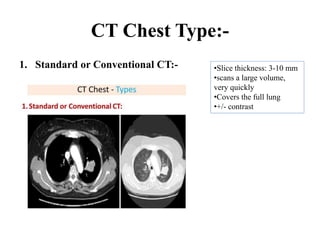
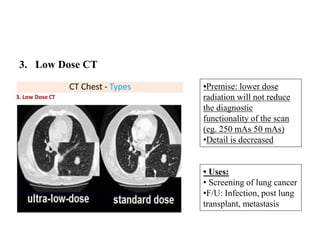
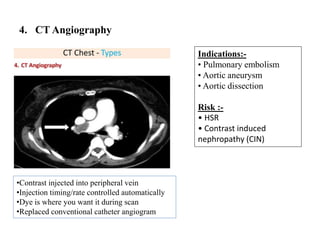
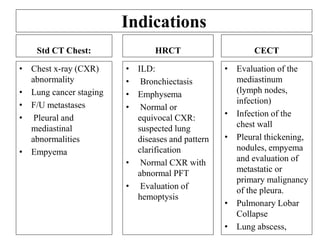
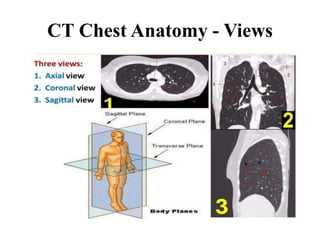
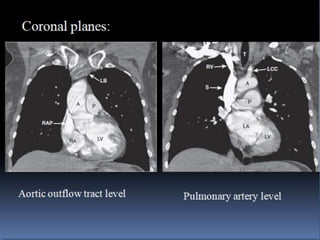
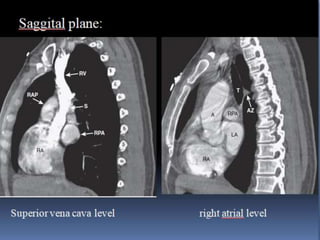
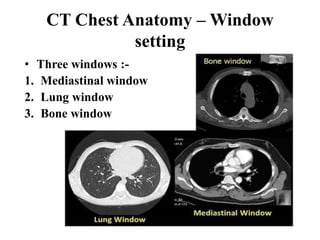
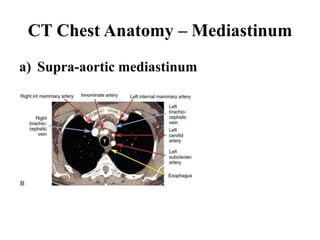
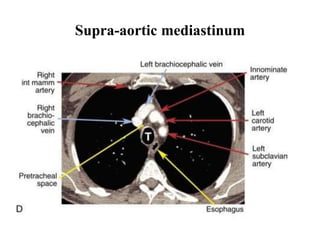
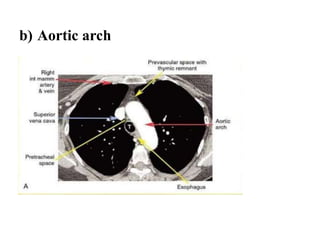
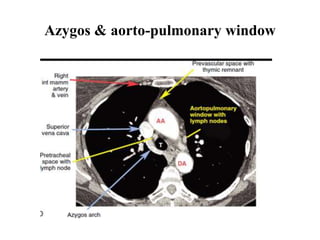
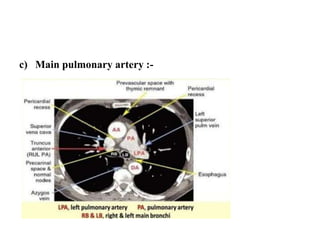
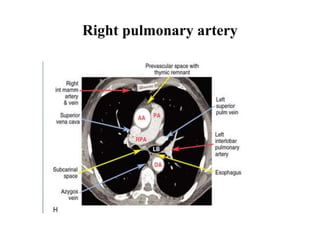
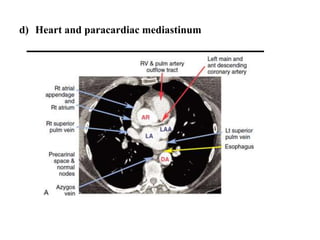
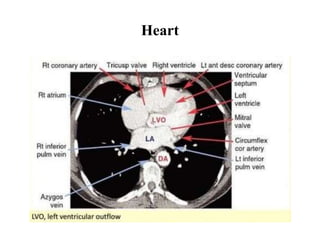
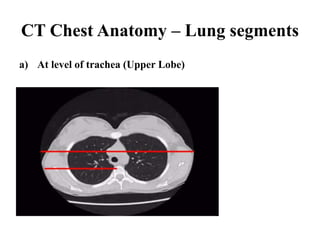
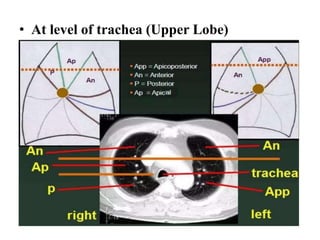
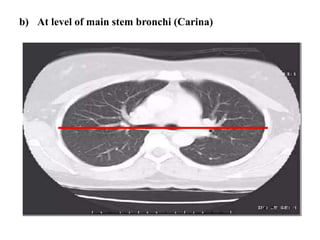
