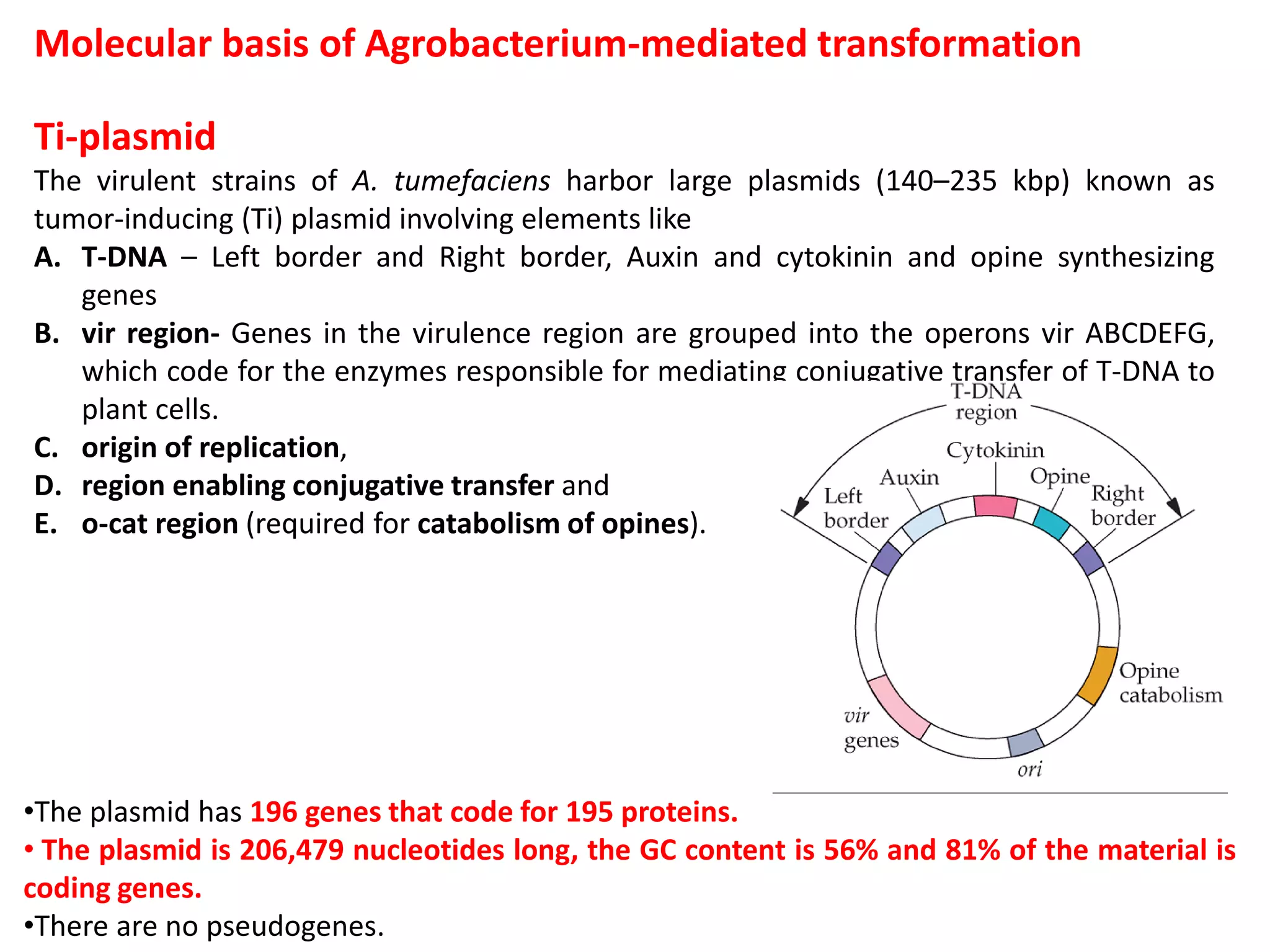
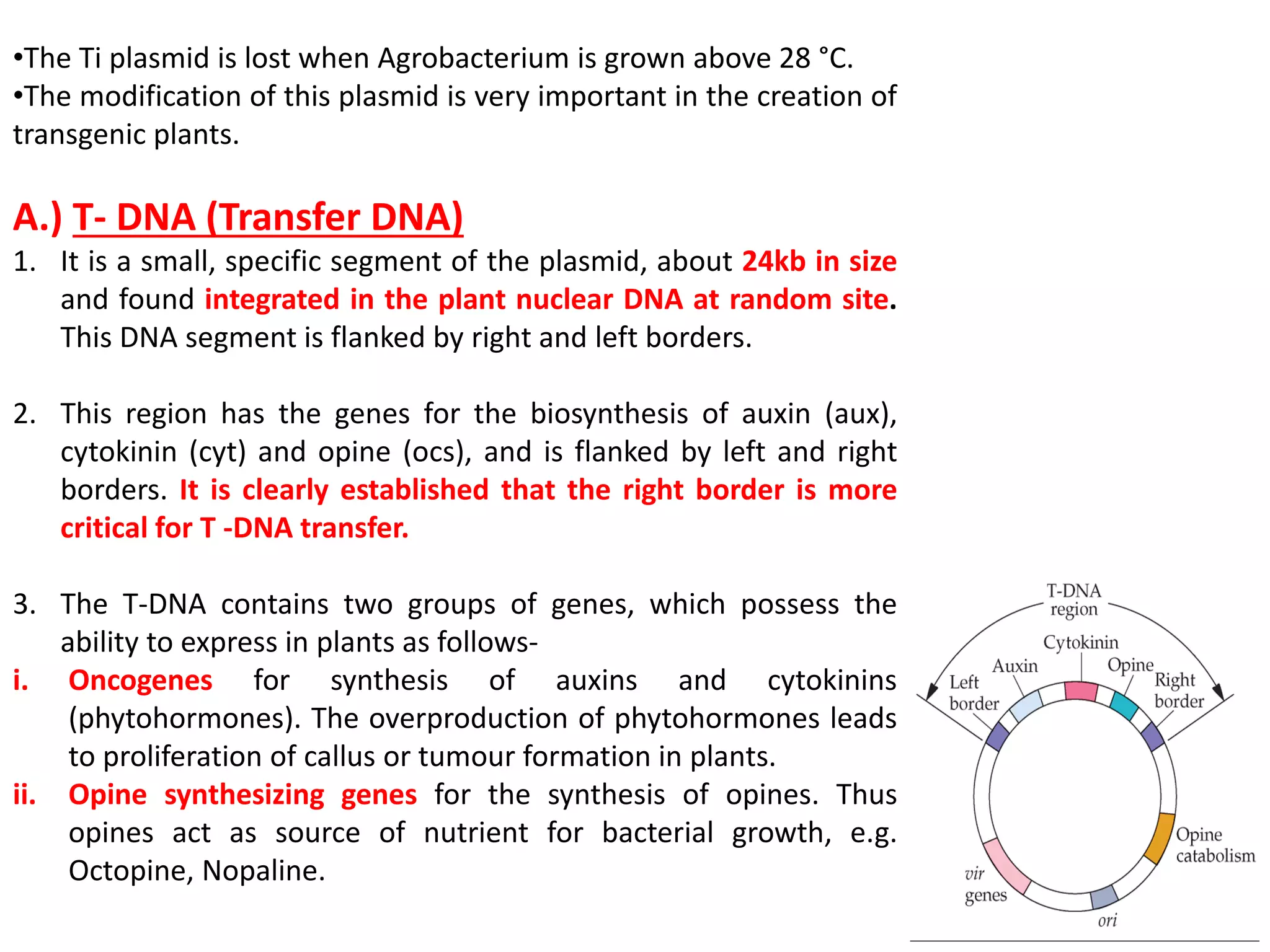
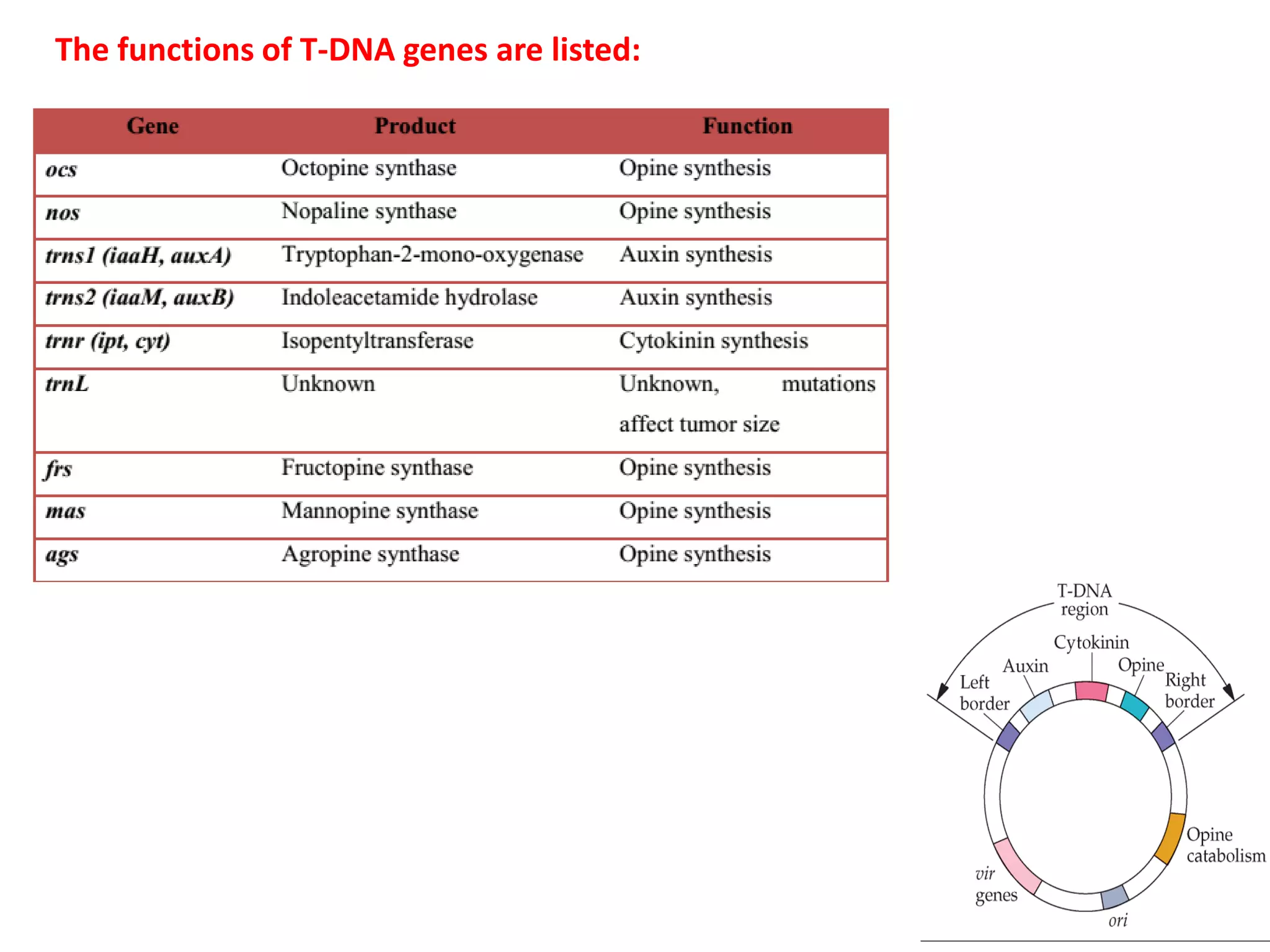
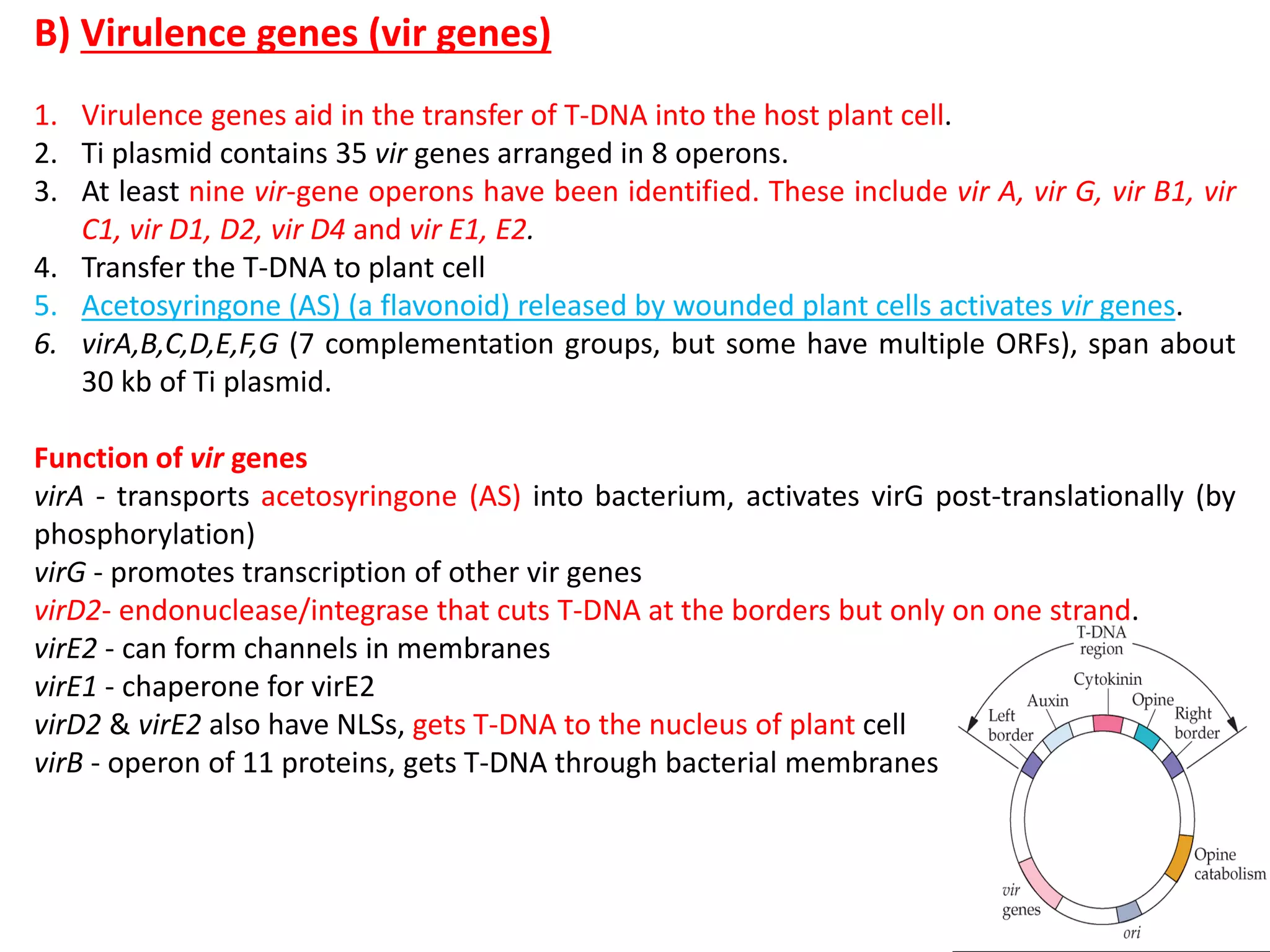
