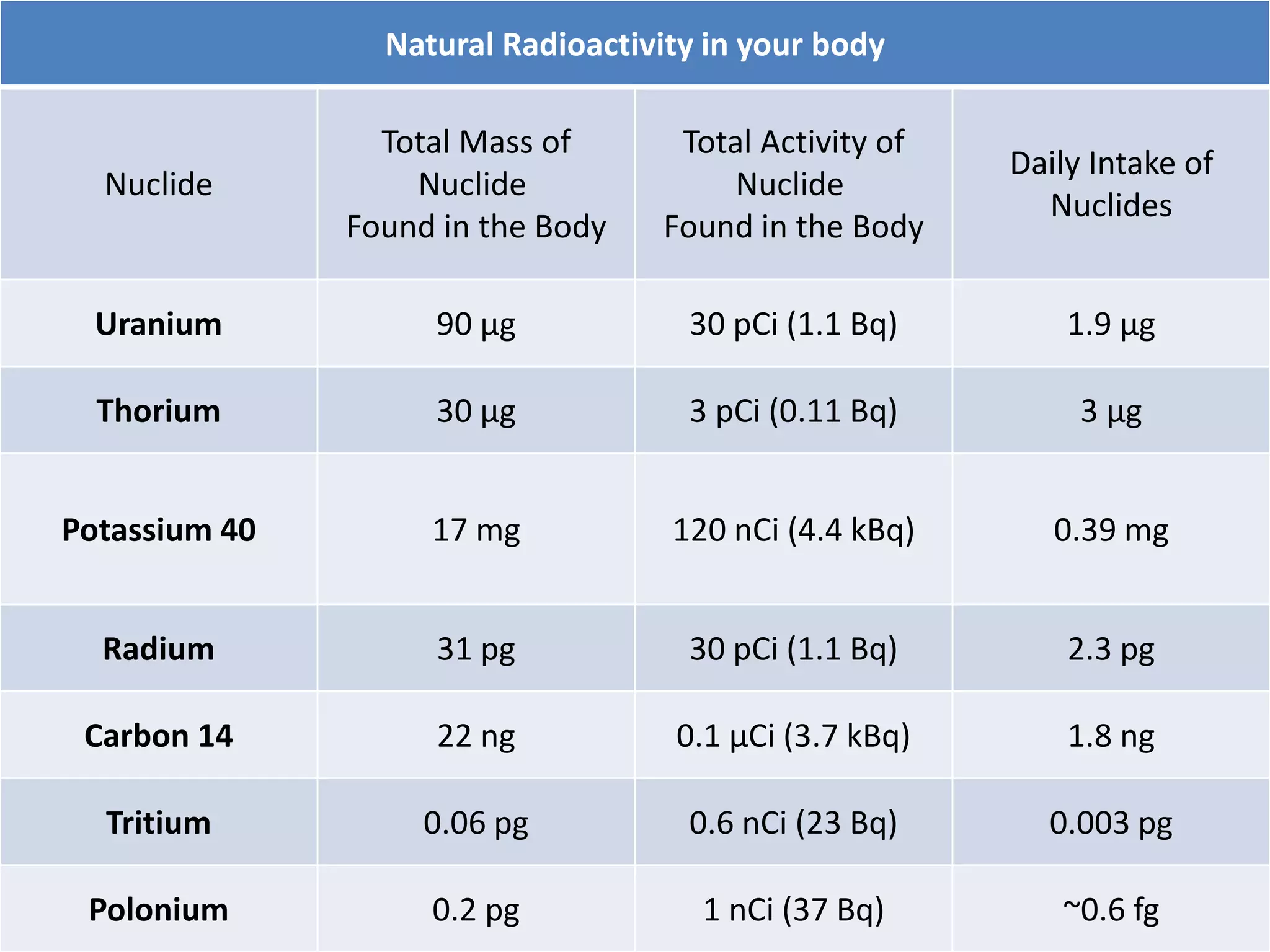
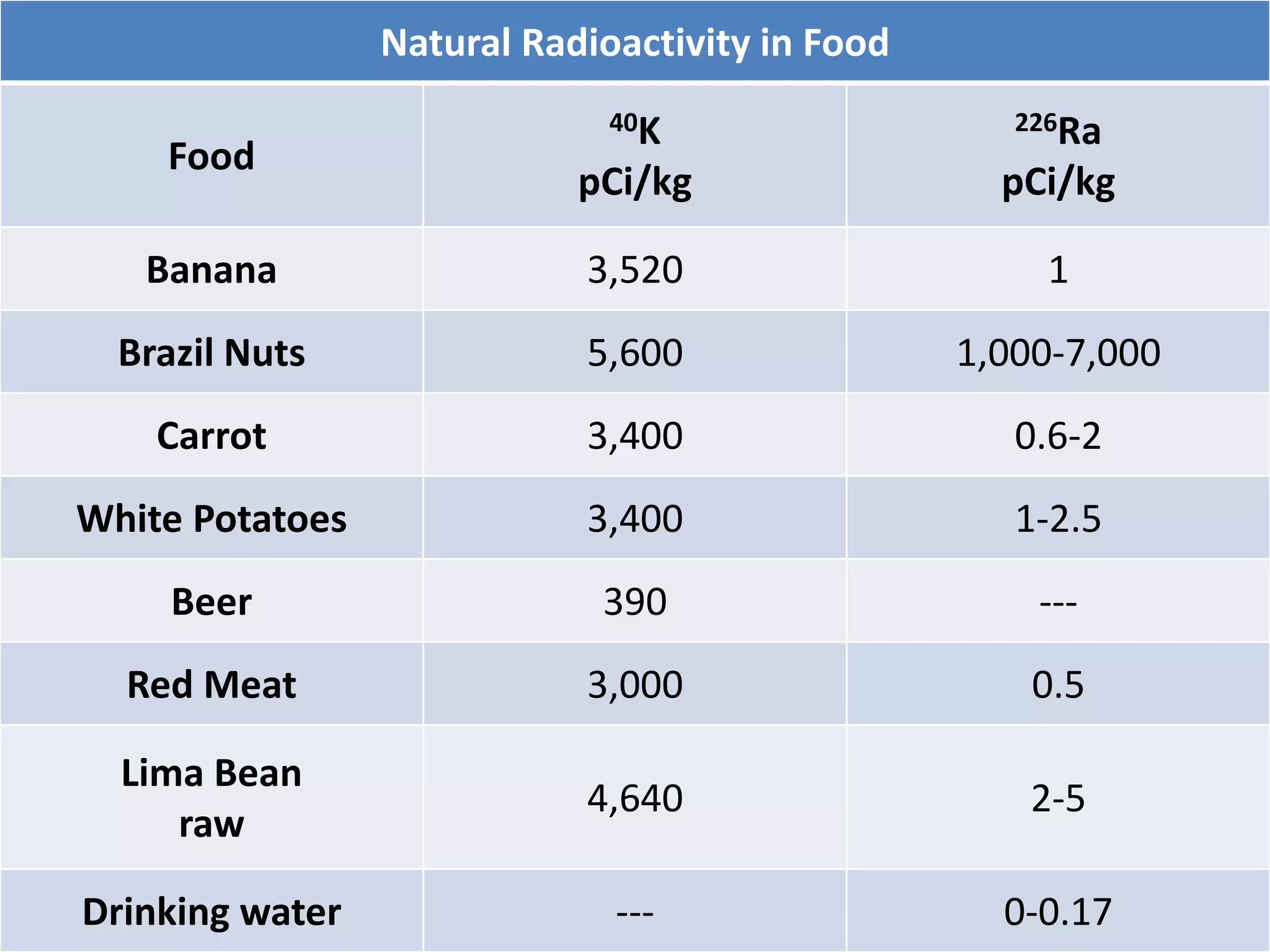
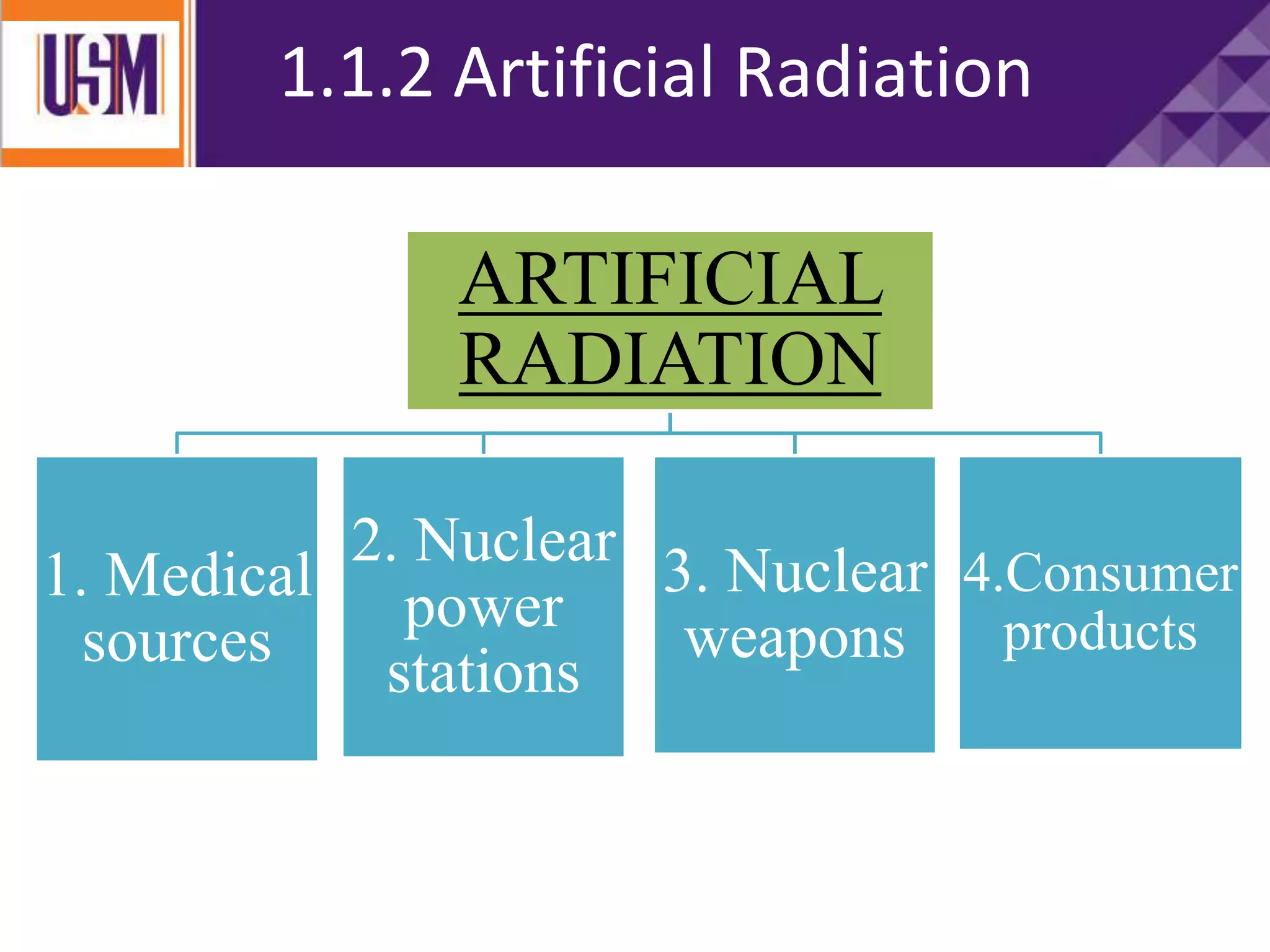
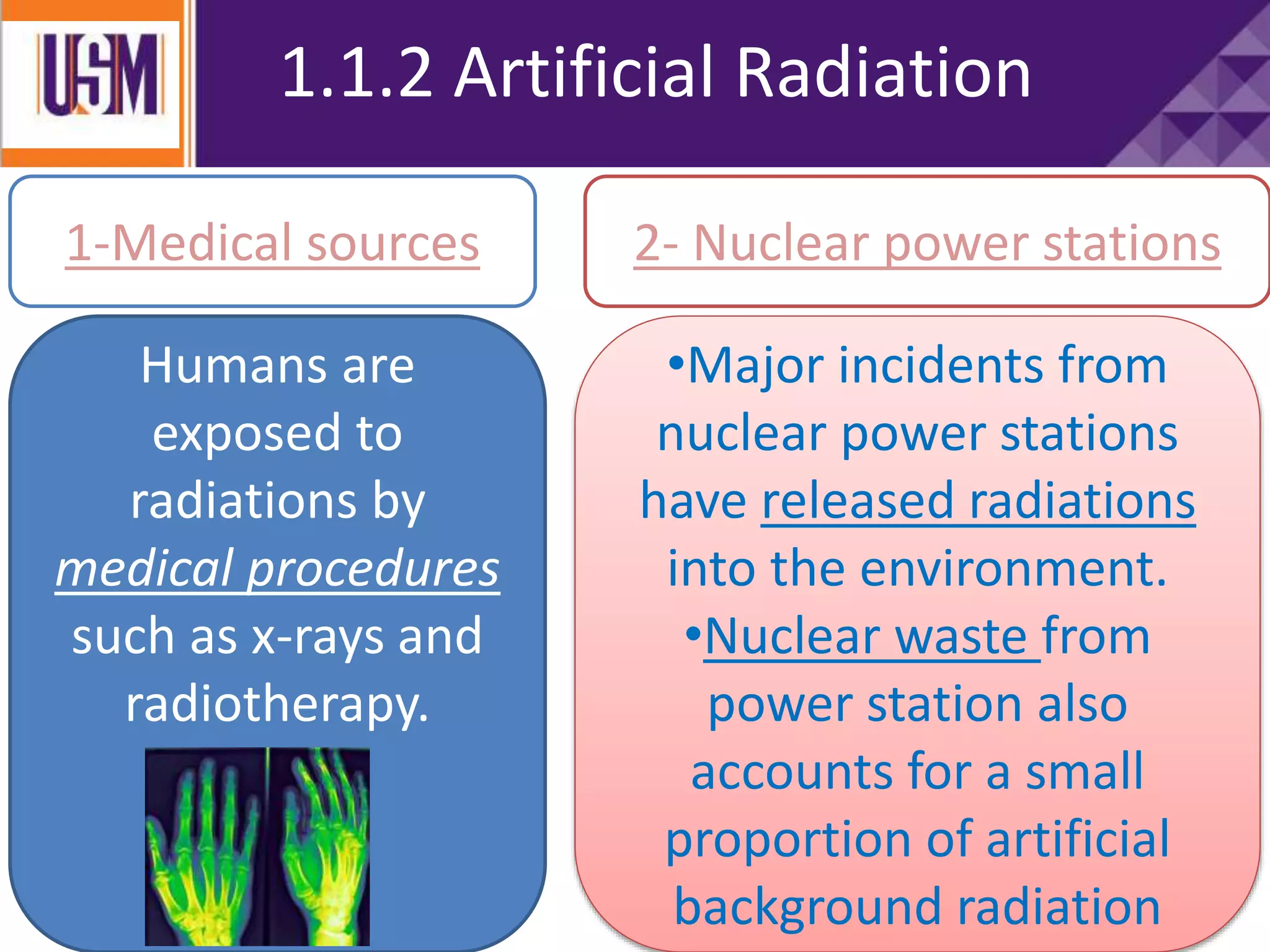