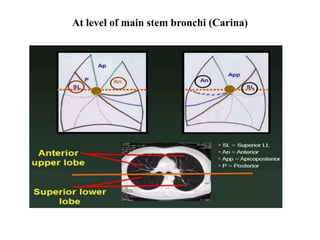
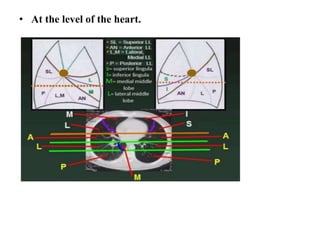
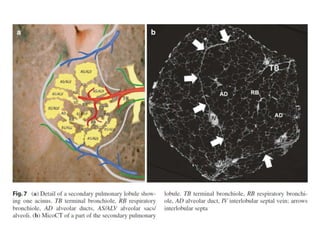
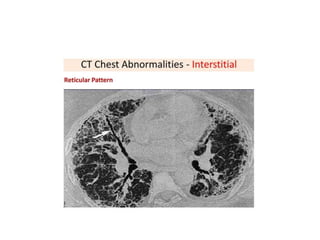
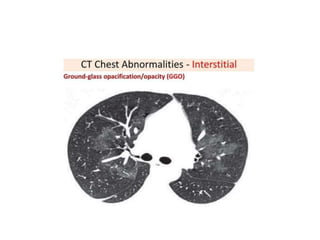
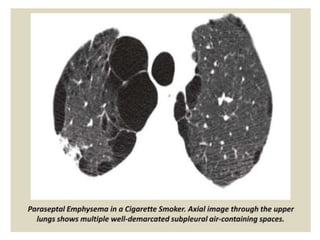
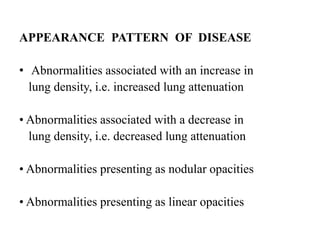
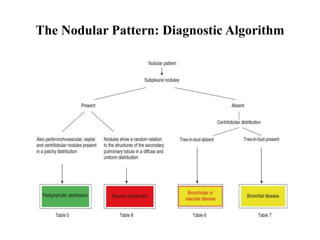
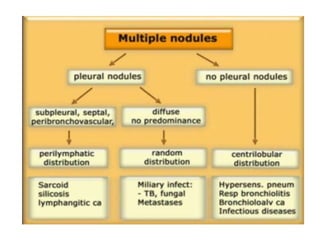
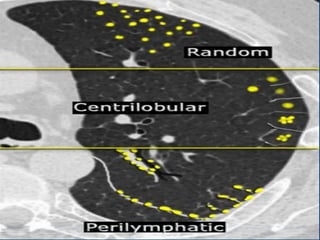
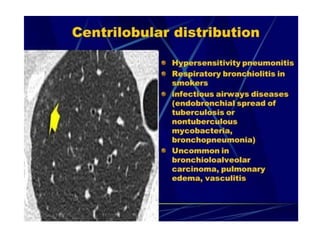
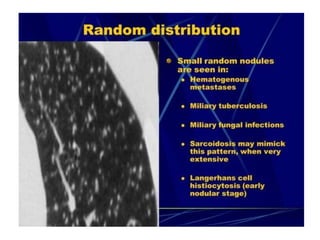
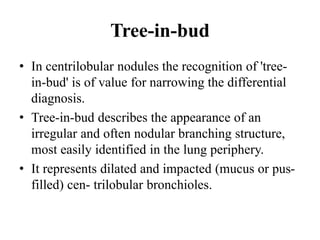
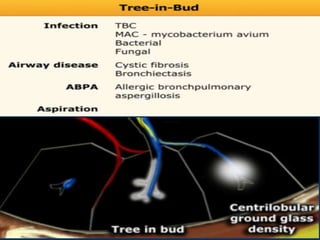
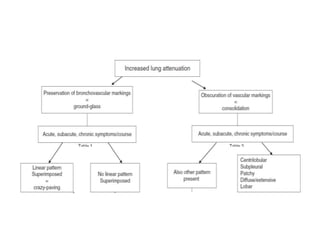
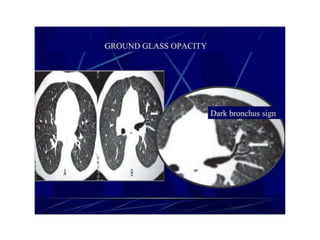
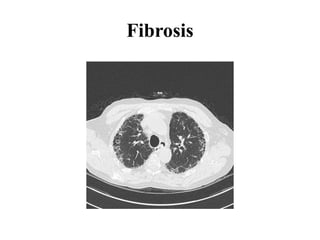
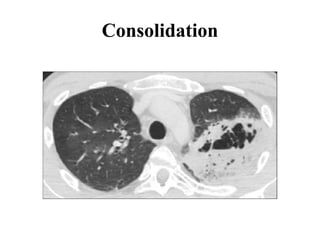