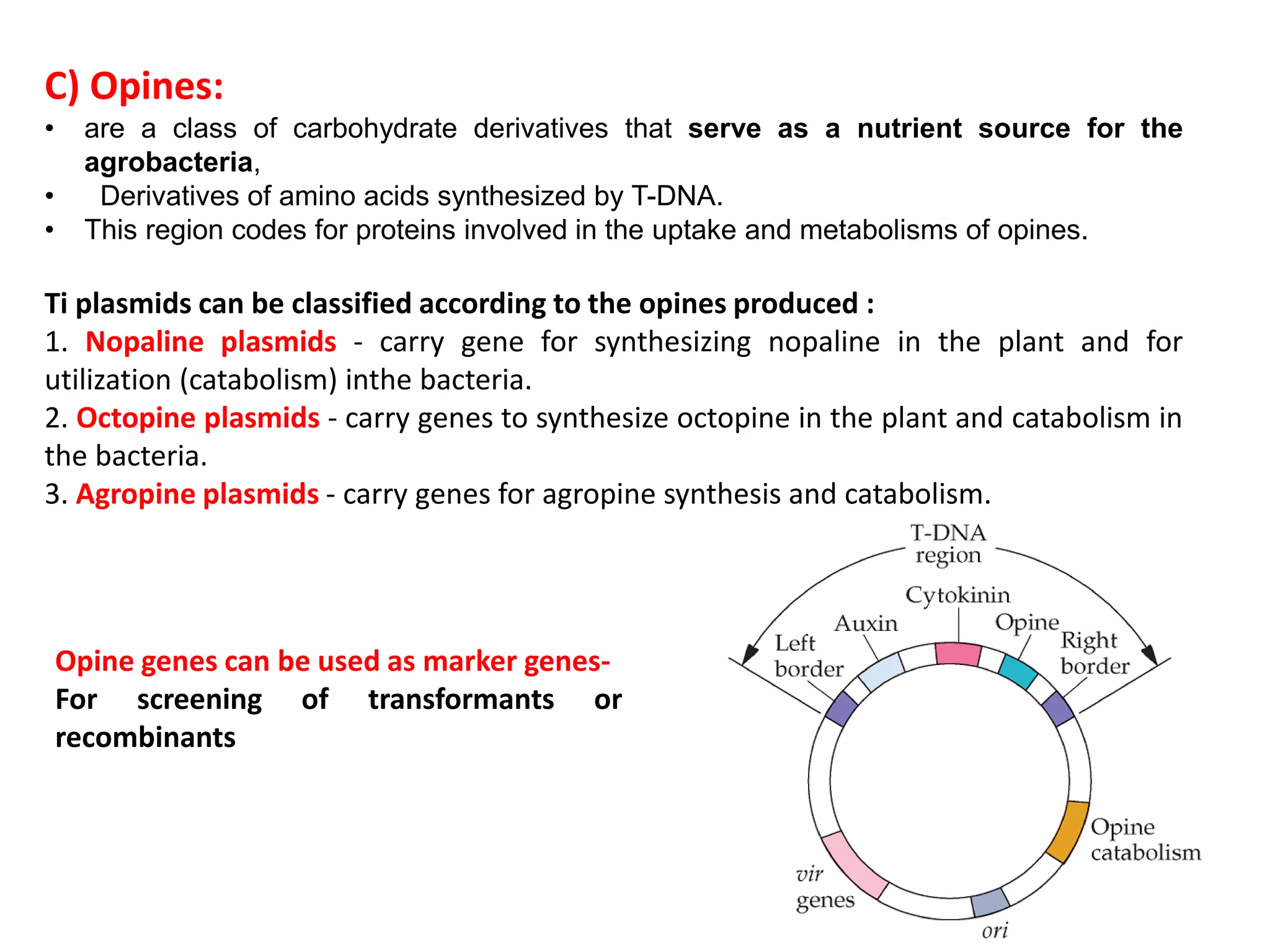
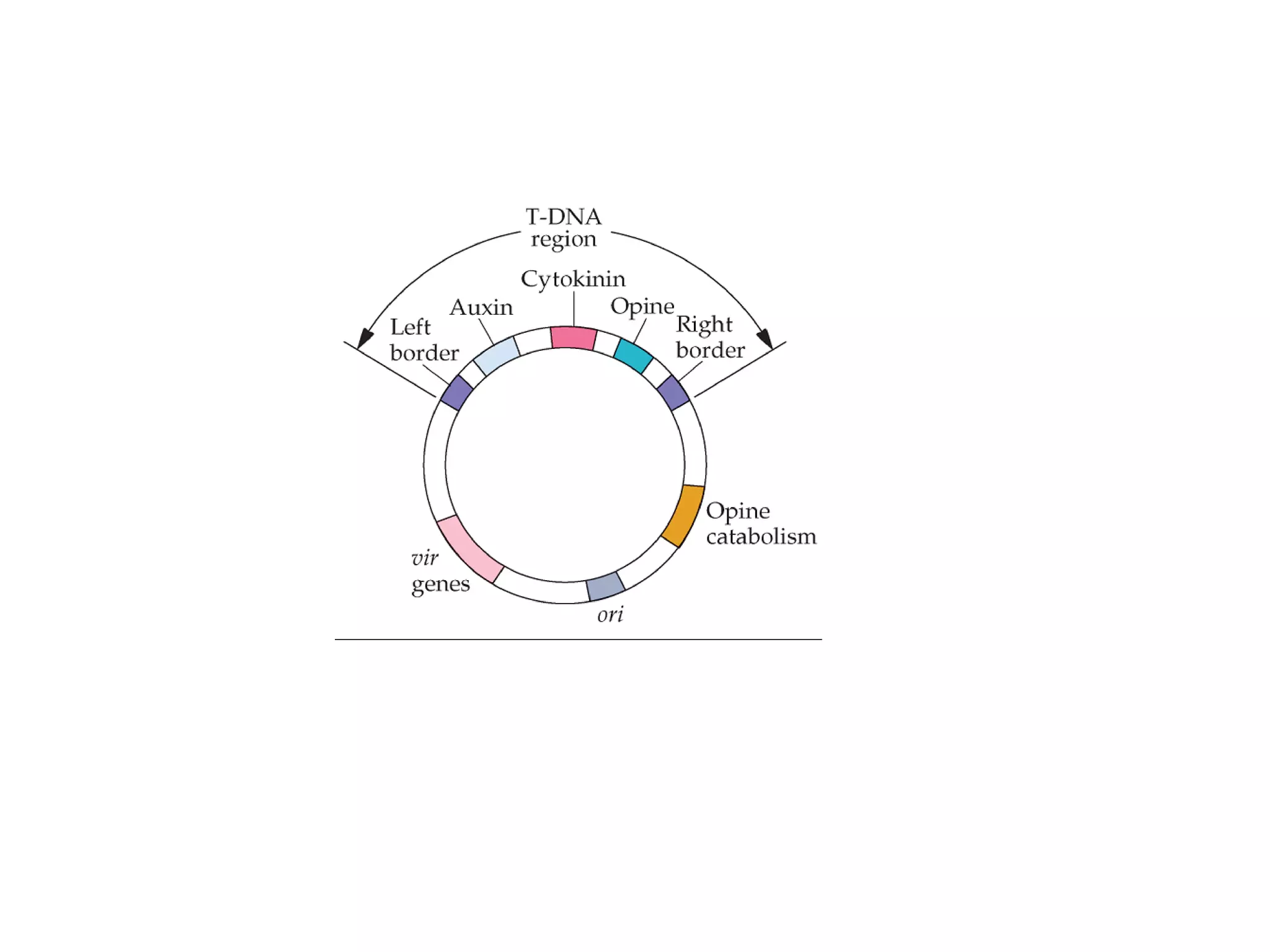
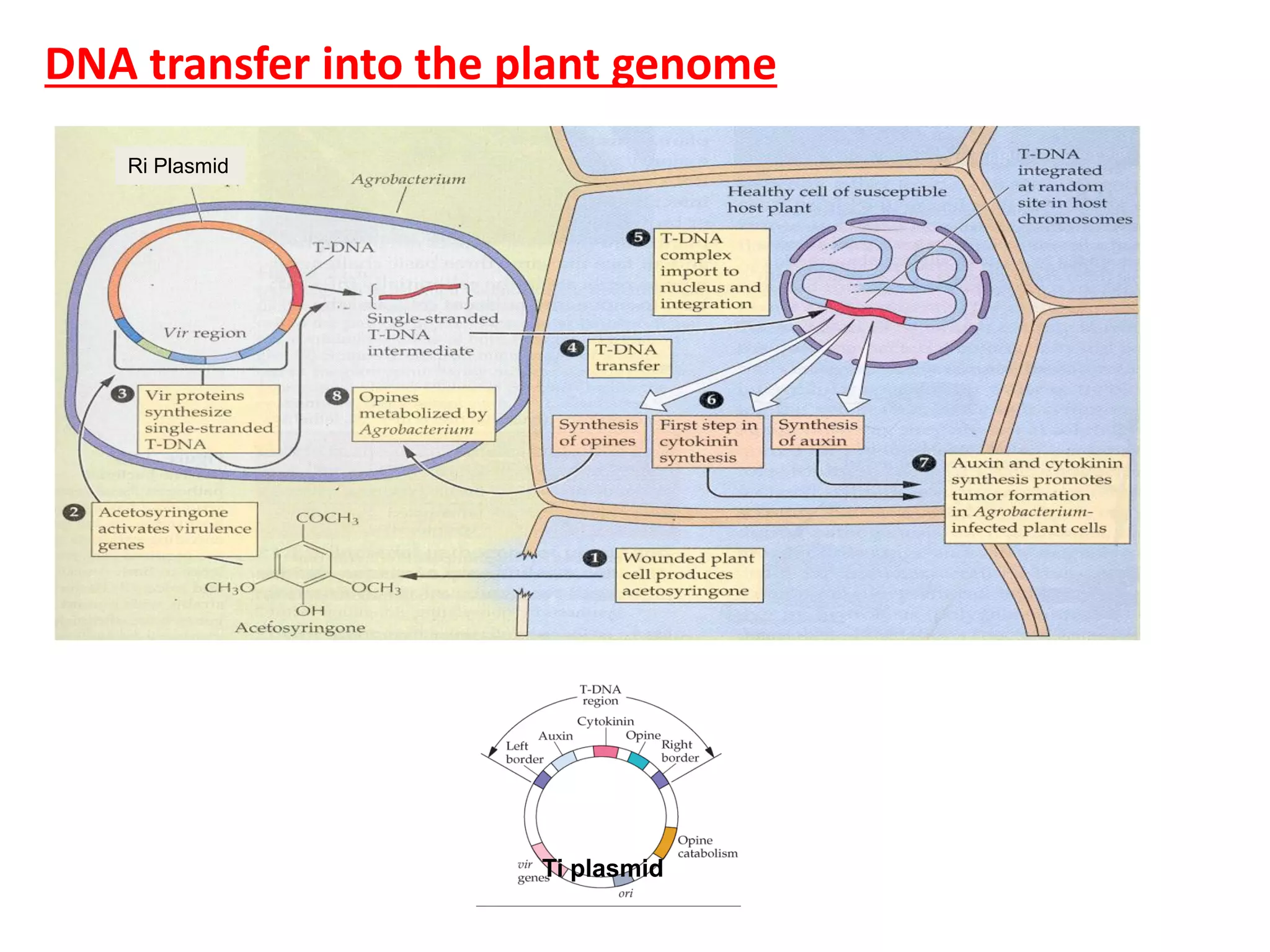
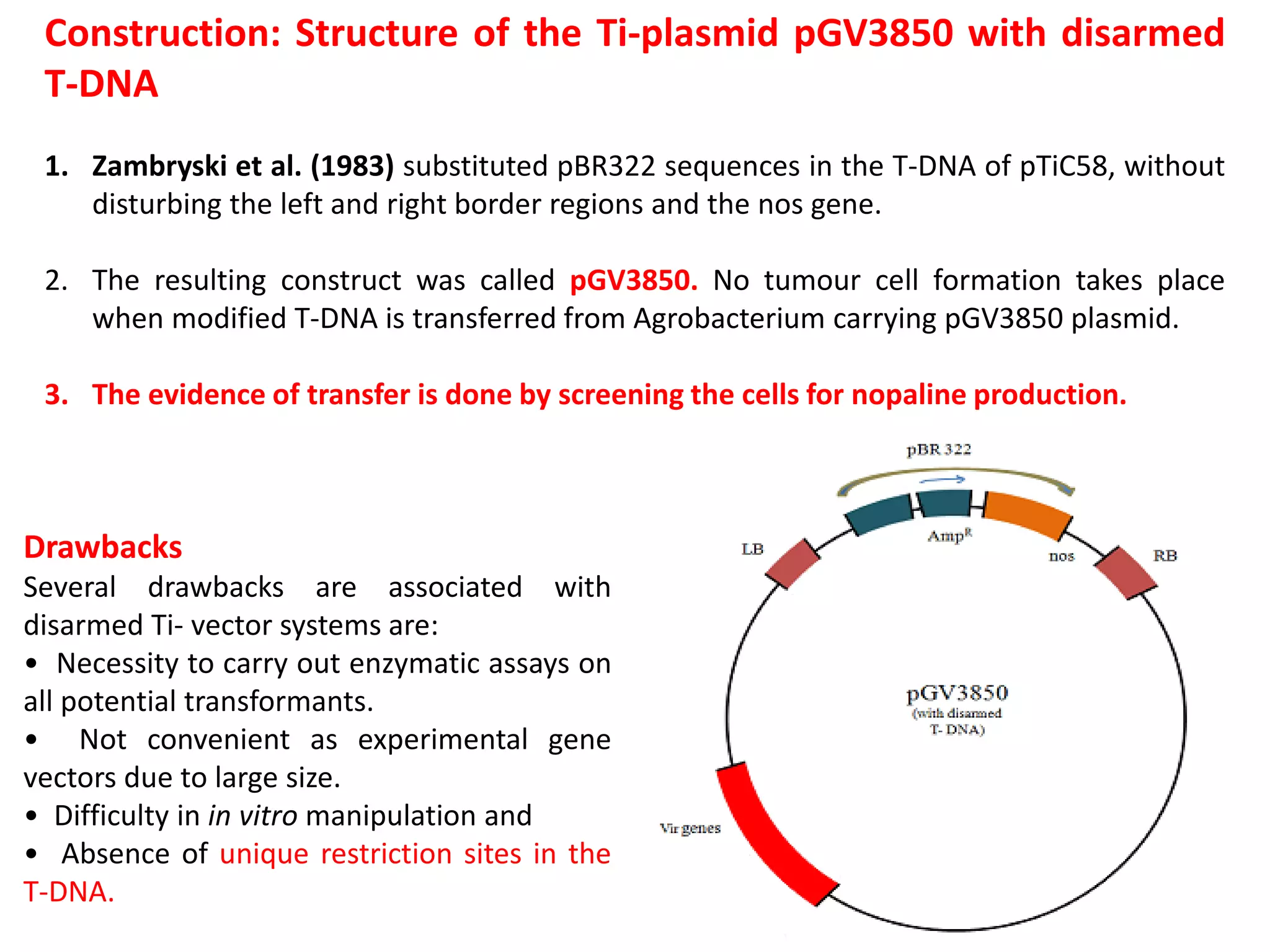
