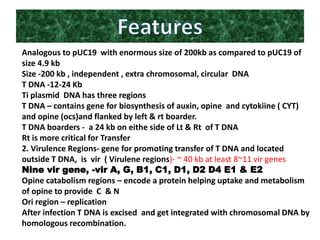
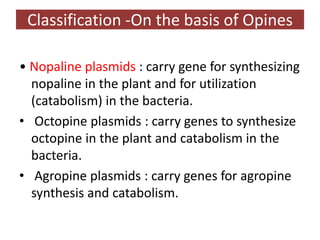
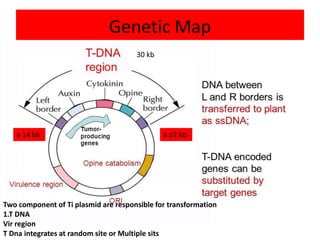
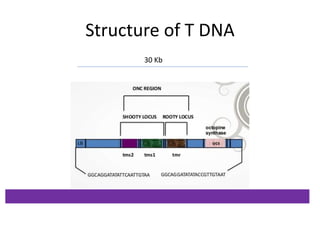
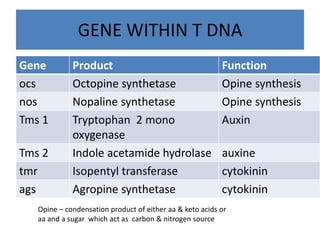
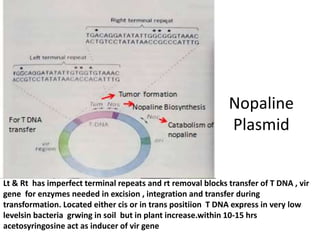
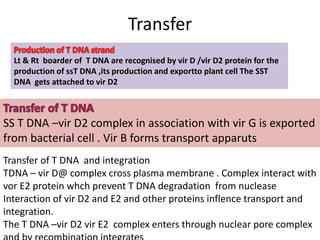
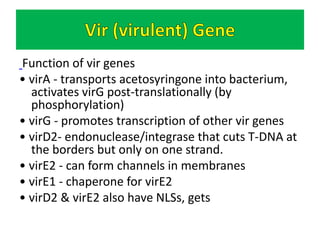
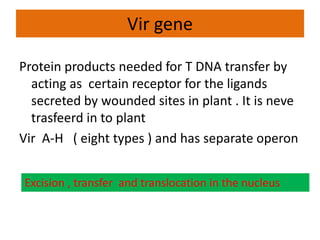
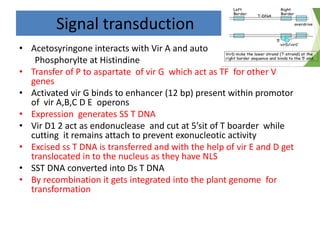
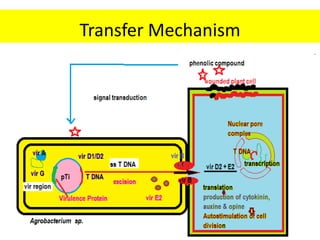
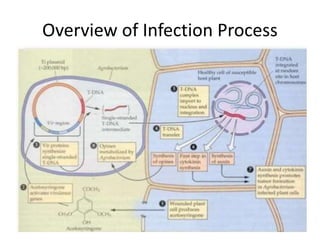
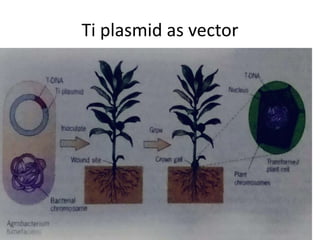
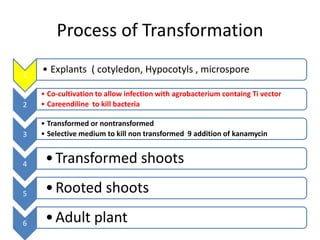
The document discusses the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens, which facilitates tumor formation in plants by transferring T-DNA, a large extra-chromosomal DNA segment, into plant cells. It details the regions of T-DNA, virulence genes, and mechanisms of transfer and integration into the plant genome, highlighting the role of signal molecules and various proteins involved in the process. Additionally, it covers genetic engineering applications, the challenges of using Ti plasmids as vectors, and the methodology for successful Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation.