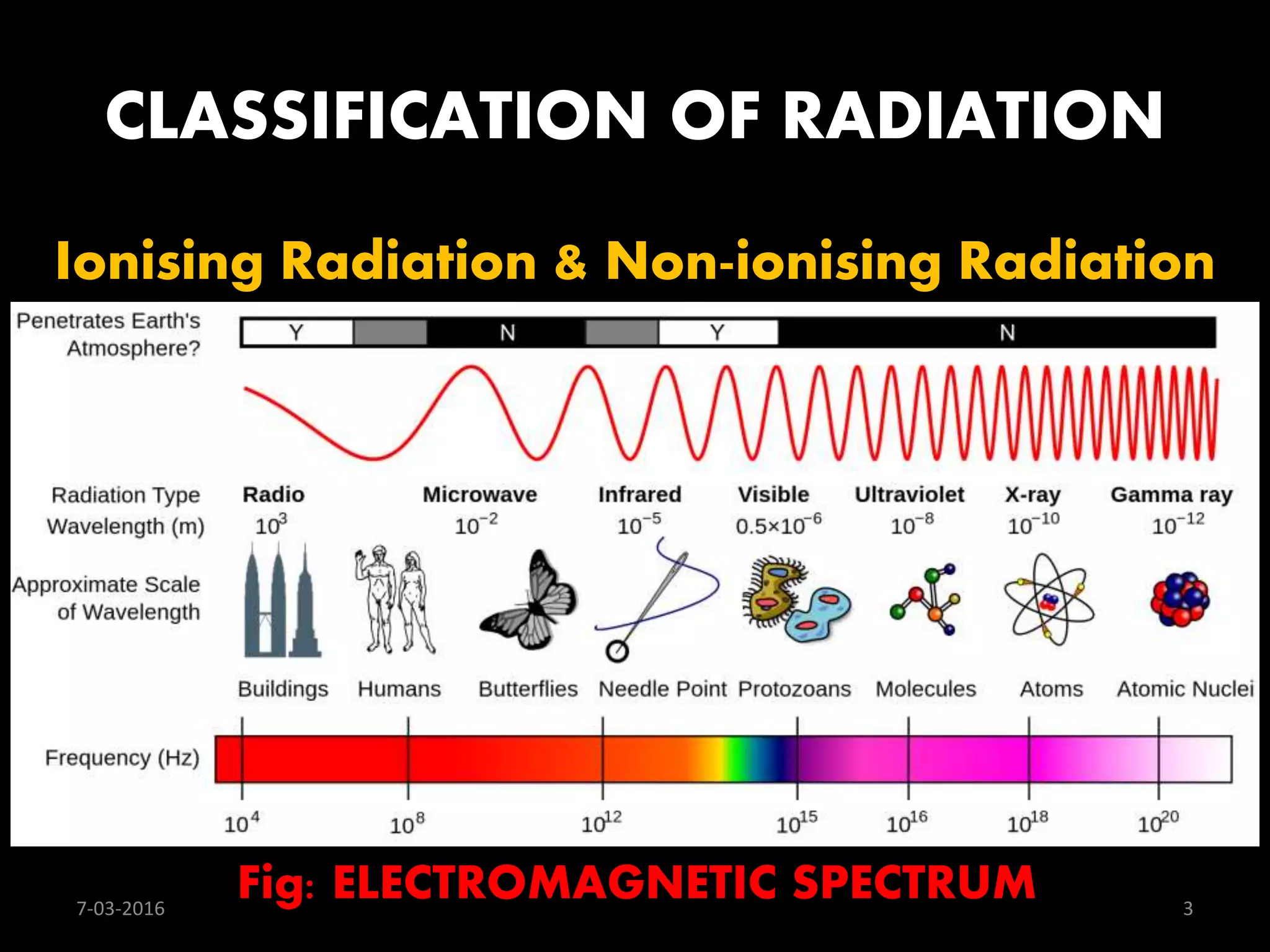
1) Radiation is energy transmitted through space or matter in the form of waves or particles. It is classified as ionizing or non-ionizing.
2) X-rays are a type of ionizing electromagnetic radiation that was discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Röntgen. They are produced within diagnostic X-ray tubes and are widely used in medical imaging due to their ability to pass through objects.
3) Diagnostic X-rays are the largest man-made source of radiation exposure to the general population. While they provide medical benefits, high doses can cause radiation sickness or increase cancer risk. Risk is kept as low as reasonably achievable.