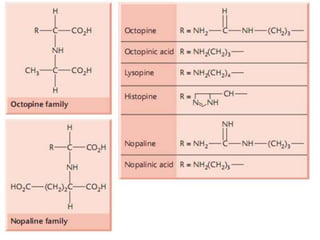
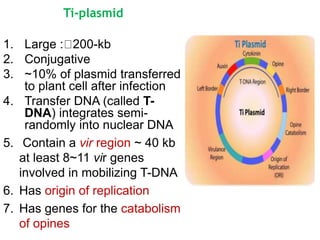
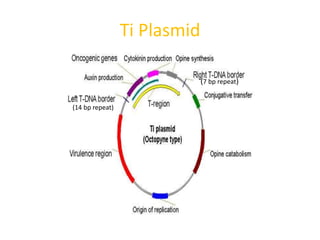
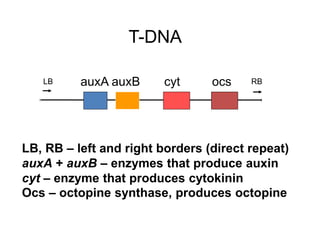
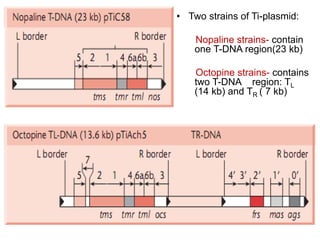
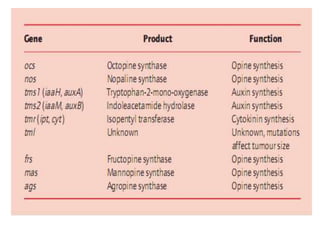
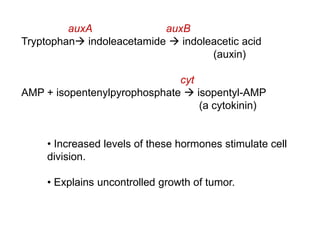
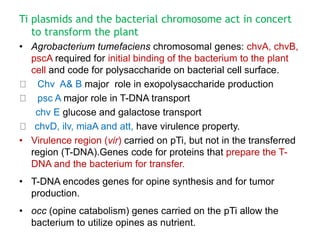
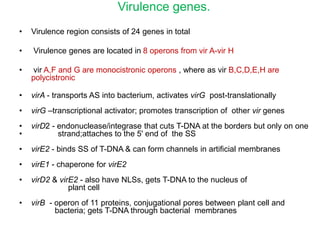
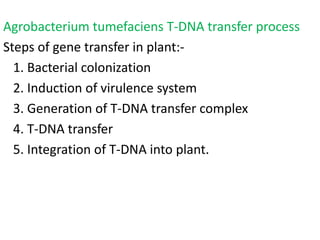
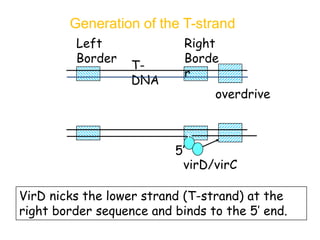
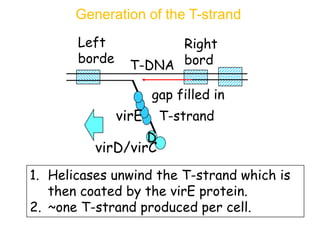
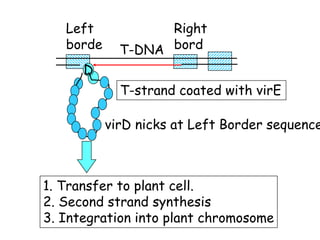
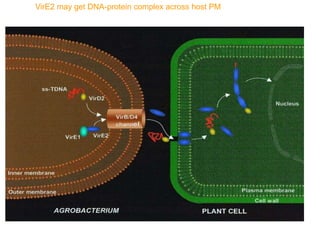
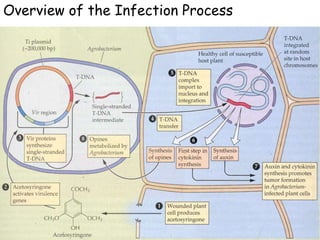
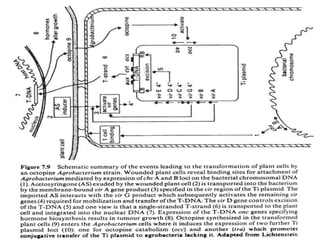
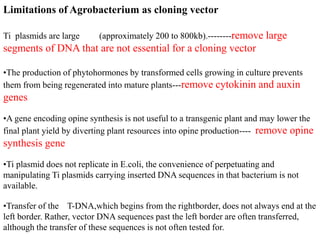
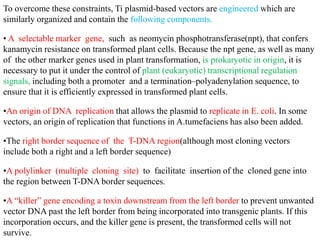
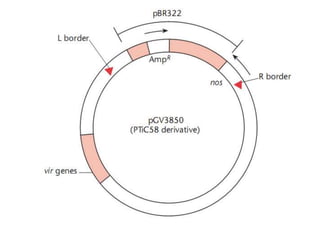
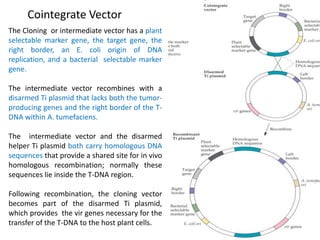
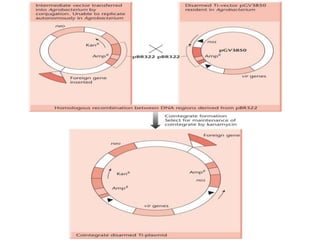
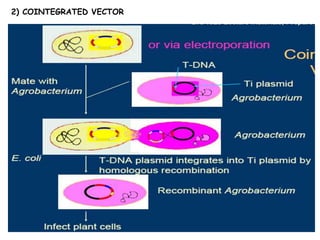
