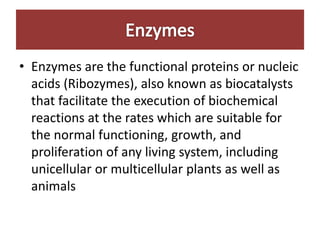
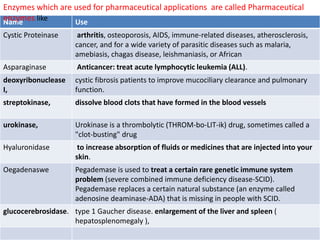
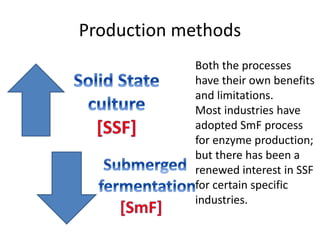
Enzymes are biocatalysts that facilitate biochemical reactions essential for the functioning of living organisms and have numerous applications in the pharmaceutical industry, including drug production and treatment of various diseases. Most industrial enzymes are derived from microorganisms through fermentation, with common strains including bacteria and fungi, which can be genetically engineered for higher yields. The production methods vary, with submerged fermentation being predominant, although solid-state fermentation presents advantages in certain contexts.


![• The ability of enzymes to remain viable and perform catalytic activities
even outside their source organism, allows them to be exploited for
carrying out a number of industrial processes that rely on chemical
transformations of substrates to their corresponding products.
• [E] +[S] =[P] + [E]
• The reactions catalyzed by enzymes are highly efficient, that is, they occur
under ambient environmental conditions, that is, temperature, pH, and
pressure (the conditions depend on the physiological conditions of the
source organisms and its environmental conditions).
• For instance, an enzyme obtained from a mesophilic organism (optimal
growth temperature is 37◦C and growth temperature range from 20 to
40◦C), inhabiting neutral environments, shall work efficiently at mild
temperatures, neutral pH, and atmospheric pressure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmaceuticalenzymeskkg-210816121705/85/Pharmaceutical-enzymes-kkg-4-320.jpg)



![• At present,around 200 types of microbial
enzymes from 4,000 known enzymes are used
commercially .Nearly 75% of the total
enzymes are produced by three top enzyme
companies,that is, Denmark-based
Novozymes, US-based DuPont, and
Switzerland-based Roche [10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmaceuticalenzymeskkg-210816121705/85/Pharmaceutical-enzymes-kkg-9-320.jpg)
![Source of enzymes
[Fermentation culture]
• Most of the industrial enzymes including those used in
pharmaceutical industries are produced through fermentation
of suitable microbial strains of bacteria and fungi due to their
easy handling,
• fast growth rates, and
• convenient scale up in large vessels (fermenters).
• Bacteria - Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, lactic acid bacteria
• filamentous fungi such as Aspergillus oryzae, Aspergillus niger,
Trichoderma atroviride, and Yeasts ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae,
Pichia pastoris,)
• As the strains have been improved through genetic engineering,
they produce enzymes in very high yields.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmaceuticalenzymeskkg-210816121705/85/Pharmaceutical-enzymes-kkg-10-320.jpg)

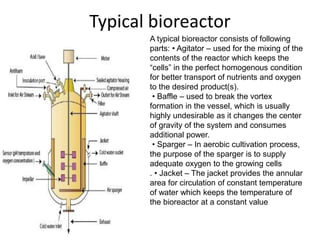



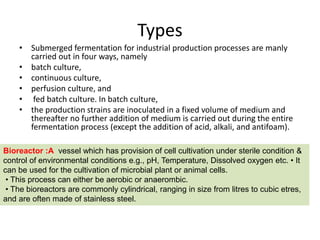





![• In continuous culture, the fermentation process is initiated in the batch
mode. However, after certain time period fresh medium or nutrient
concentrate is added into the fermenter at a rate which approximately
matches the growth rate of the microorganism used and simultaneously
the medium containing the product and biomass is continuously
withdrawn from the overflow line of the vessel .
• A perfusion culture is somehow similar to a continuous culture process, in
that it also involves the constant feeding of fresh media and removal of
spent media and product. However, it differs from the previous in
retention of high numbers of viable cells by using alternating tangential-
flow and standard tangential-flow filtration or by binding the cells to a
substrate (capillary fibers, membranes, microcarriers in fixed bed, and so
on) in the fermenter [26]. In the case of fed batch culture, the
concentrated components of the nutrients are added to the batch culture
in small lots at regular time points or based on the requirement of the
process [24, 25].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmaceuticalenzymeskkg-210816121705/85/Pharmaceutical-enzymes-kkg-25-320.jpg)