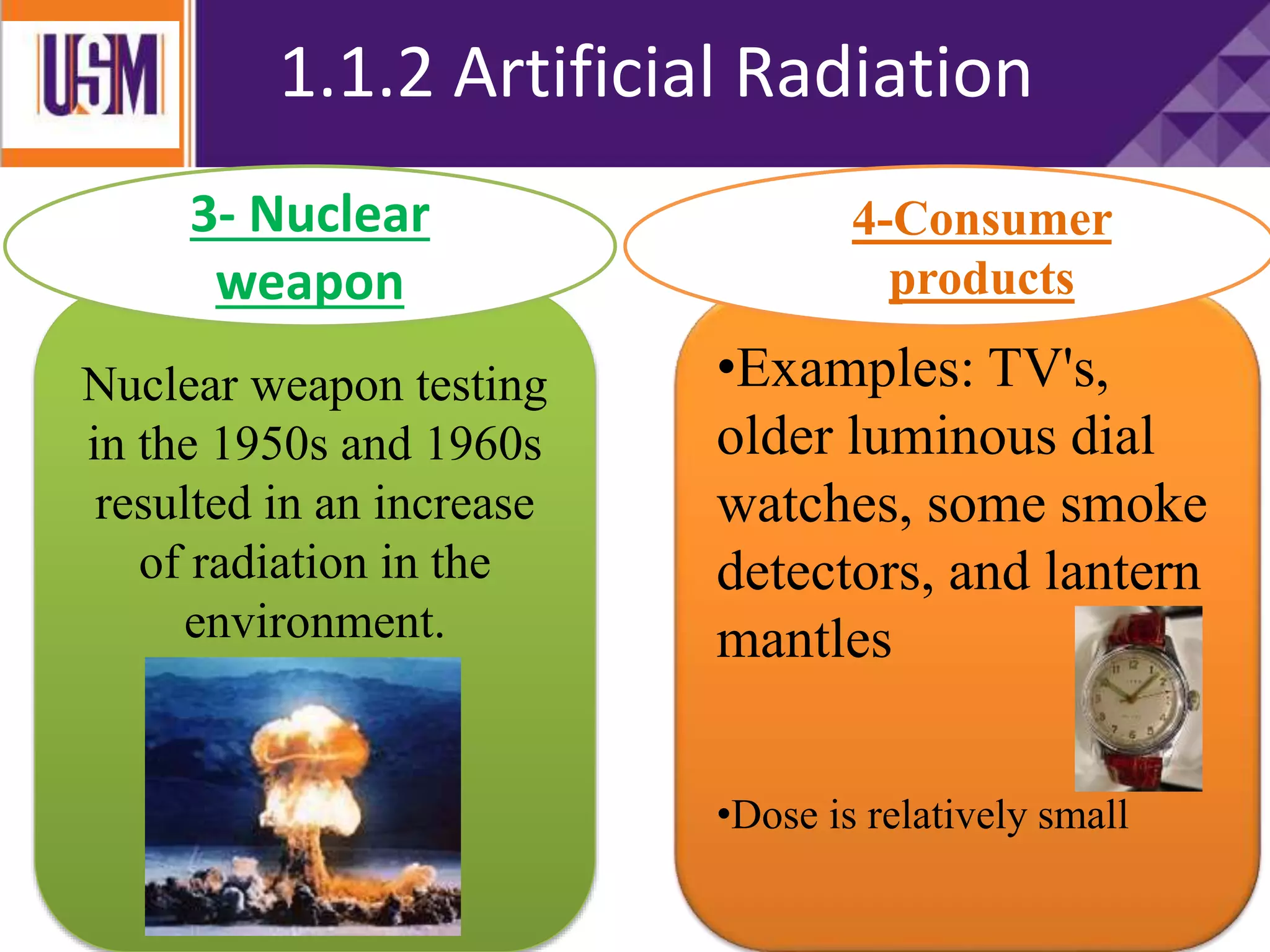
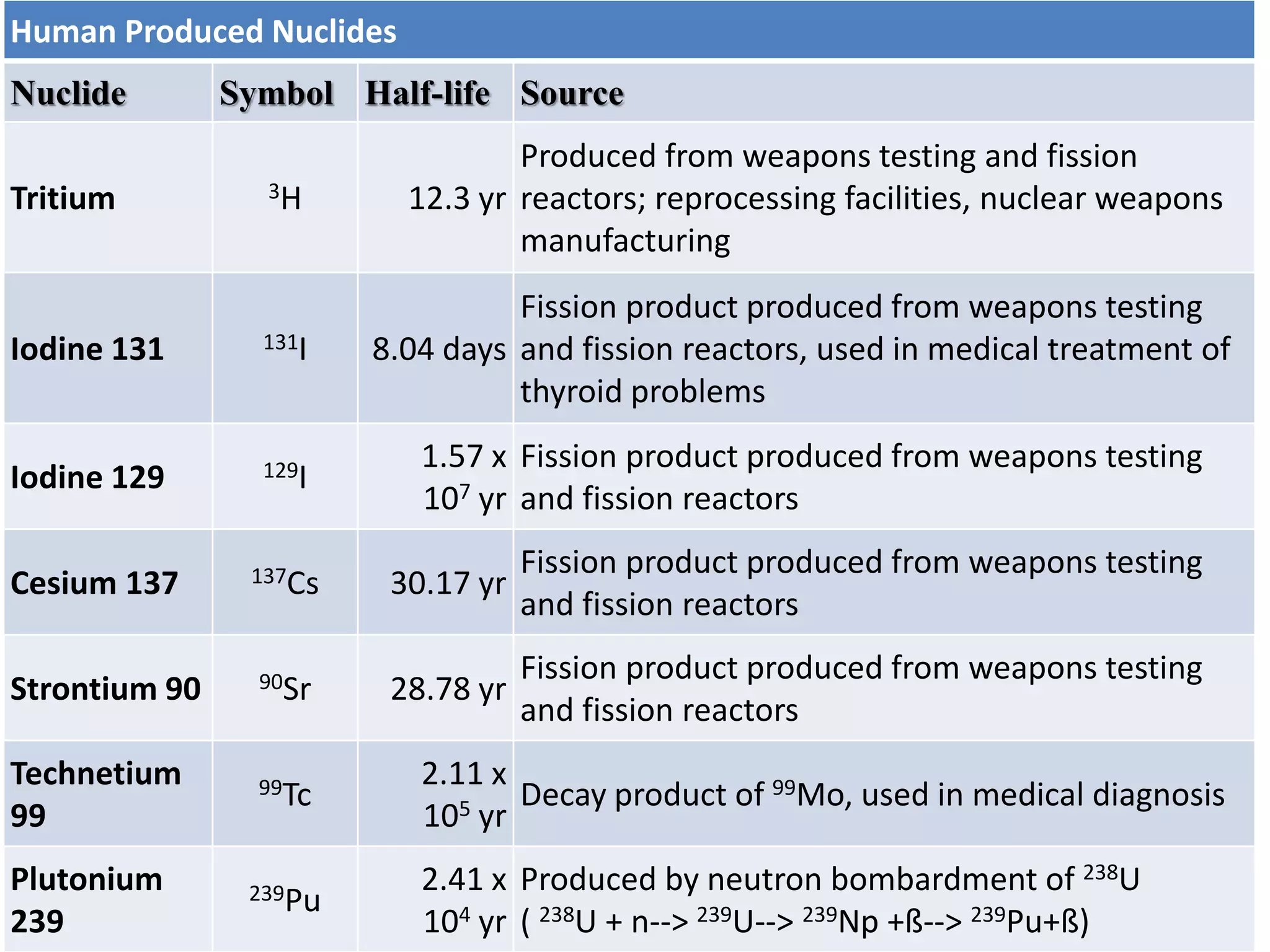
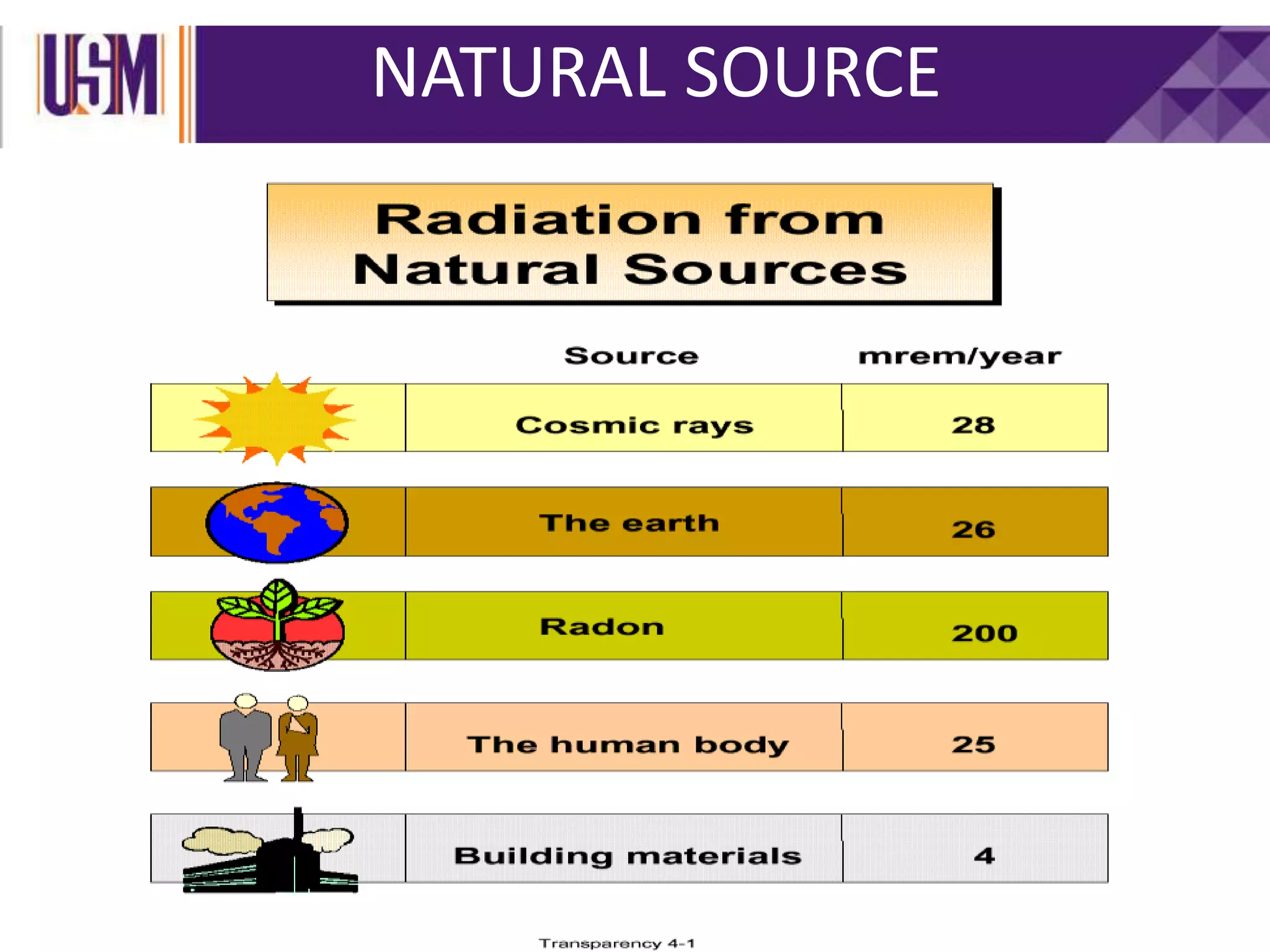
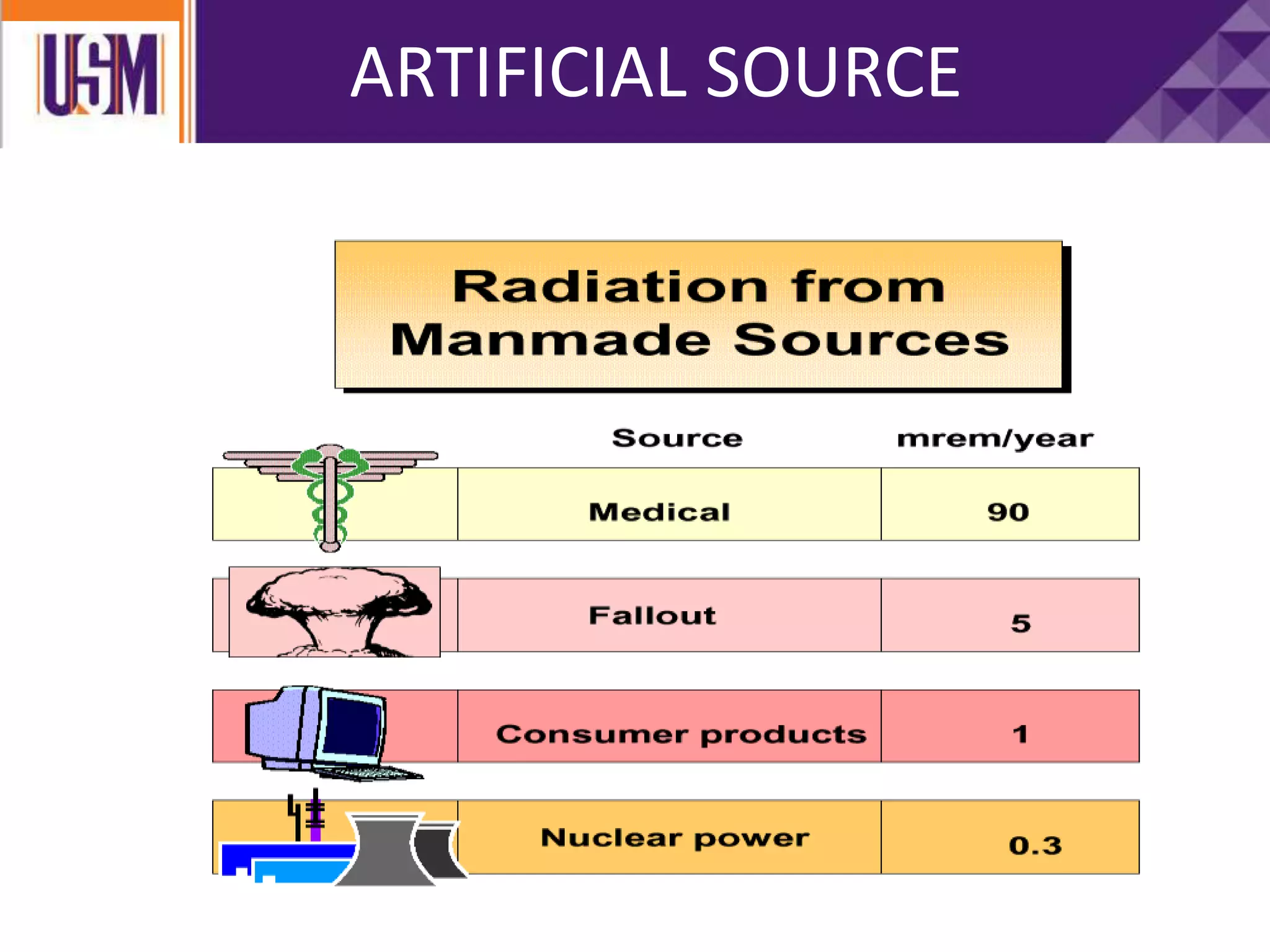