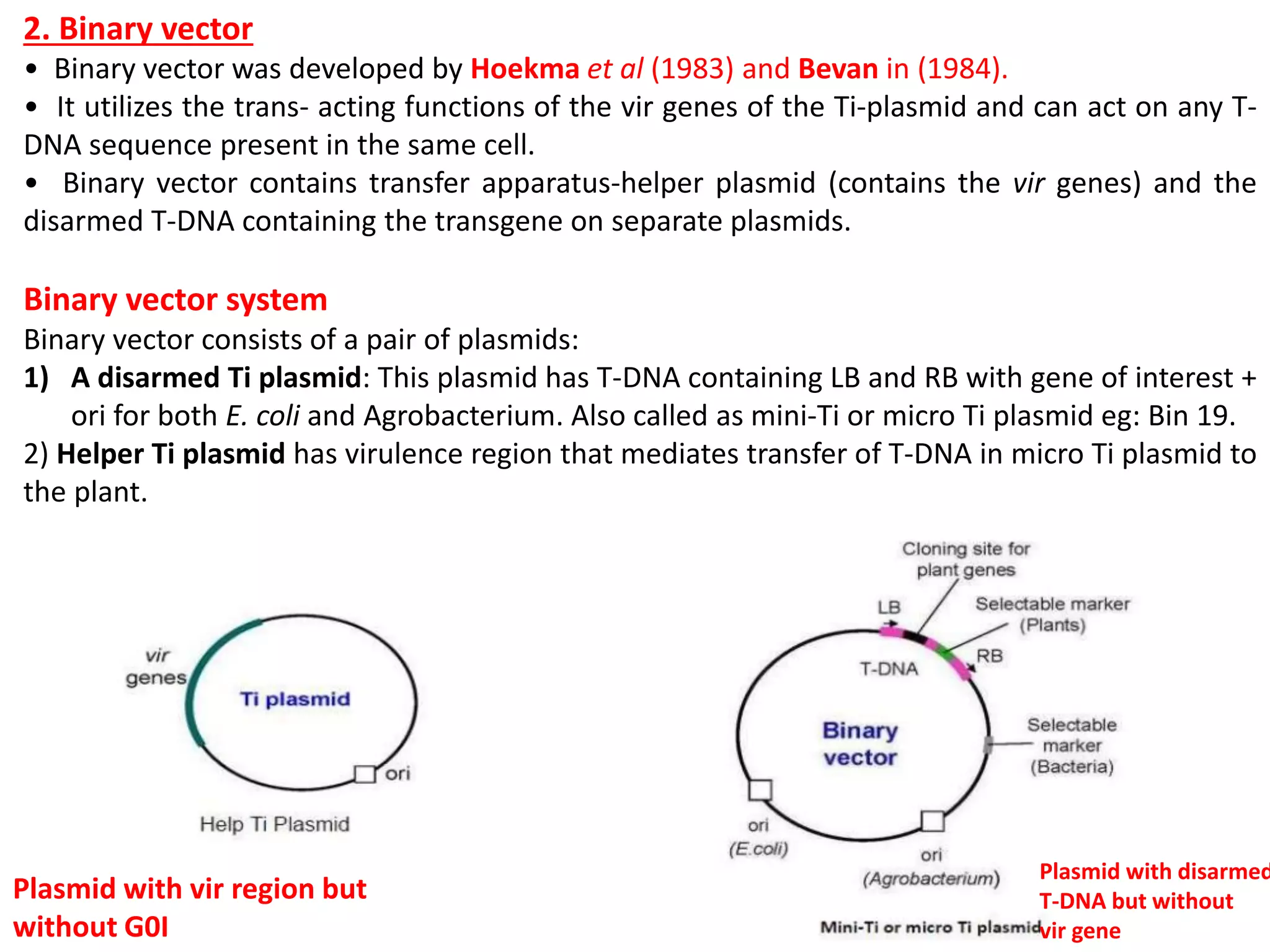
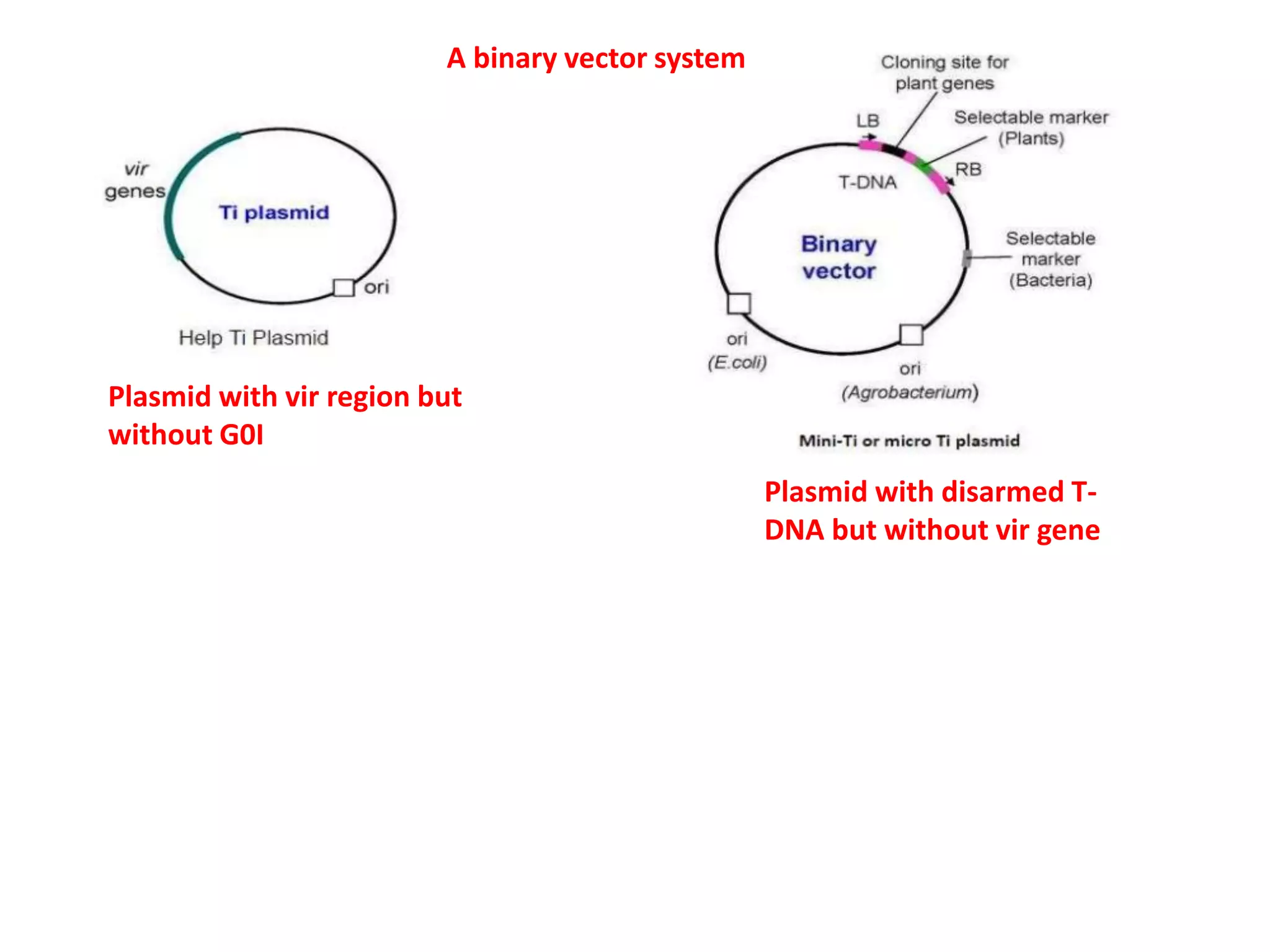
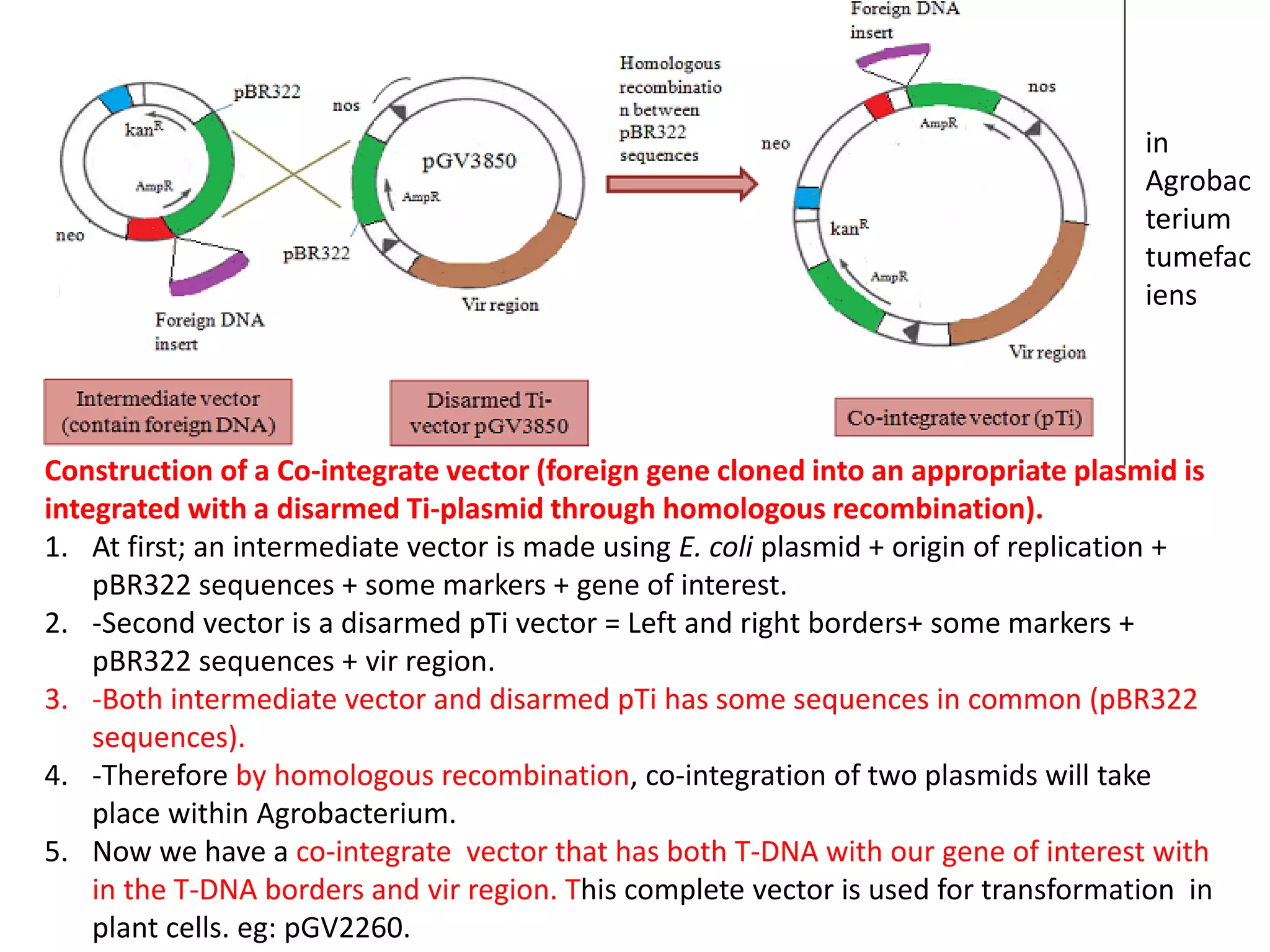
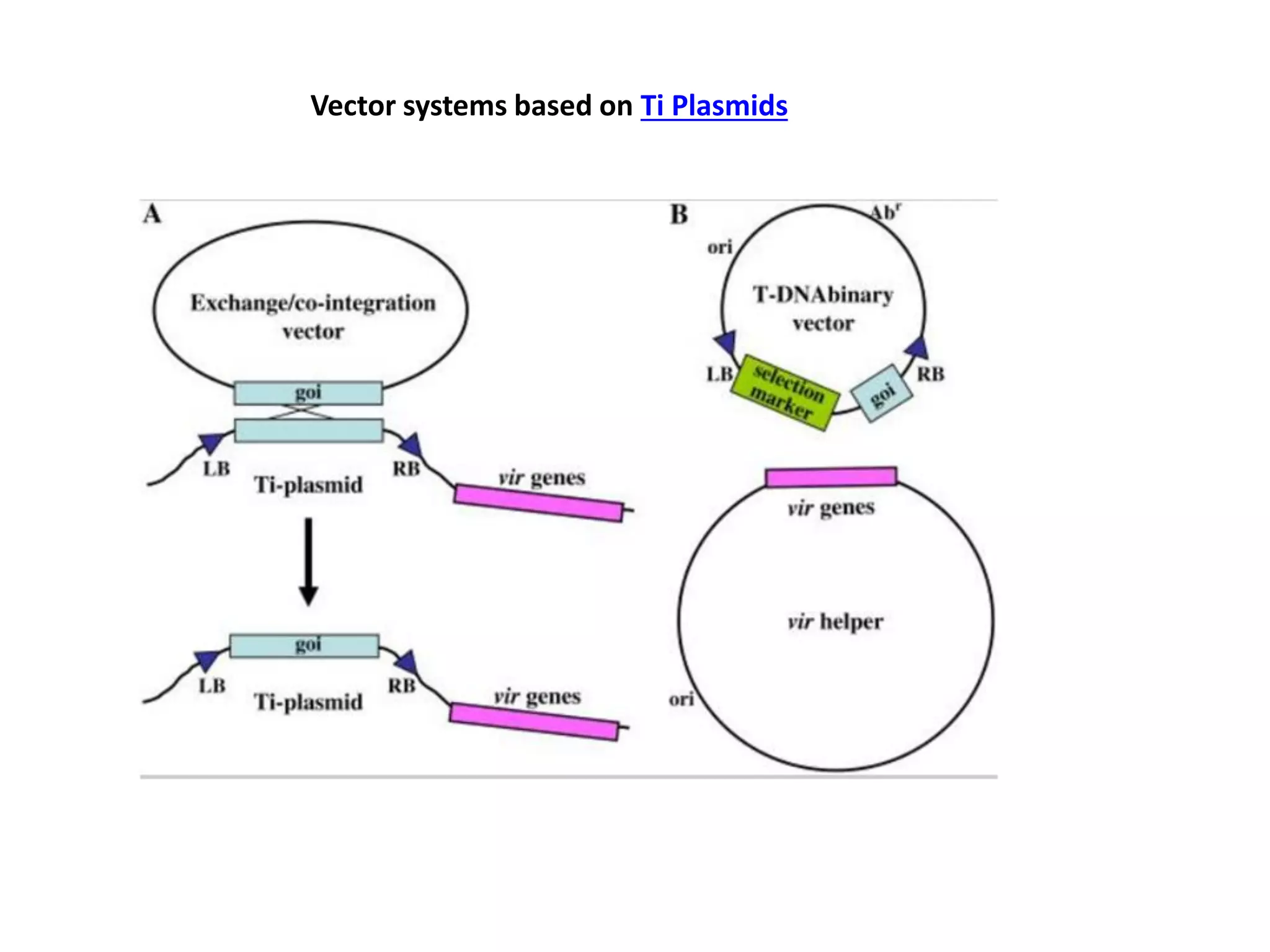
