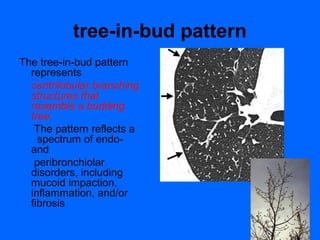
The document presents a glossary of updated terms for thoracic imaging compiled by members of the Fleischner Society, replacing previous glossaries from 1984 and 1996. It includes definitions for various conditions such as bronchiectasis, bronchocele, and centrilobular emphysema, alongside descriptions of imaging patterns like the tree-in-bud pattern. This resource aims to unify the language used in thoracic radiography and computed tomography.