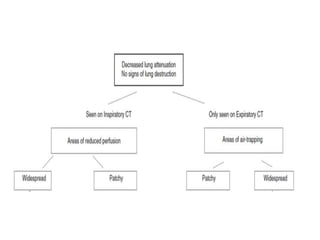
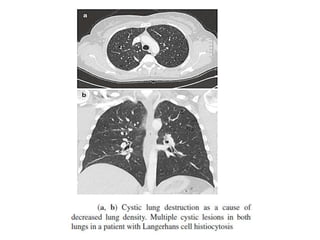
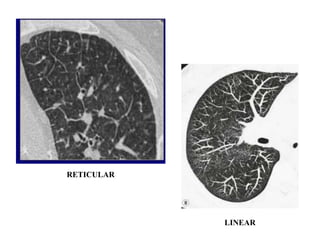
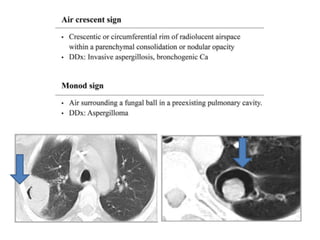
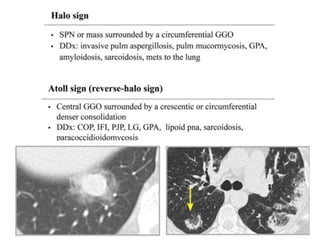
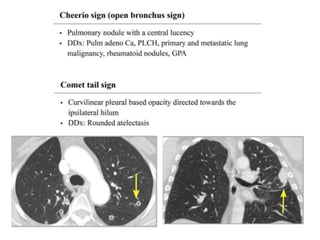
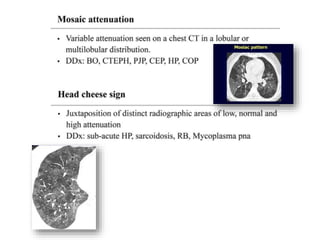
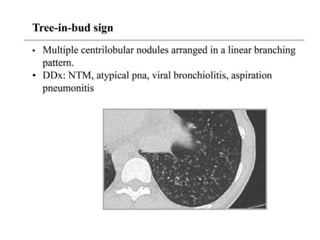
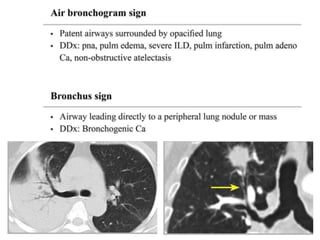
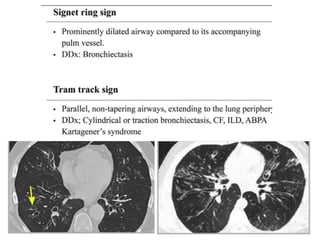
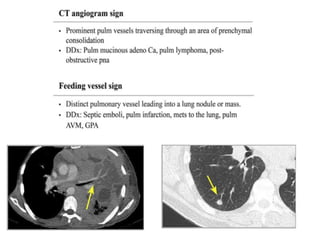
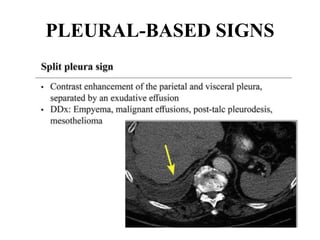
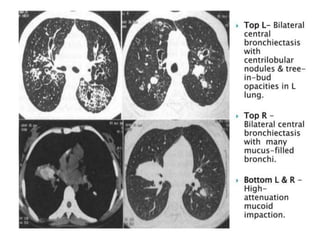
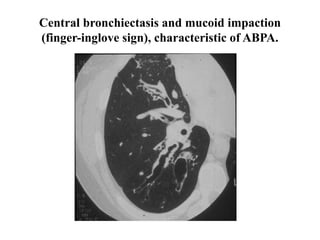
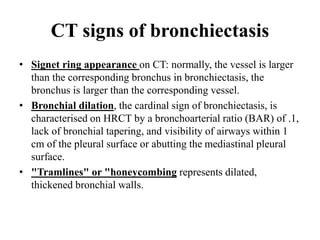
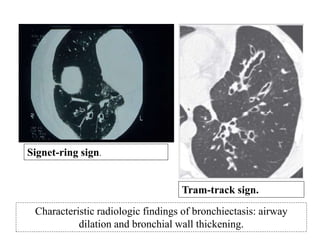
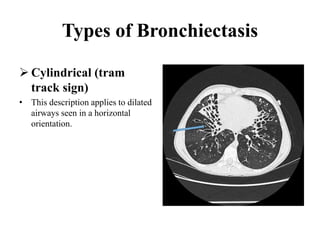
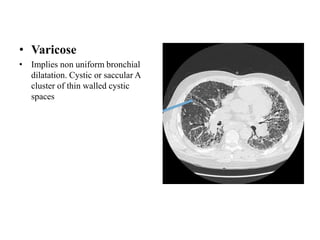
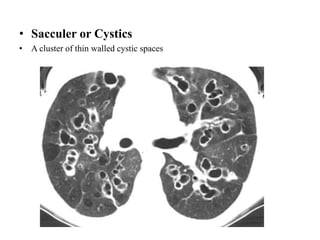
