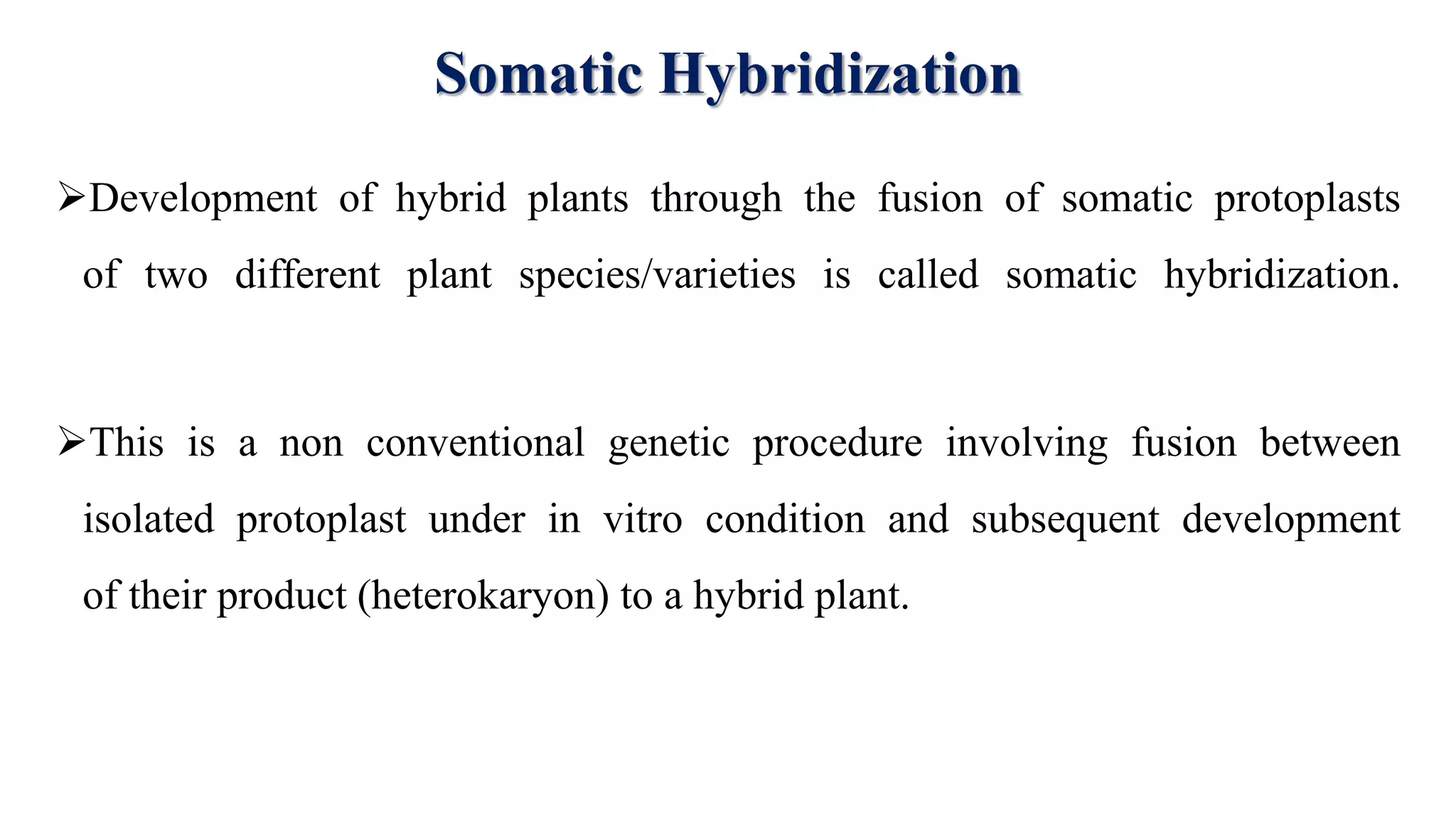
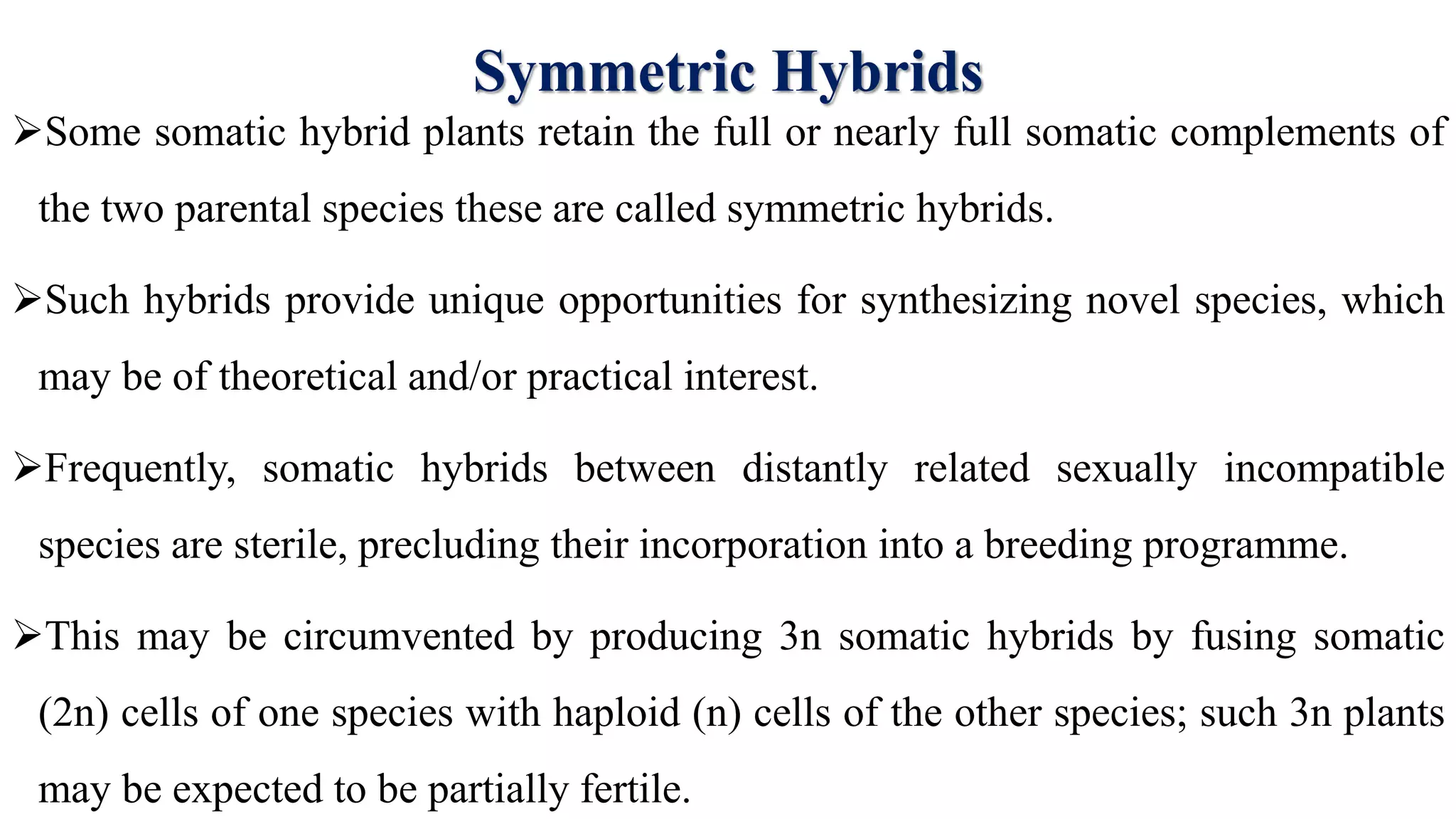
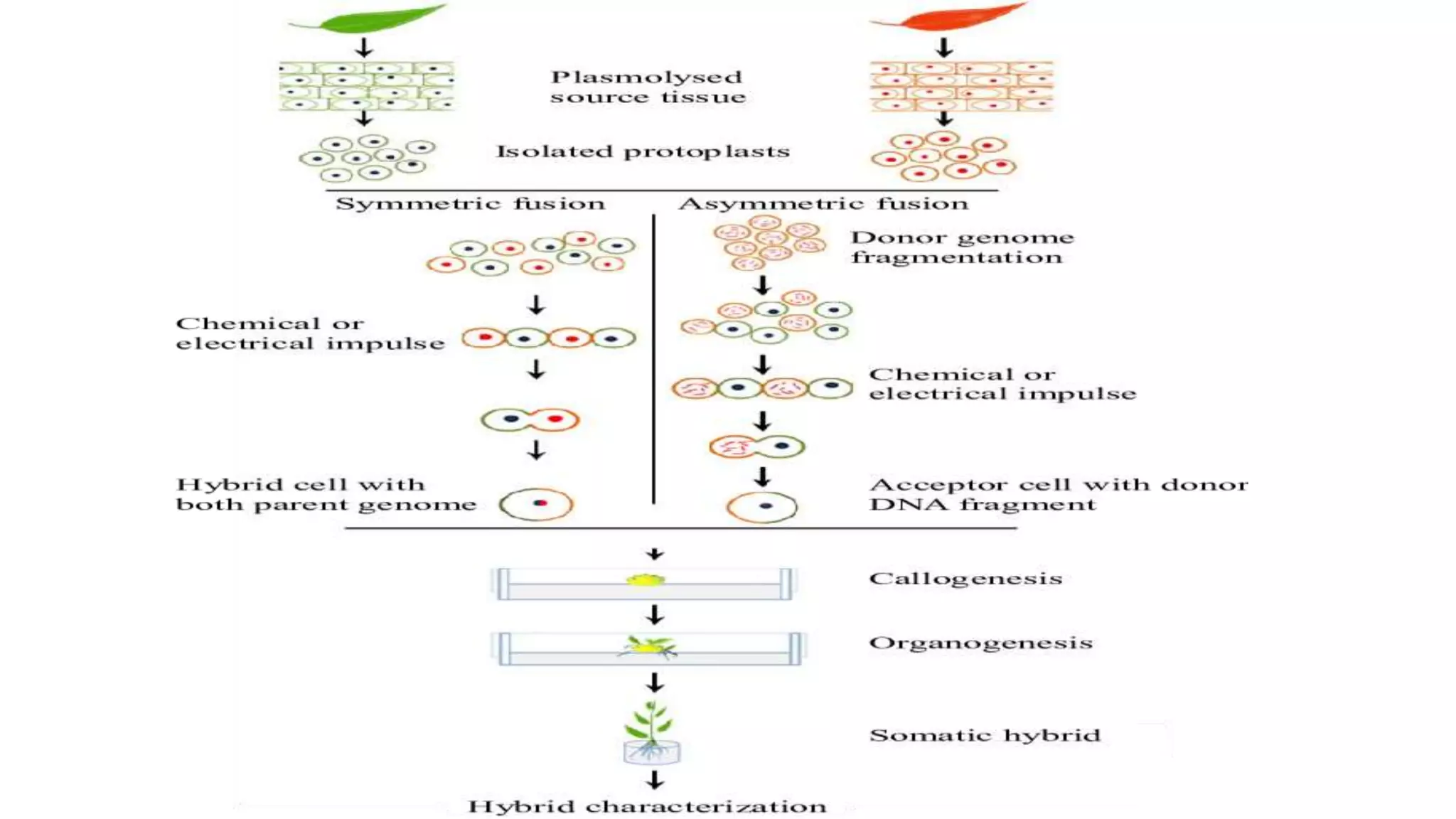
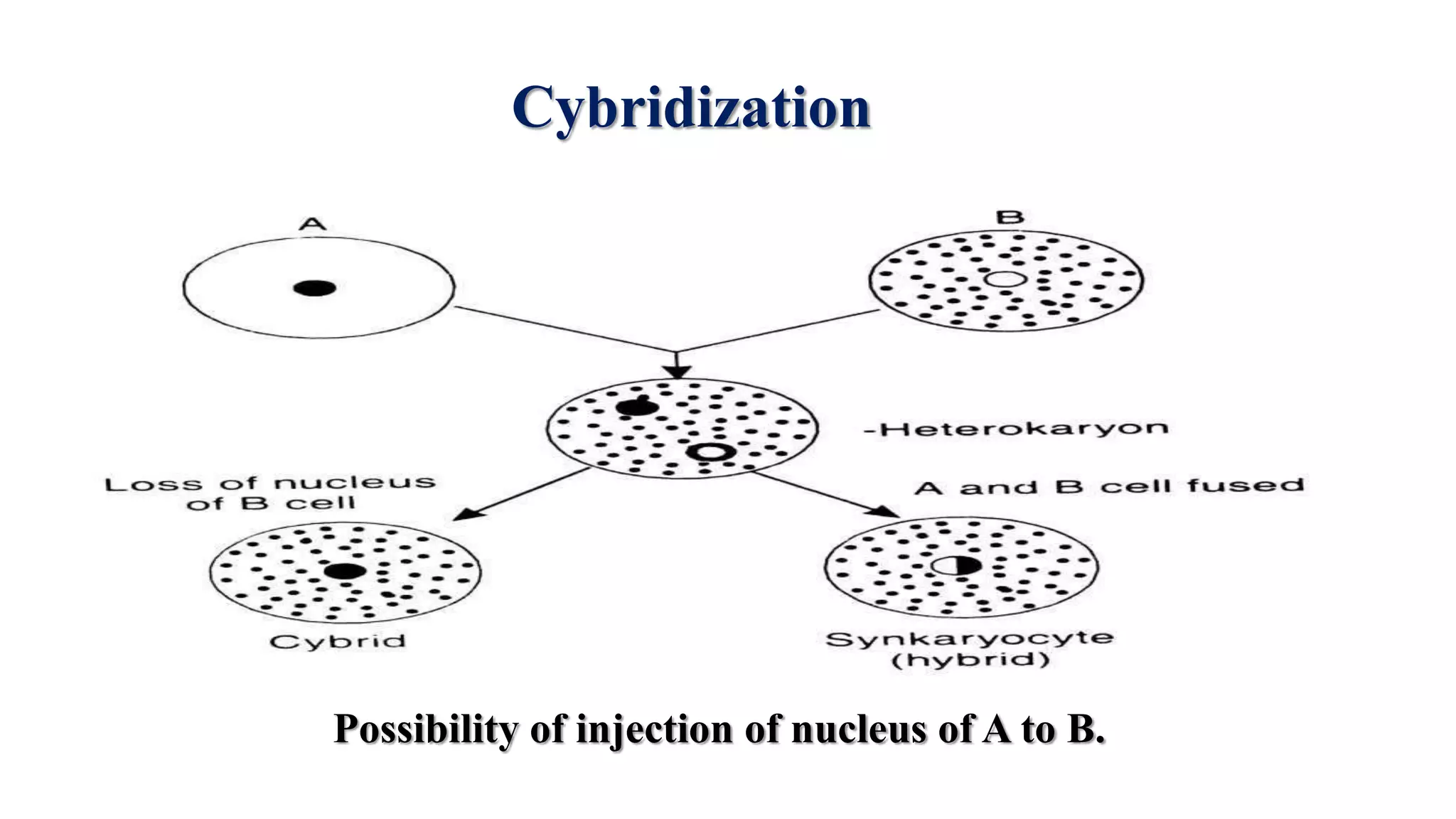
The document discusses symmetric and asymmetric somatic hybrids and cybrids in plant tissue culture. It defines symmetric hybrids as retaining chromosomes from both parents and asymmetric hybrids as retaining chromosomes from only one parent. Recent examples of cybrid production are provided, including transferring cytoplasmic male sterility from Satsuma mandarin to seedy citrus cultivars and introducing transformed tobacco chloroplasts into petunia. Cybridization allows for combining plant species that cannot reproduce sexually by fusing protoplasts such that the nucleus of one species is combined with the cytoplasm of another.