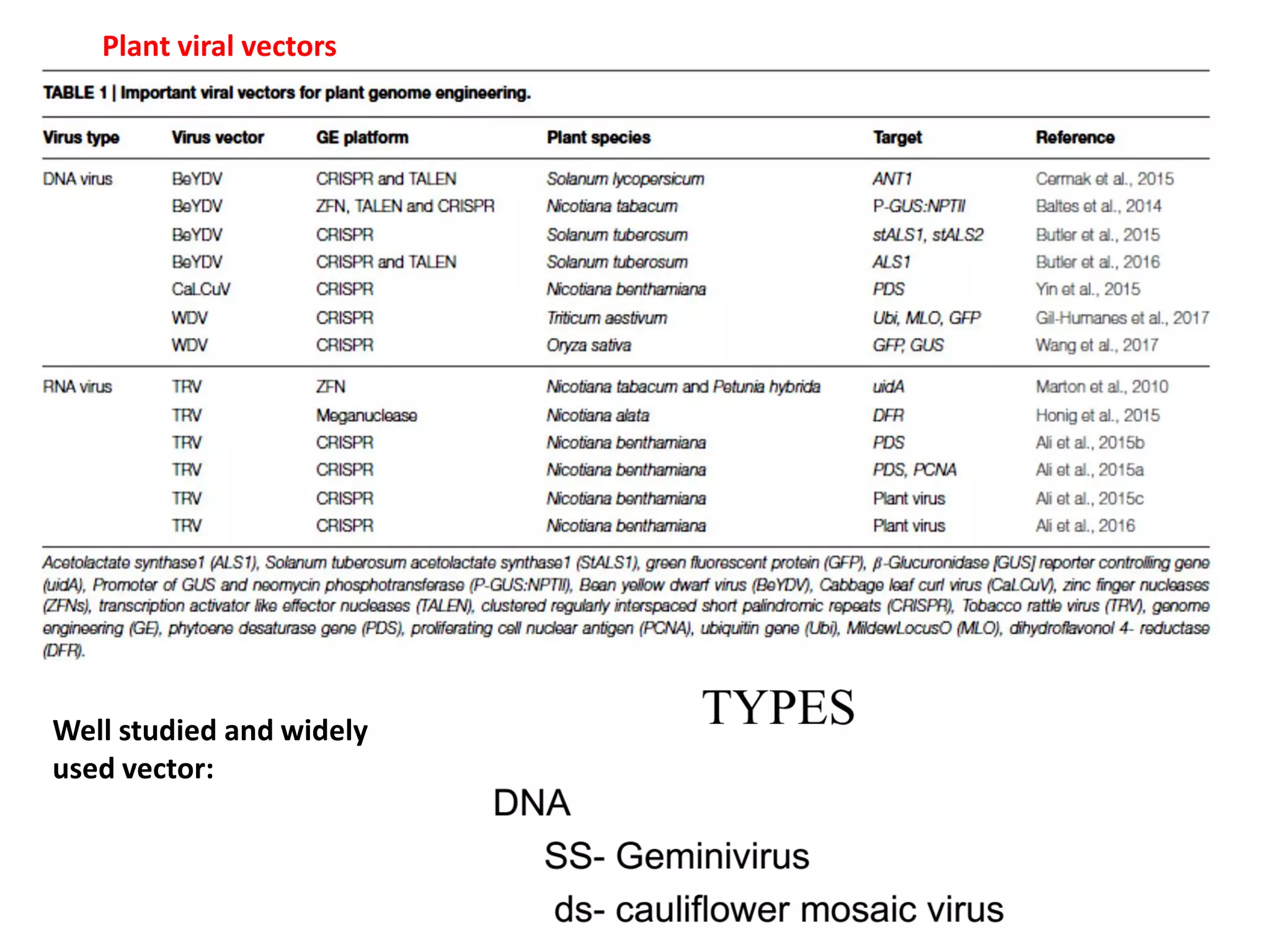
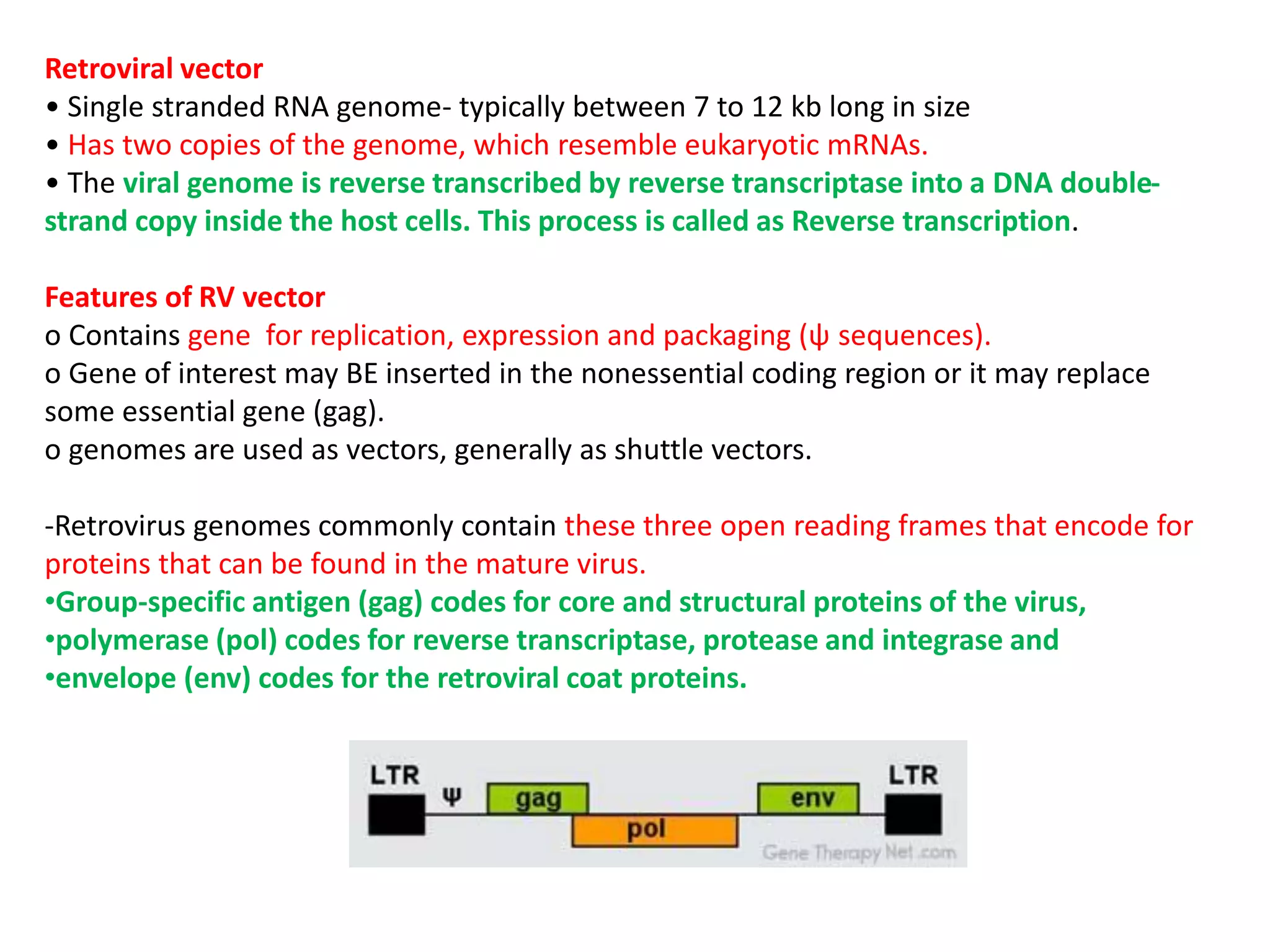
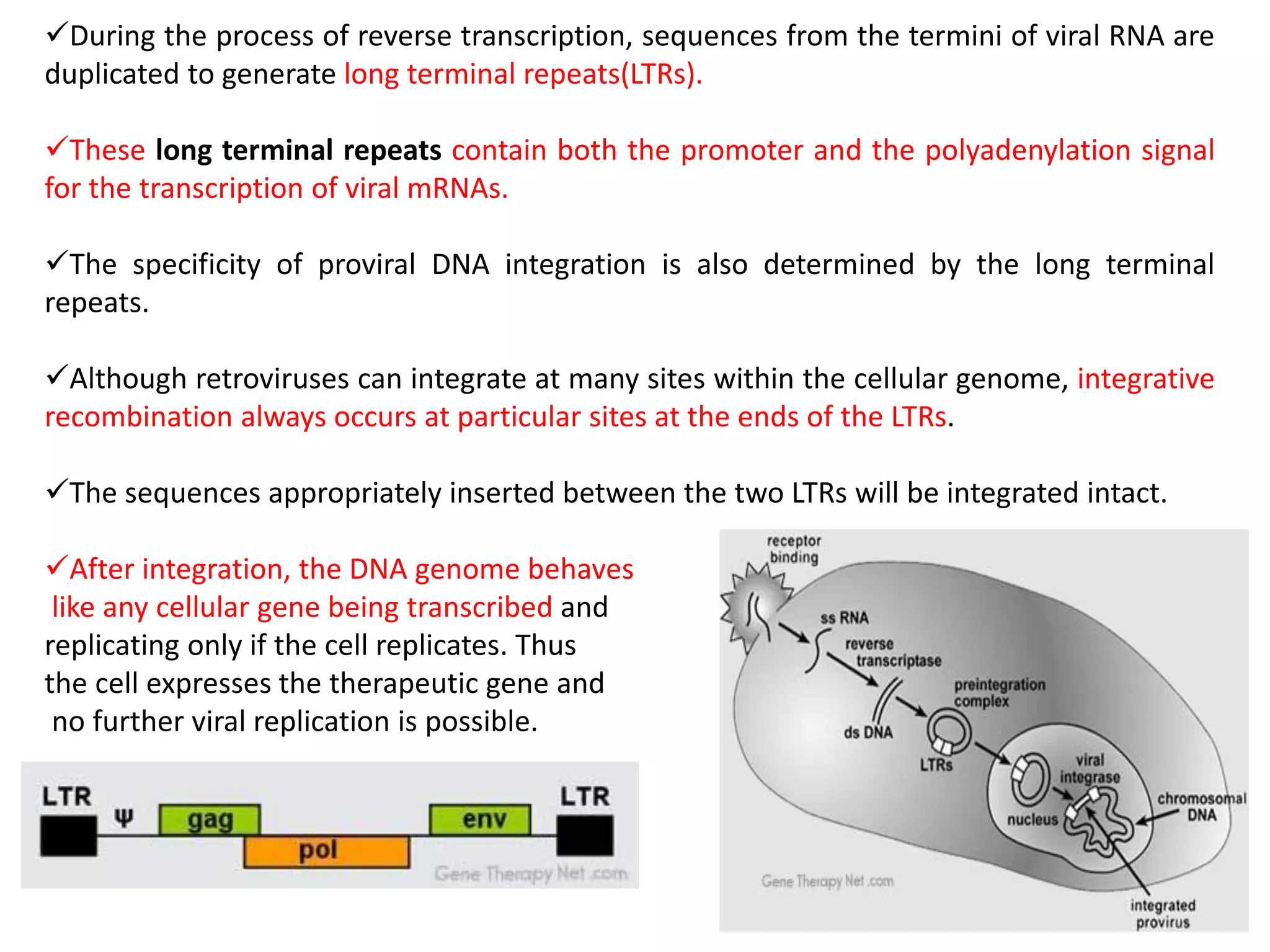
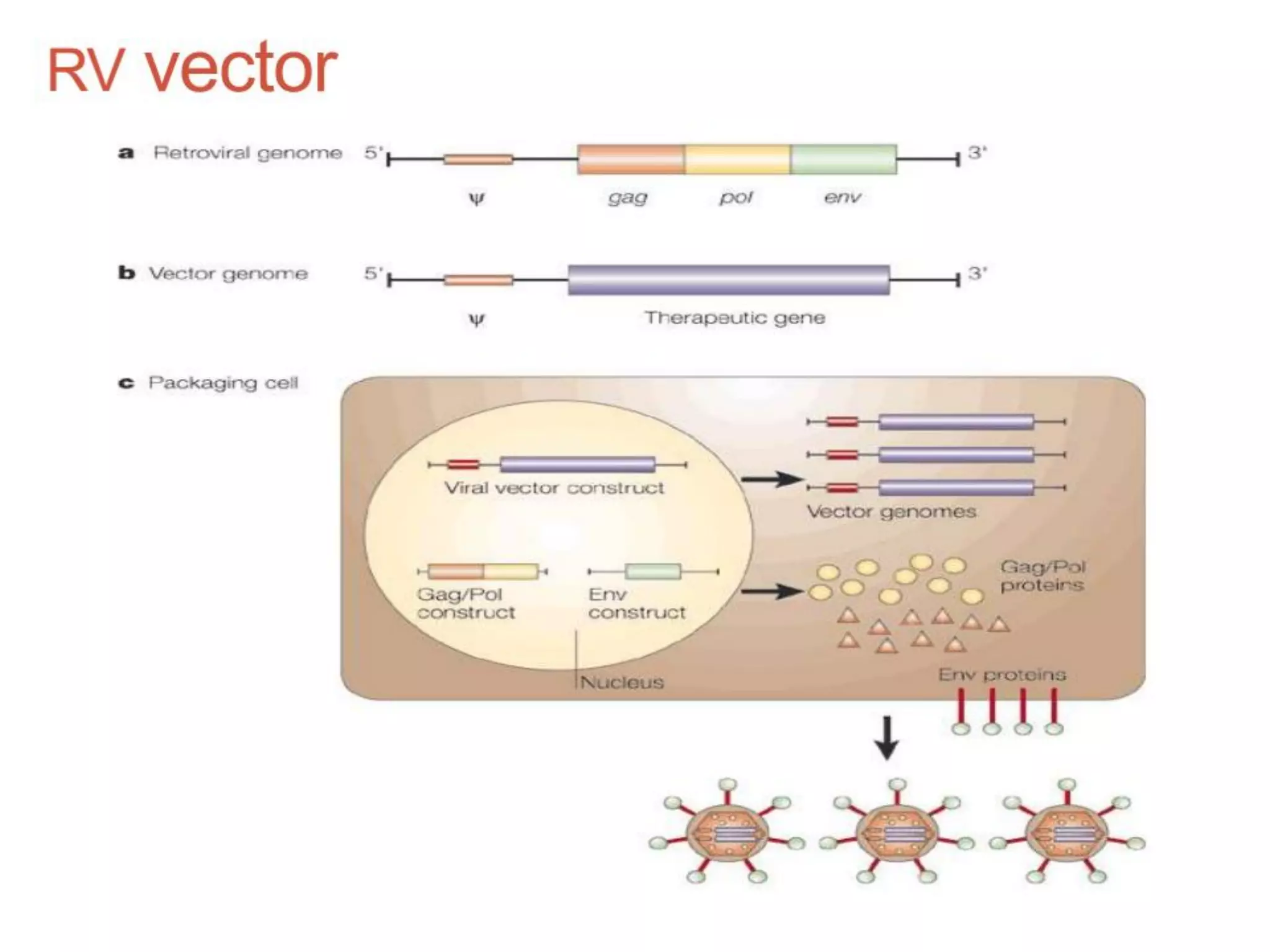