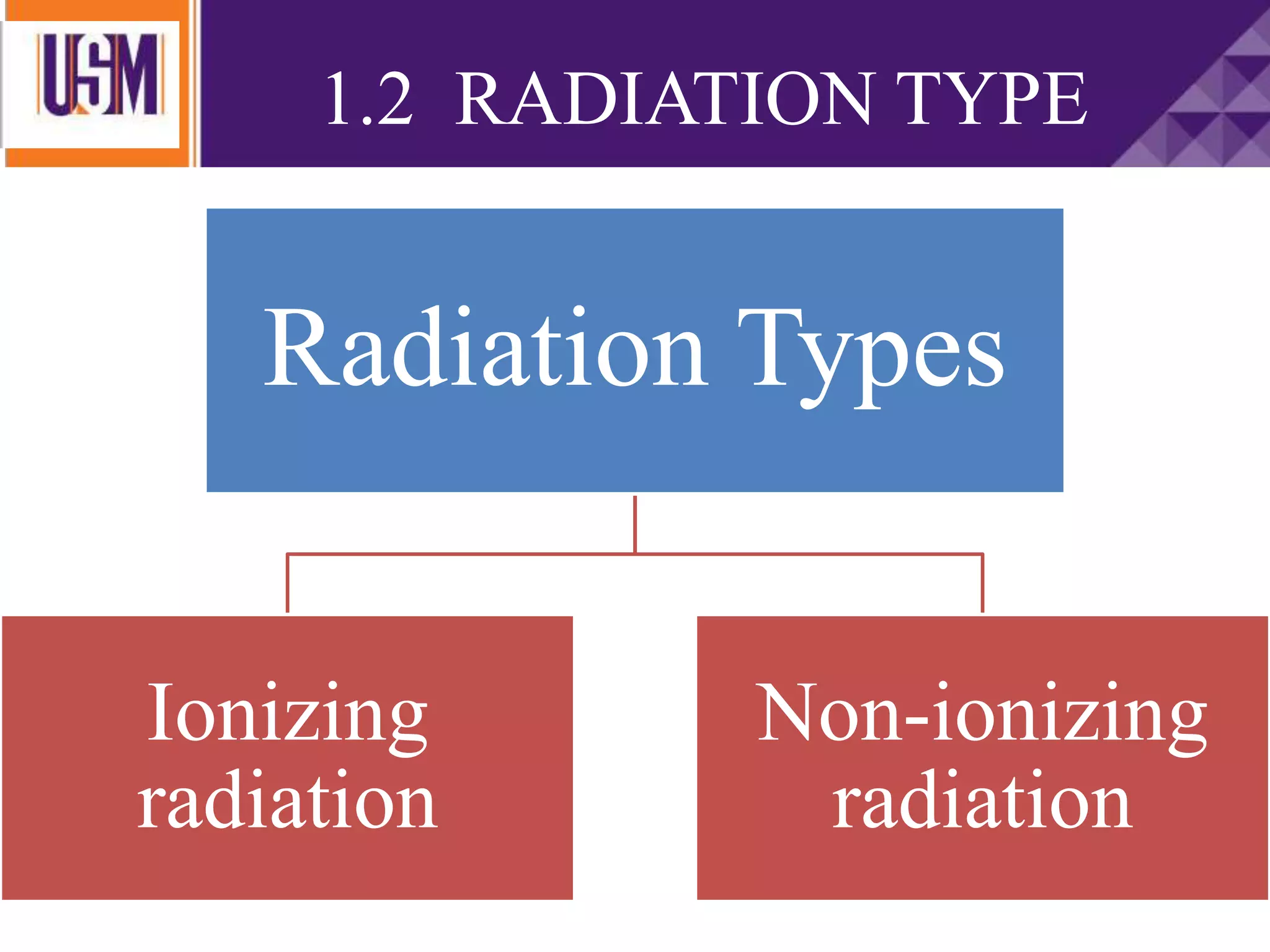
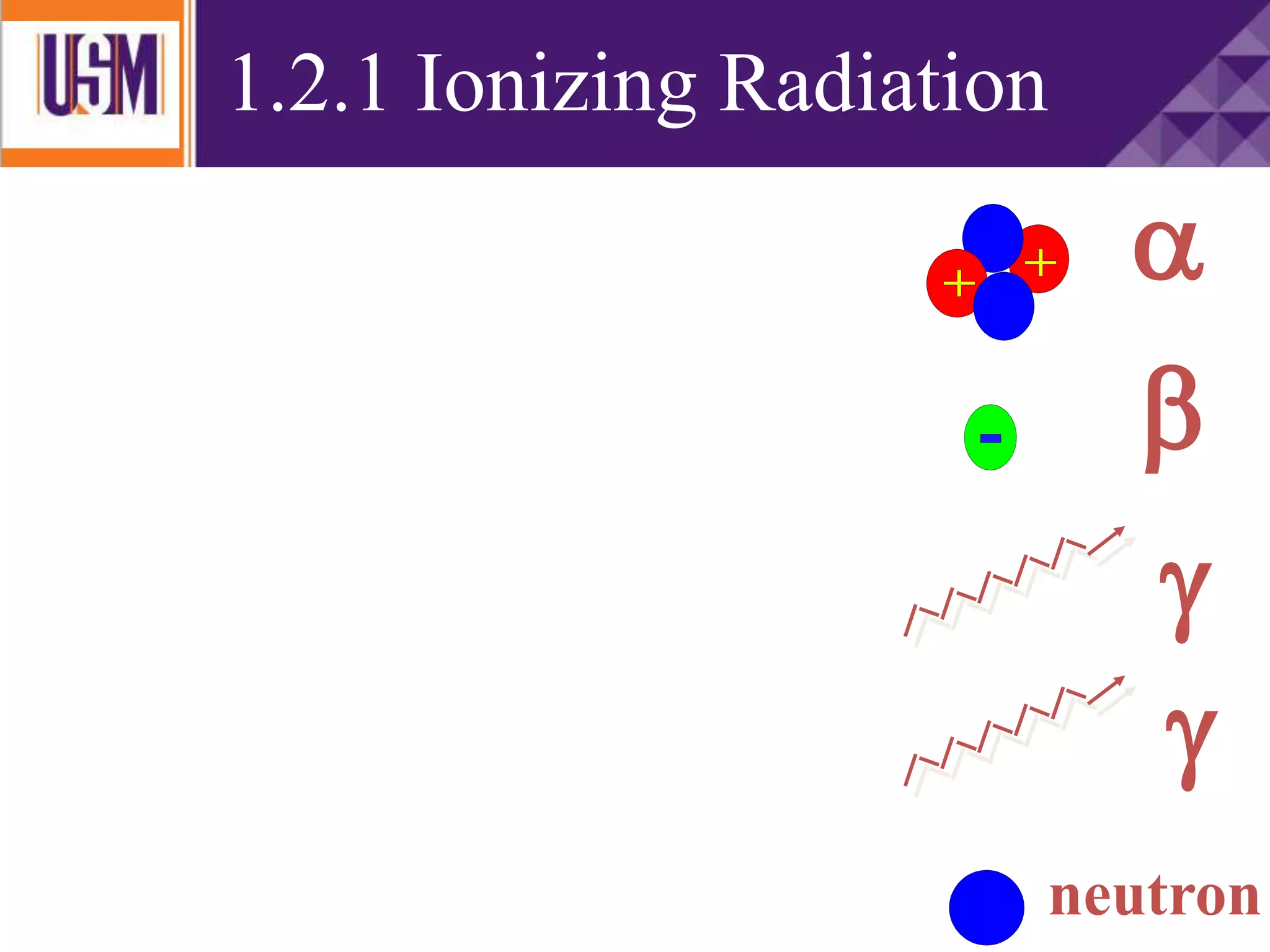
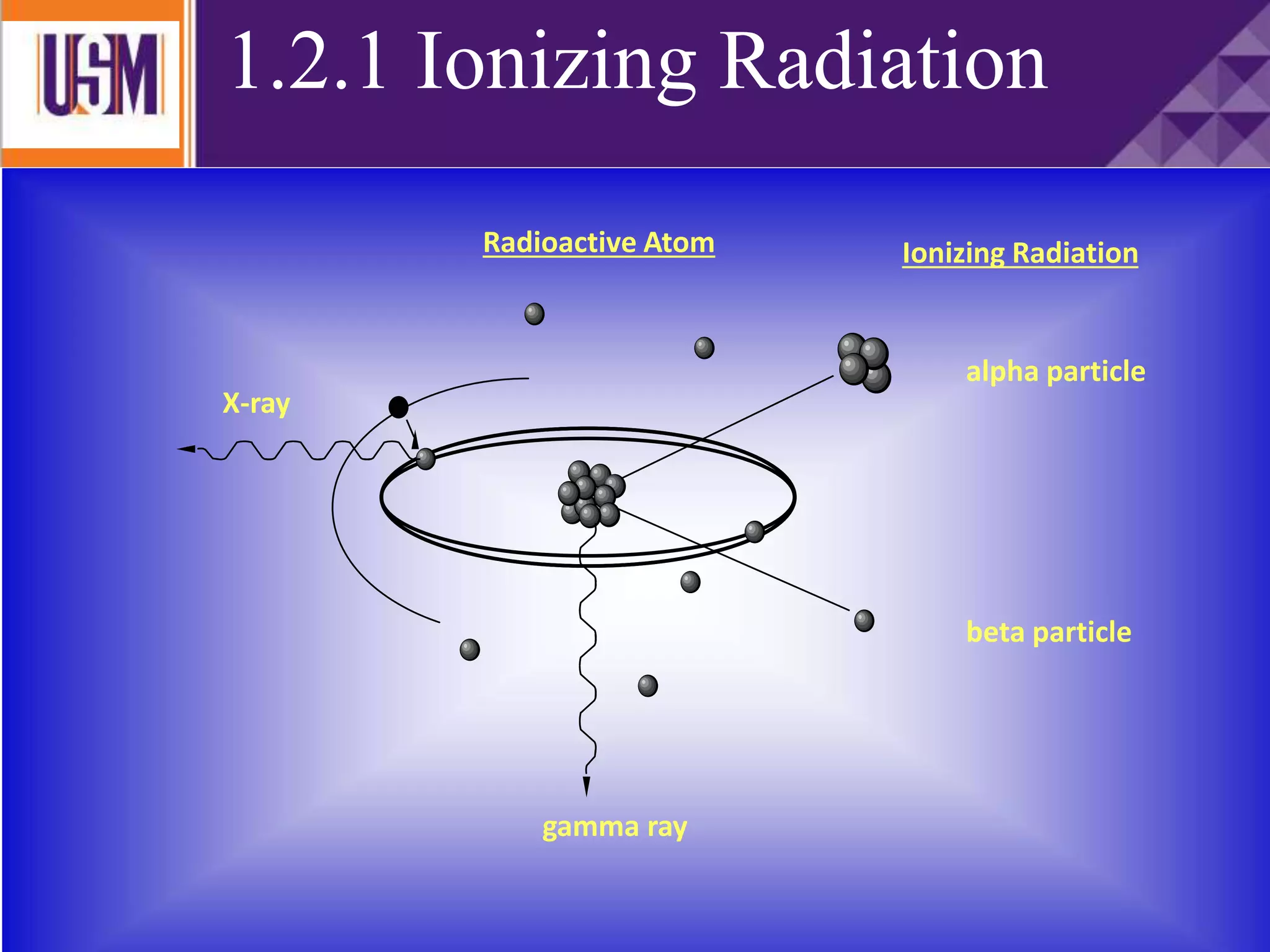
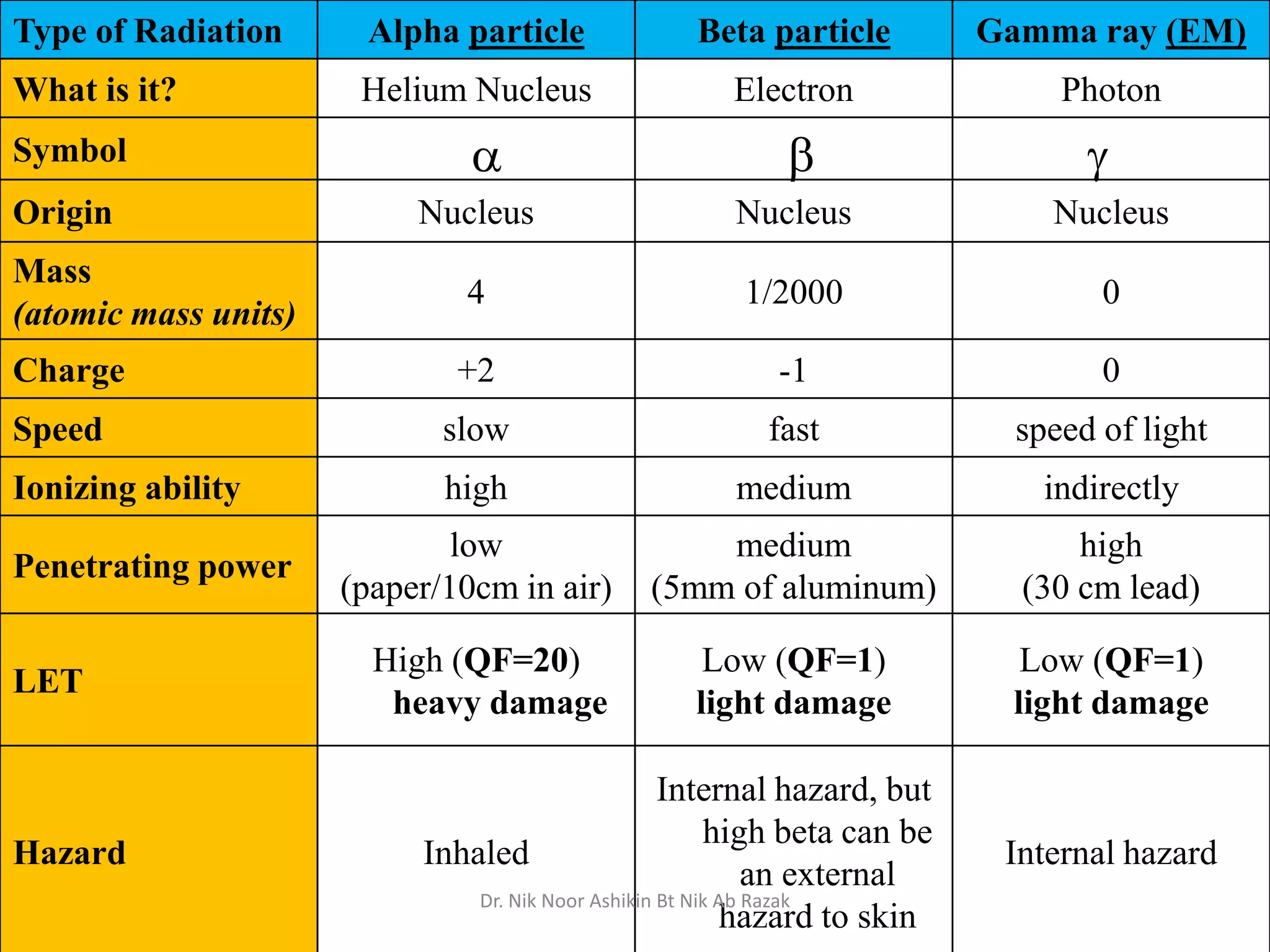