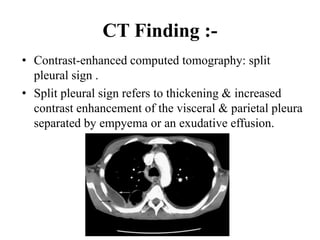
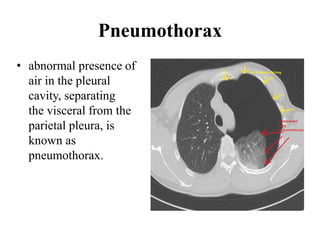
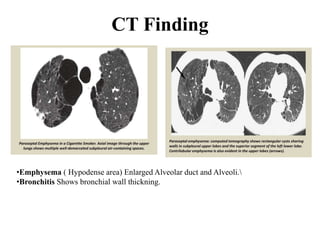
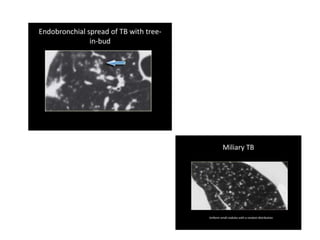
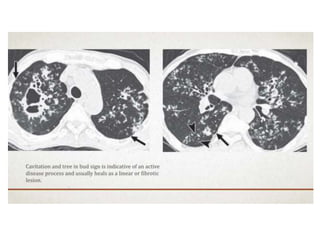
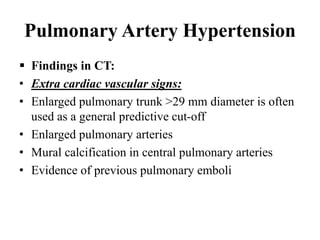
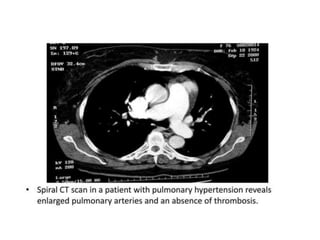
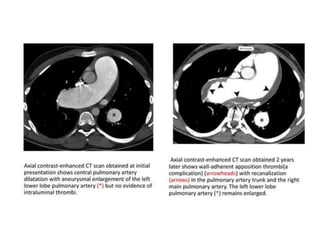
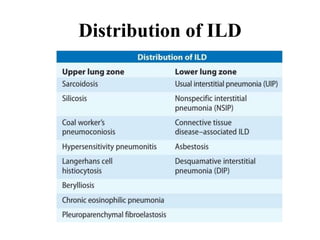
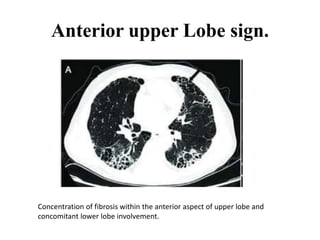
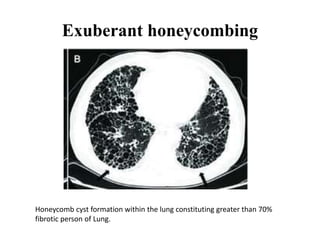
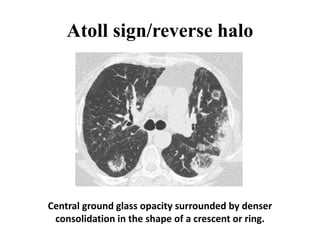
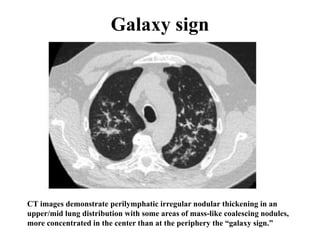
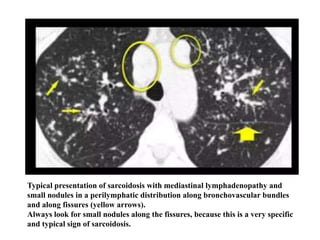
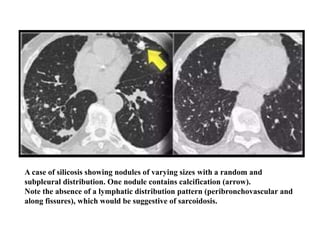
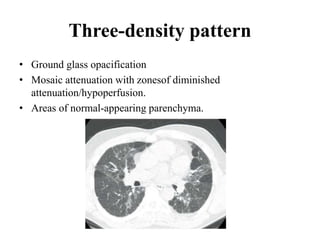
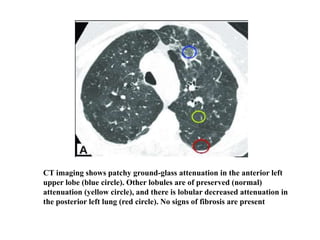
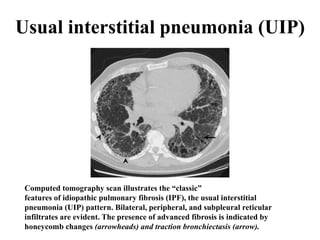
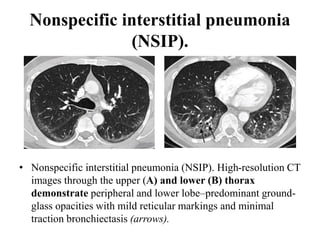