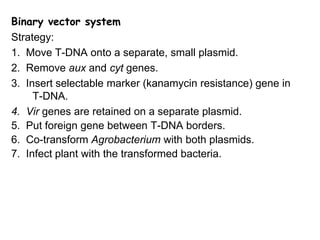
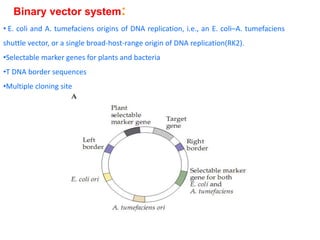
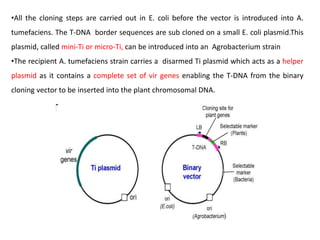
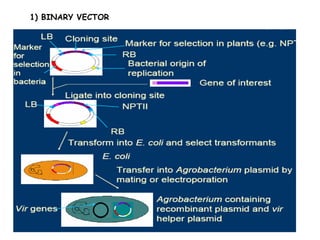
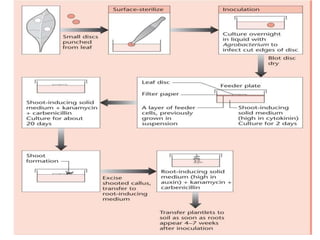
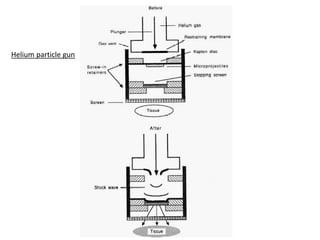
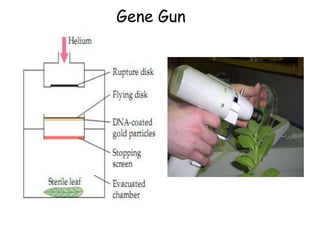
Agrobacteria are soil bacteria that can transfer genes to plant genomes. They contain Ti plasmids which transfer a segment of DNA (T-DNA) into the host plant genome. This causes tumors and induces the plant to produce unique amino acids called opines that the bacteria can use as nutrients. The Ti plasmid and bacterial chromosome work together with virulence genes on the plasmid producing proteins needed for T-DNA transfer. The T-DNA is processed and transferred via a T-strand into the plant cell nucleus where it integrates randomly. This process allows genetic engineering of plants through Agrobacterium.