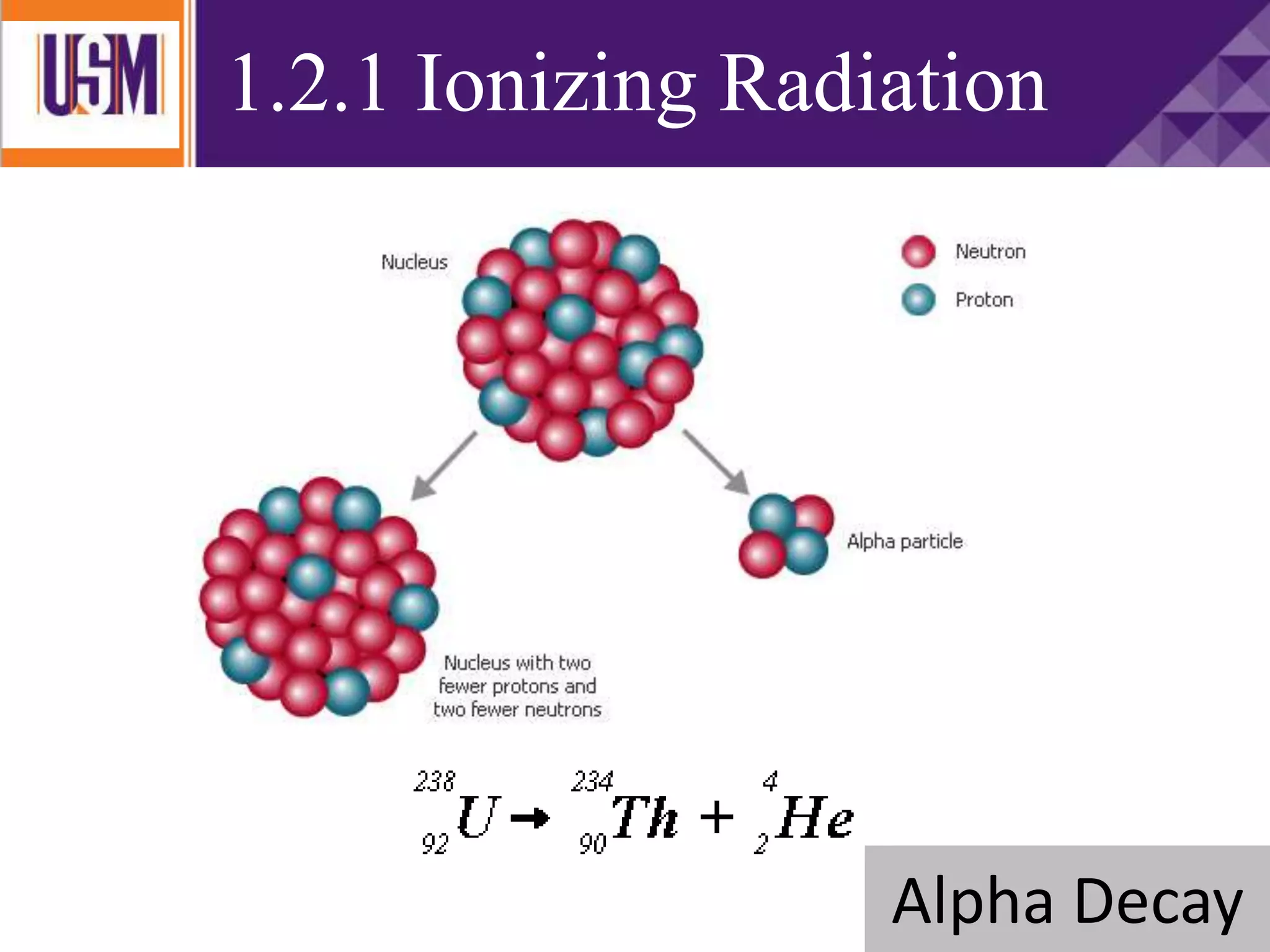
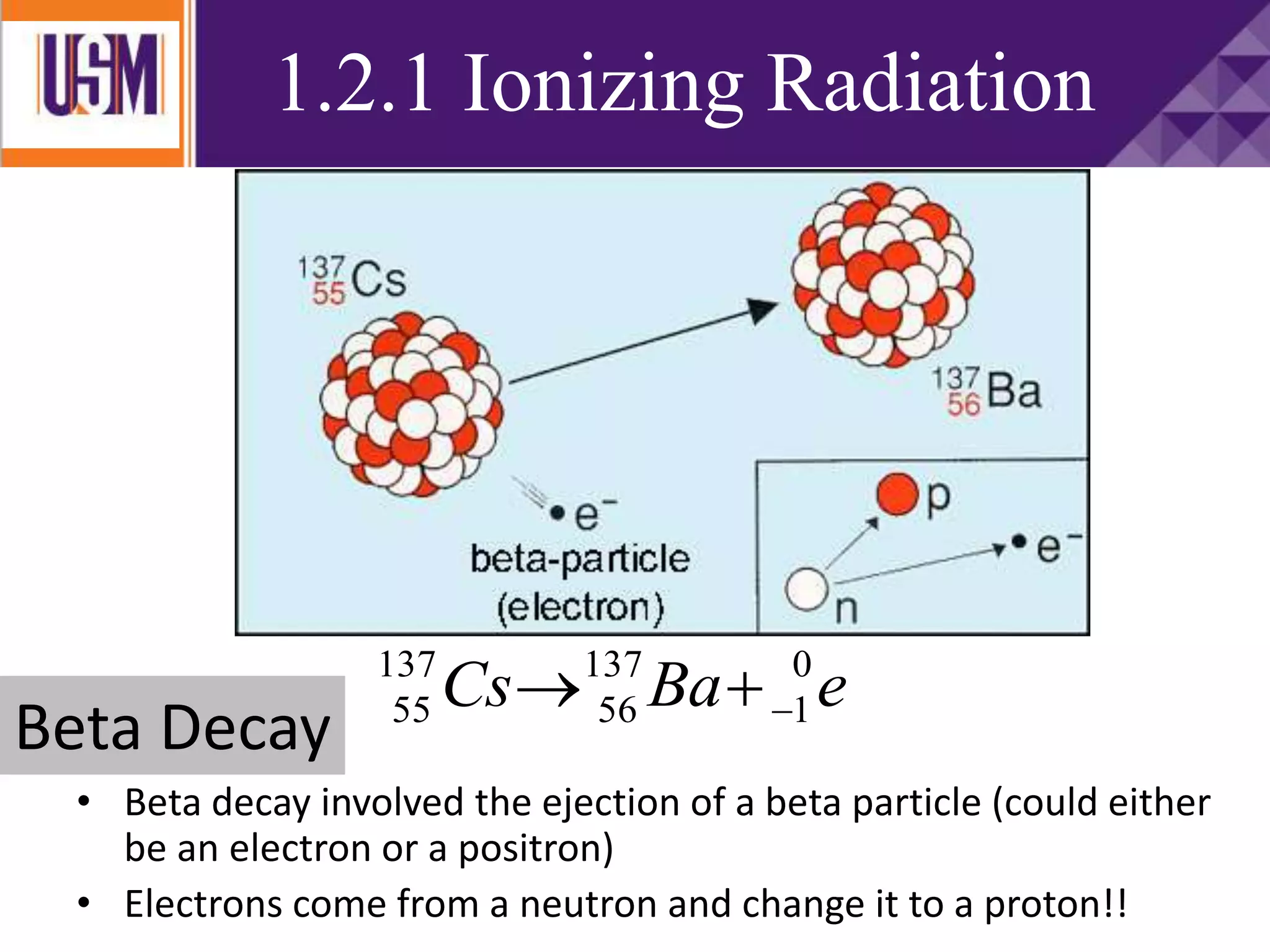
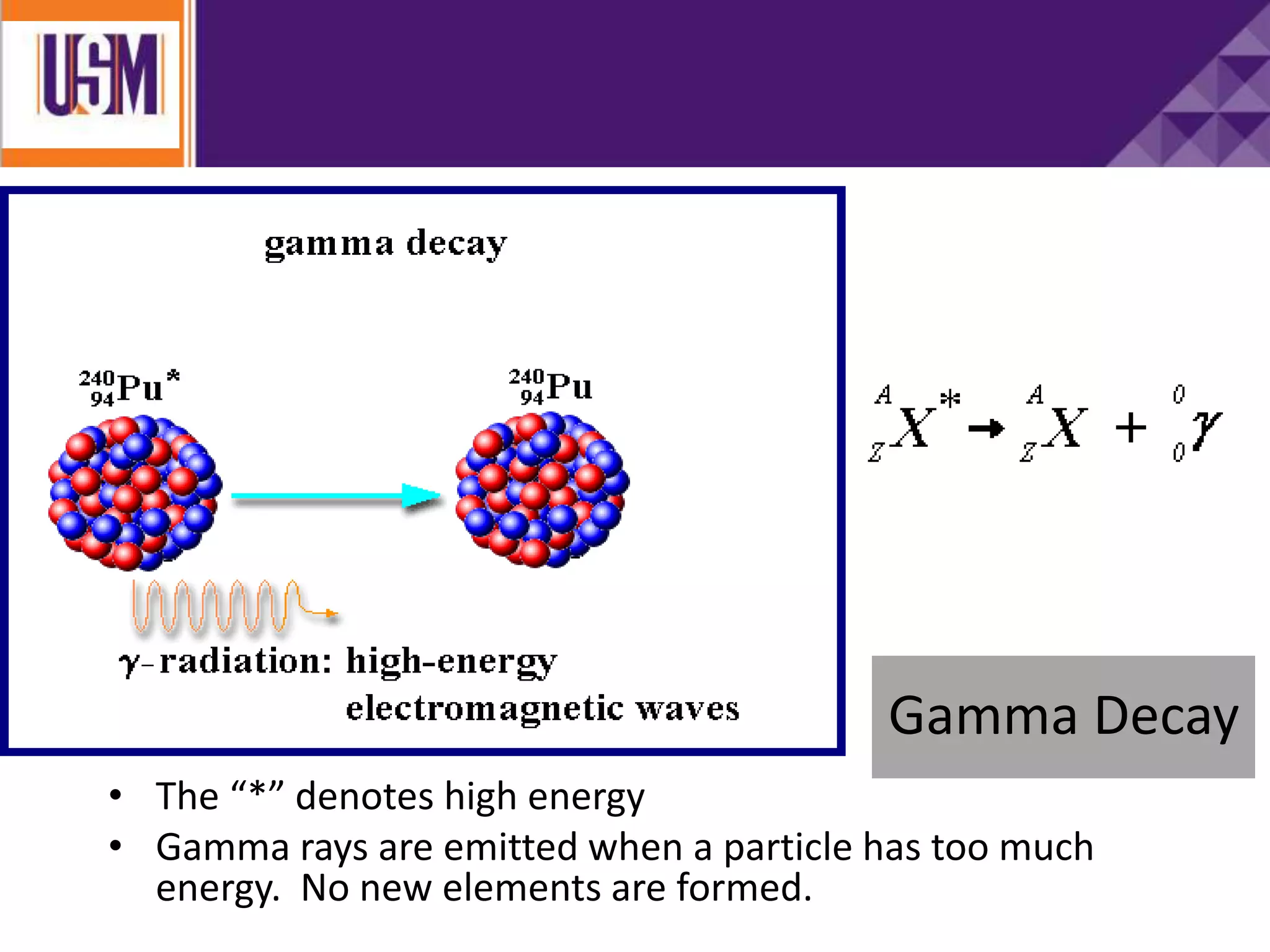
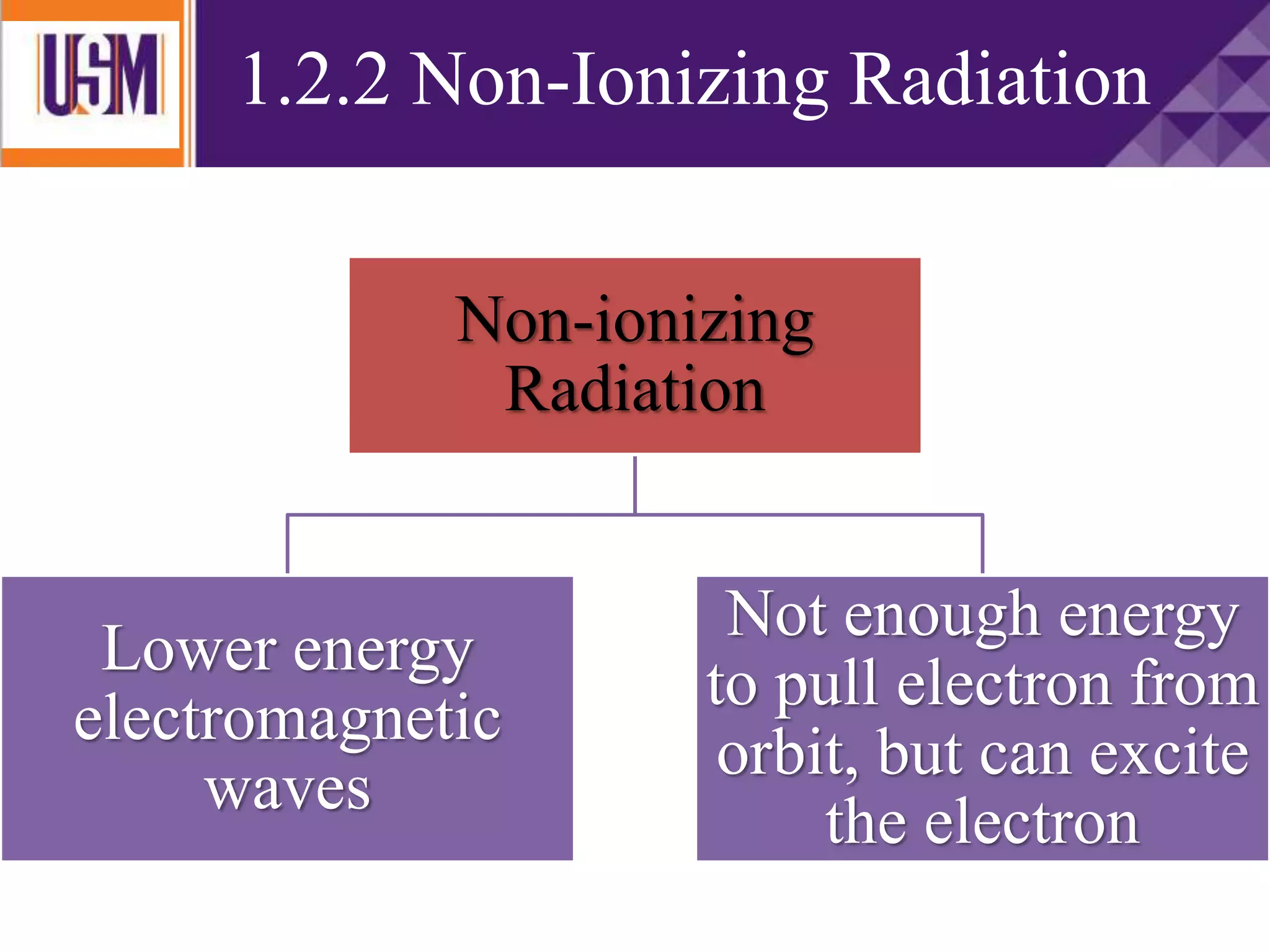