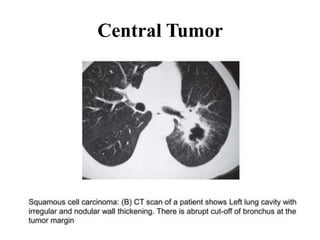
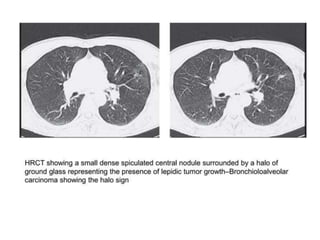
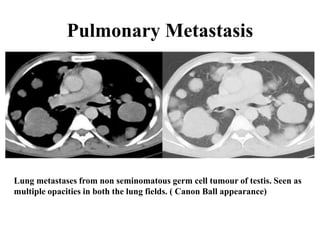
This document provides an overview of lung imaging using CT scans. It begins with the history of tomography and CT scans. It then discusses the different types of CT chest scans and their indications. Next, it covers CT chest anatomy including lung segments and windows. The document outlines patterns of abnormalities seen on CT scans like nodules, ground glass opacities, and consolidation. It also discusses specific lung diseases and their CT findings such as bronchiectasis, ABPA, and pleural effusions. In summary, the document is a guide to interpreting CT chest scans by covering scan types, anatomy, and patterns of lung abnormalities.