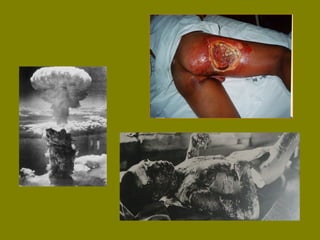
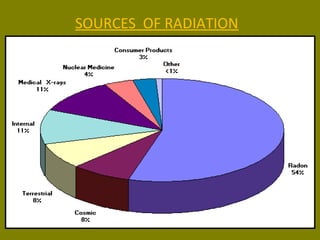
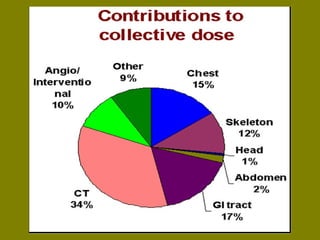
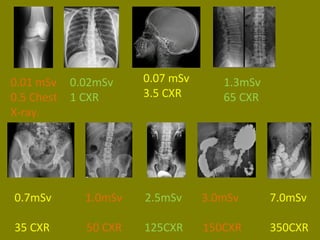
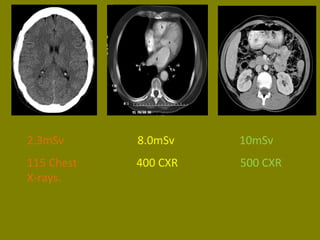
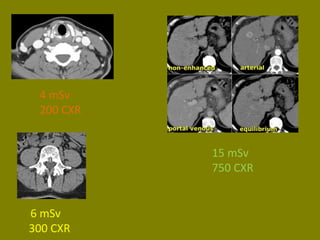
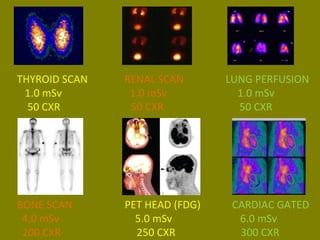
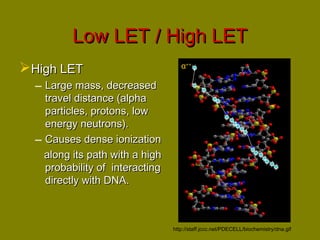
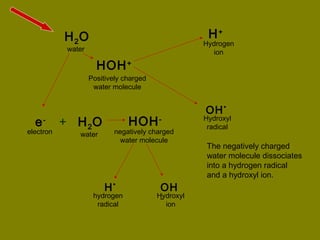
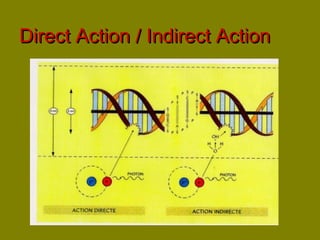
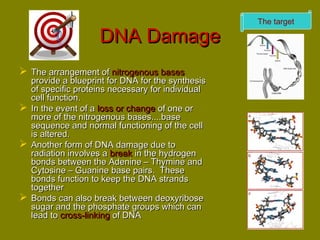
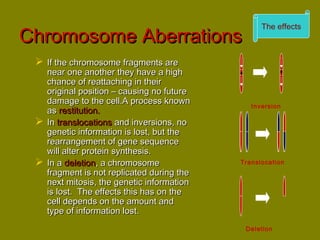
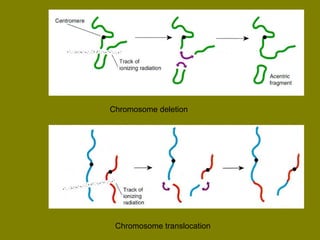
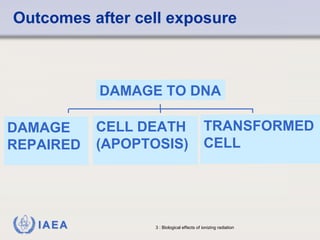
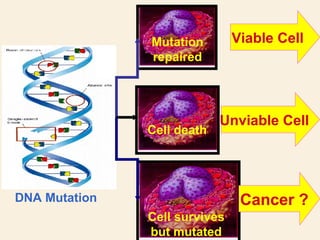
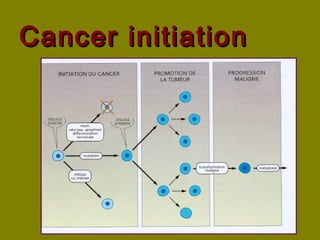
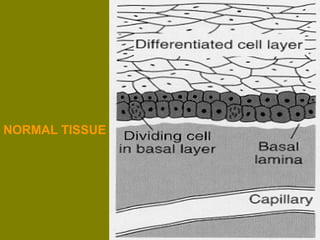
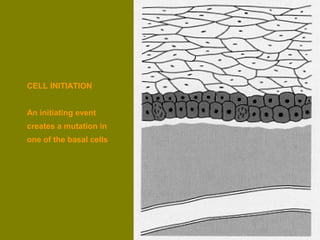
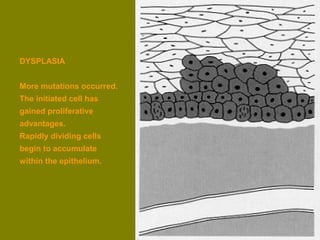
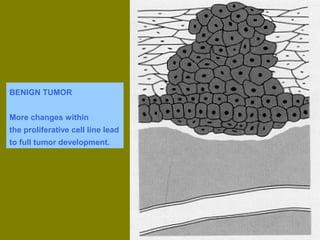
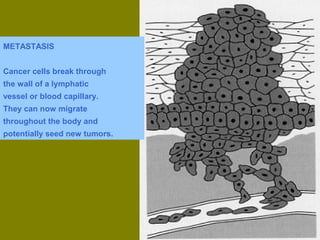
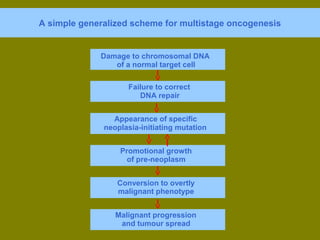
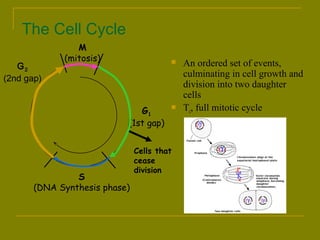
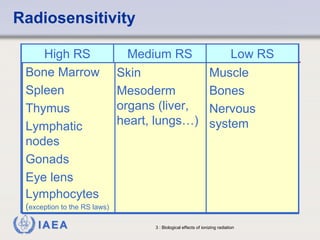
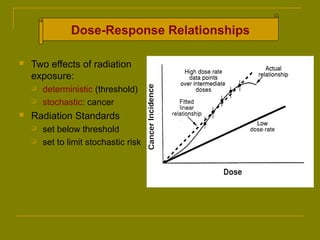
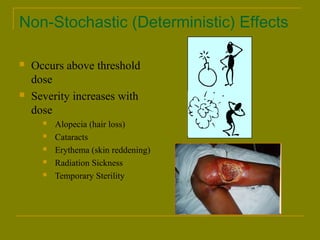
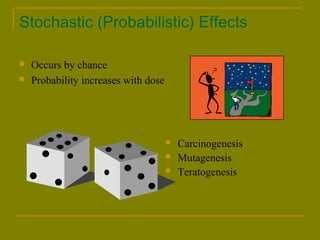
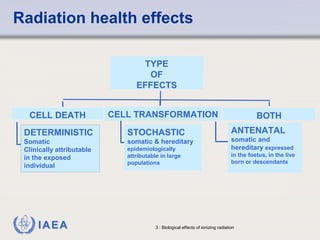