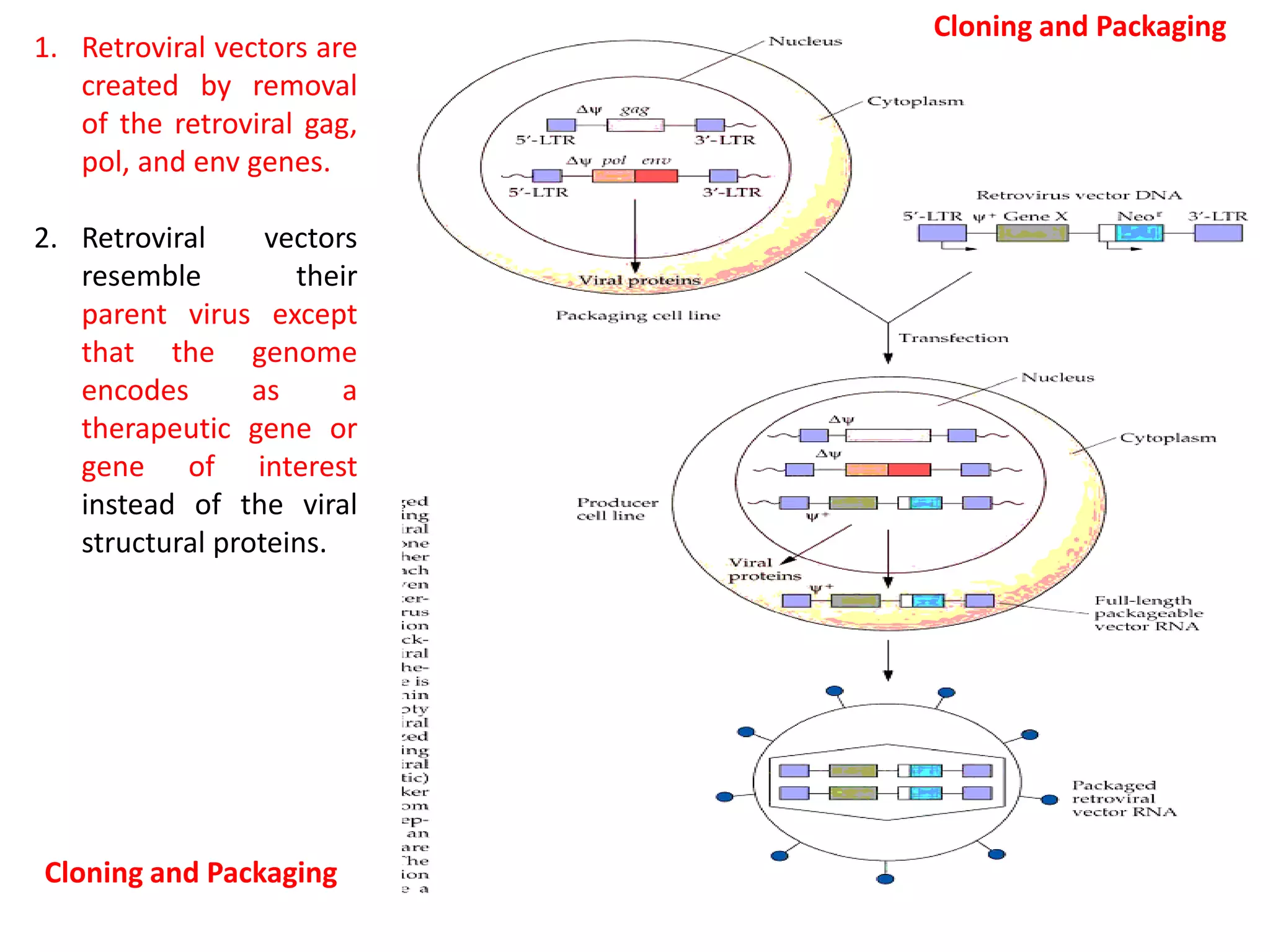
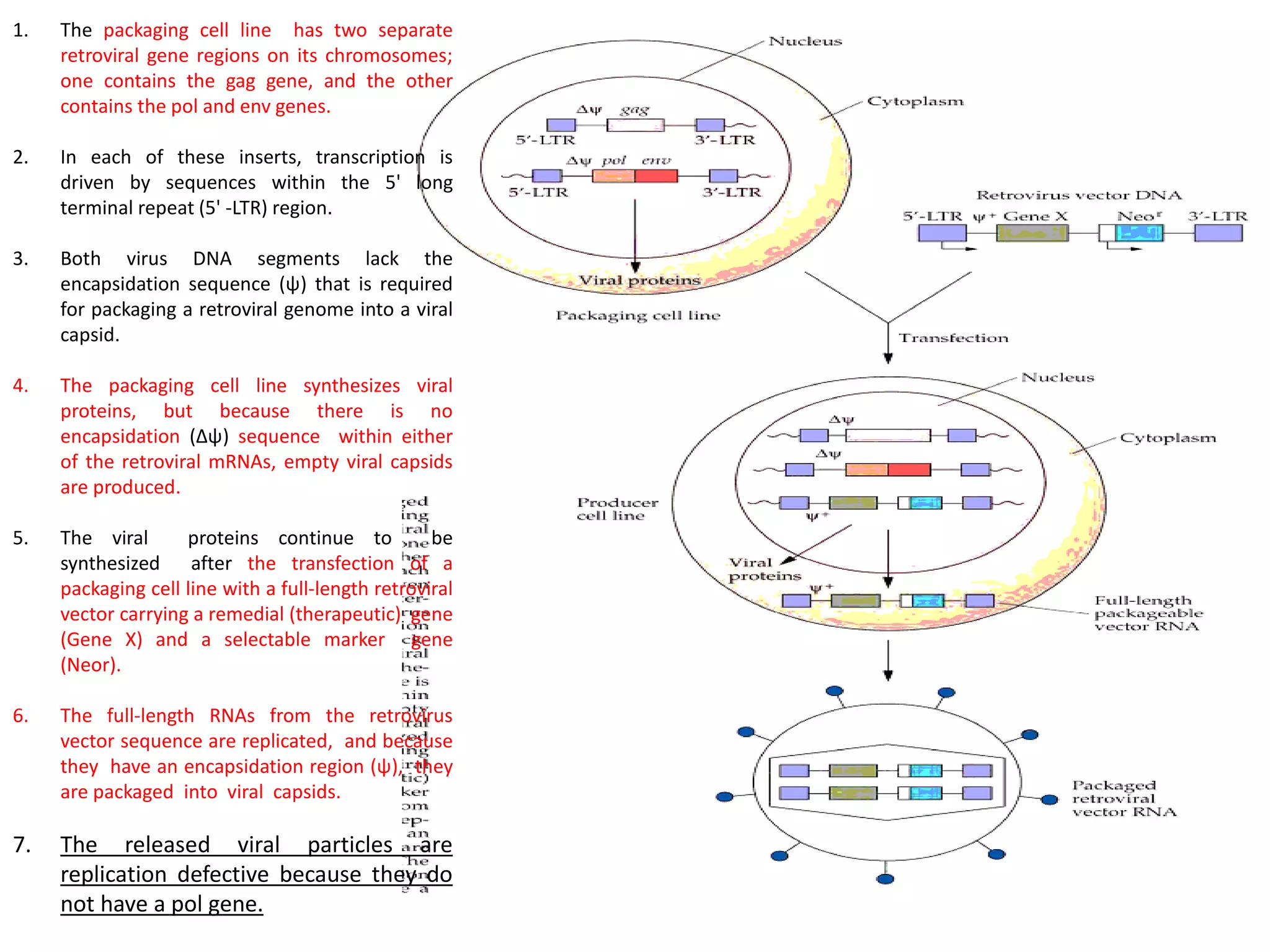
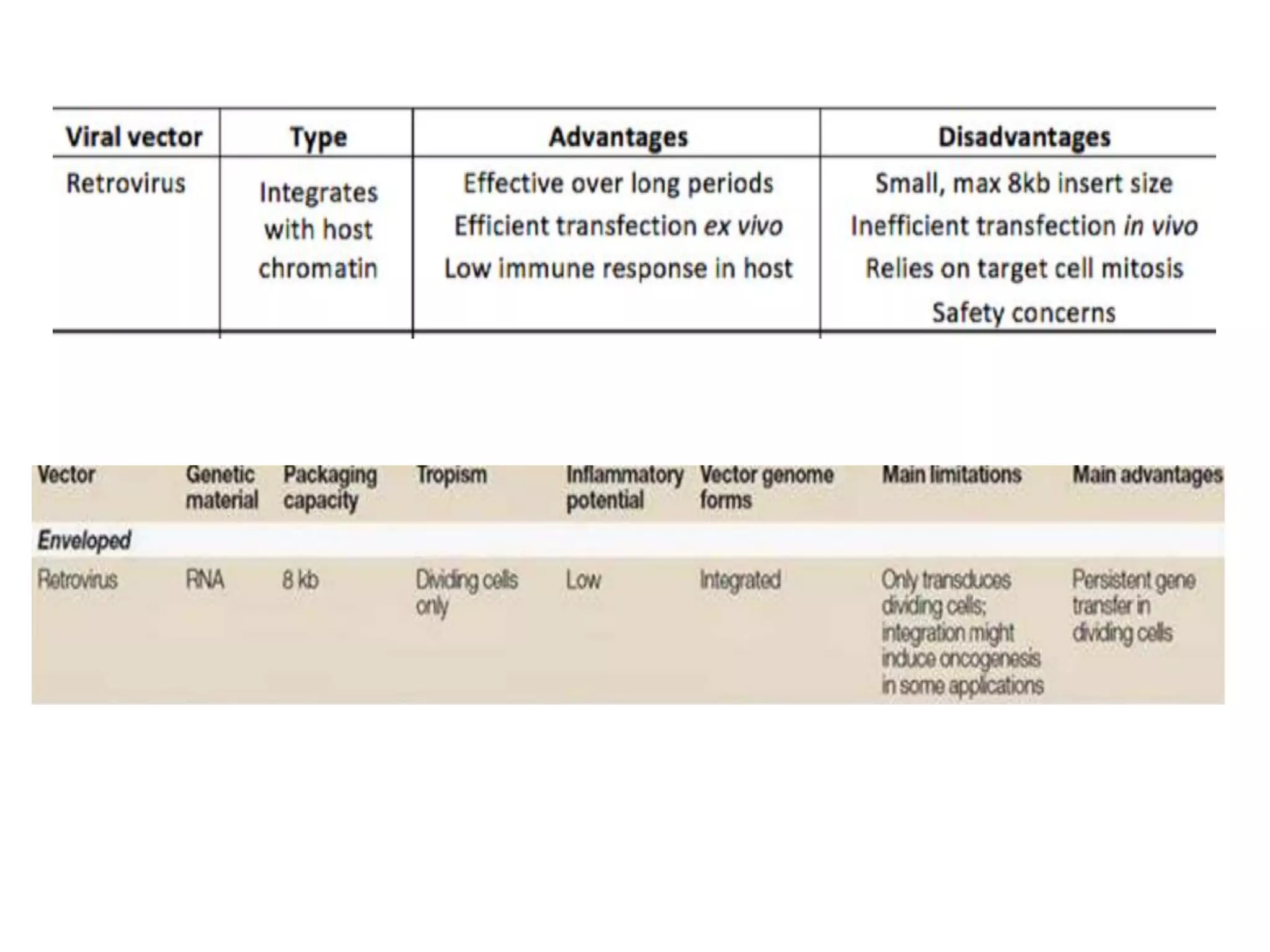
Agrobacterium and plant viruses can be used as biological vectors for plant transformation. Agrobacterium mediates transformation via its tumor-inducing plasmid, using virulence genes to transfer T-DNA containing the gene of interest into the plant genome. Plant viruses can also act as gene vectors by engineering viral genomes to contain and deliver foreign genes. Retroviruses have been developed as viral vectors for animal gene transfer due to their ability to stably integrate into the host chromosome.