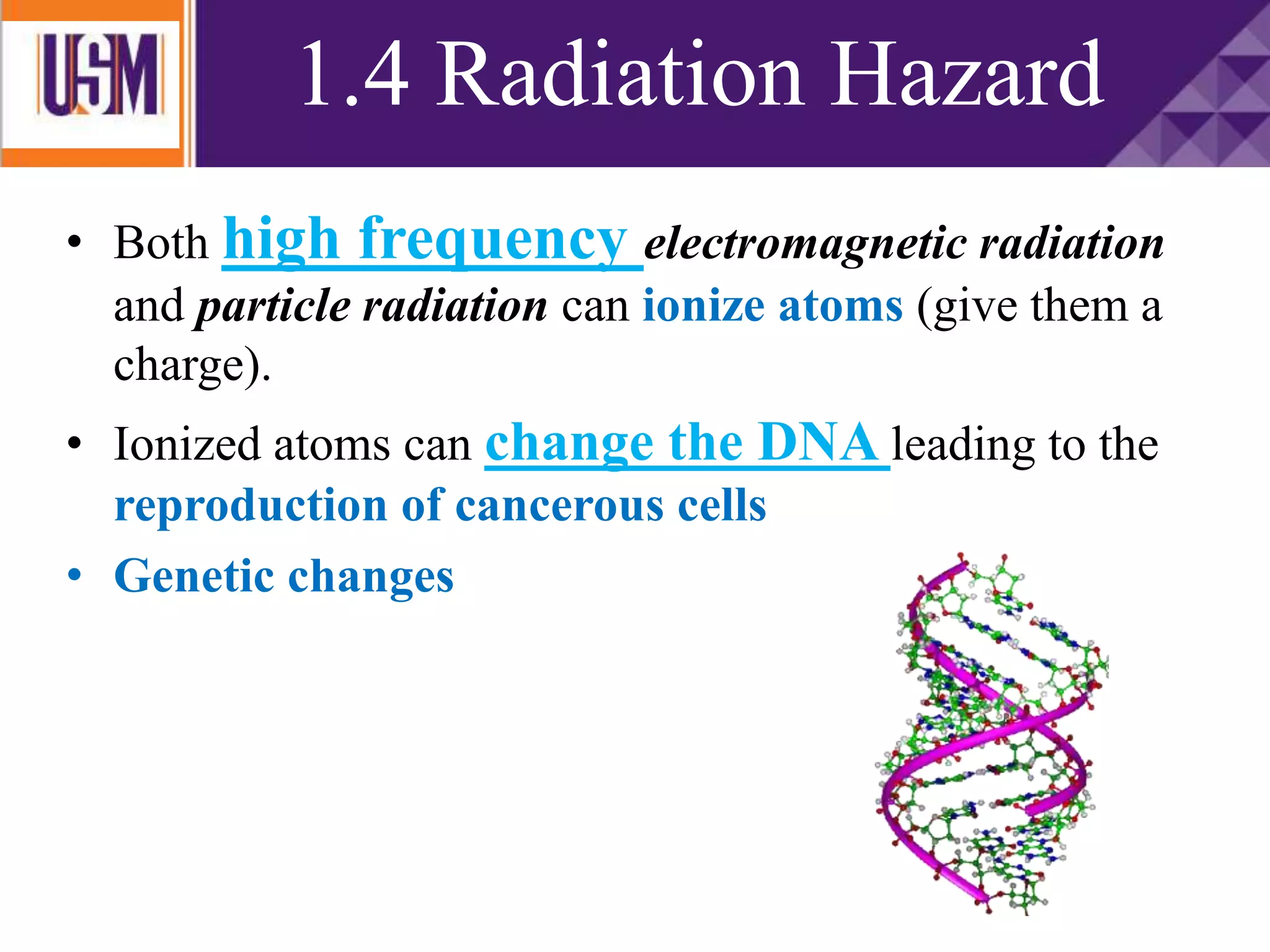
This document discusses different types of radiation sources. It describes natural sources like cosmic rays, terrestrial radiation from rocks and soil, and internal sources in the human body. It also covers artificial sources like medical procedures, nuclear power plants, nuclear weapons, and consumer products. The document defines ionizing radiation as high energy waves or particles that can strip electrons from atoms, and non-ionizing radiation as lower energy waves that can excite but not ionize electrons. It provides examples of different radioactive decays and how to balance nuclear equations.