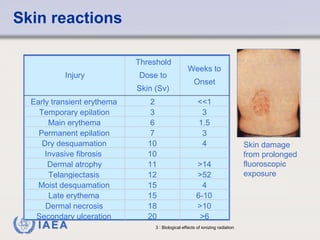
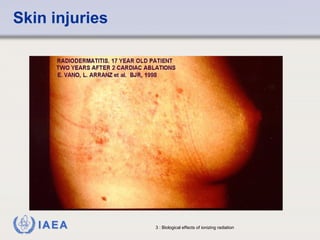
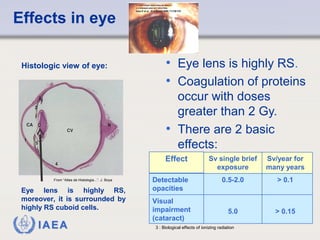
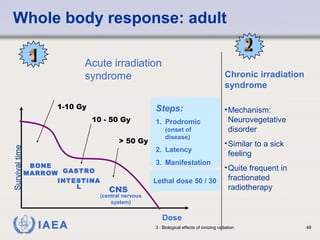
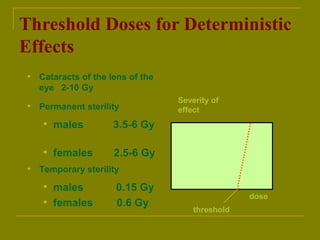
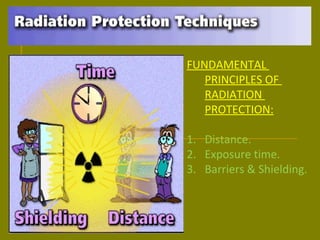
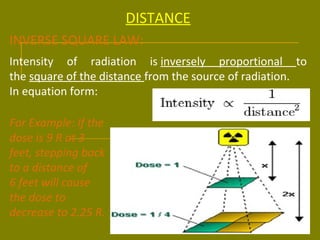
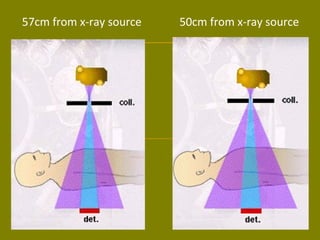
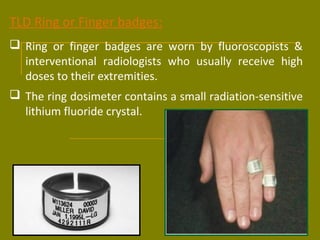
This document discusses ionizing radiation, its biological effects, and safety issues. It begins by outlining the aims of discussing the mechanisms and effects of ionizing radiation exposure, associated risks, and main safety protections. Ionizing radiation is then defined as radiation that can ionize atoms and is capable of breaking chemical bonds. Sources of ionizing radiation and its units of measurement are also outlined. The document goes on to explain how ionizing radiation can damage DNA through direct interactions or free radicals produced from radiolysis of water. This damage can lead to mutations, chromosome aberrations, cell death or cancer initiation through multiple stages. Radiobiologists assume not all DNA damage is repaired.