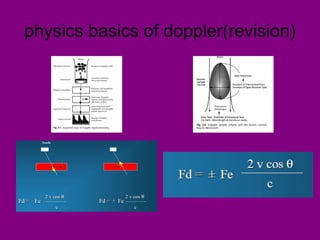
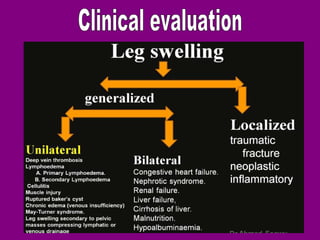
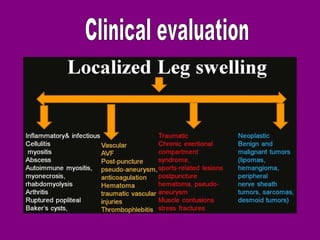
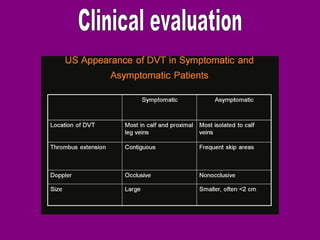
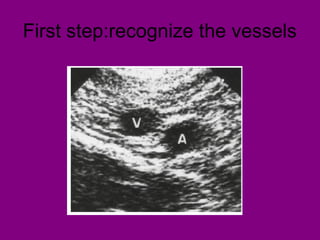
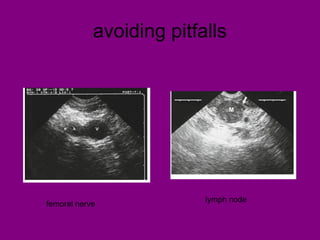
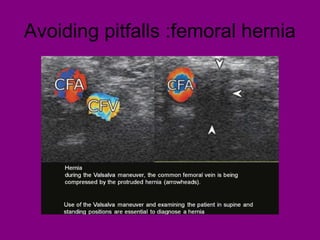
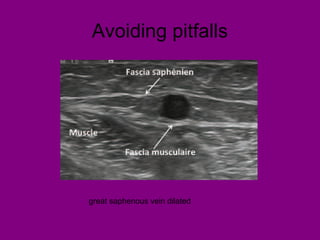
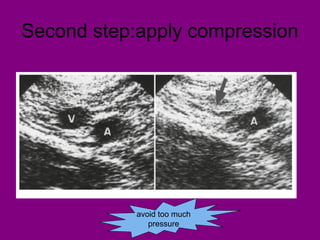
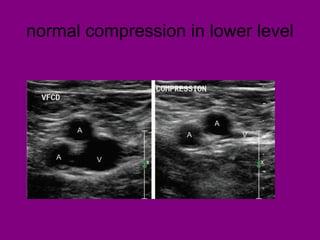
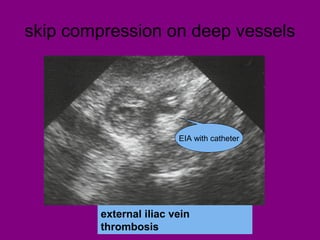
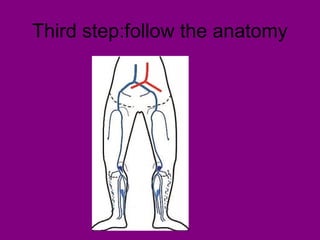
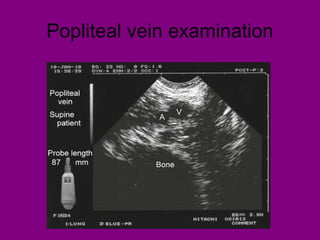
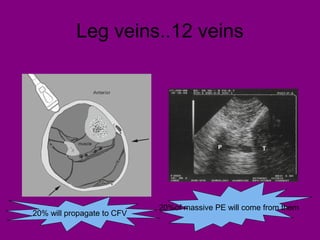
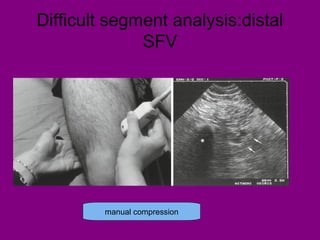
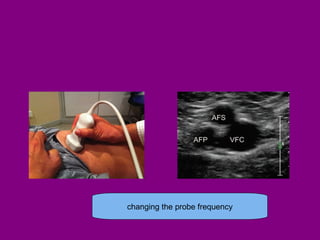
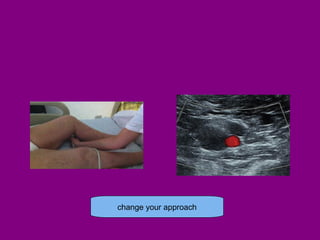
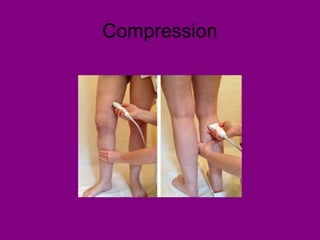
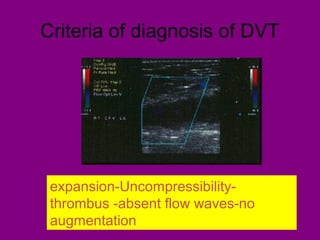
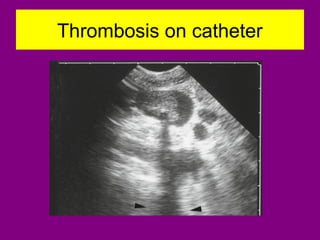
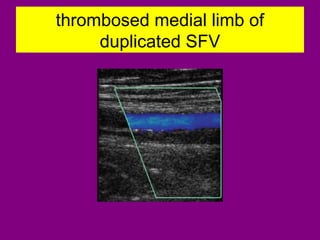
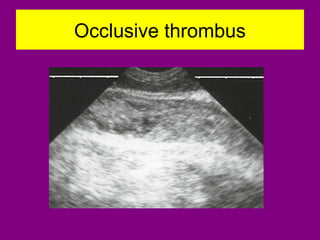
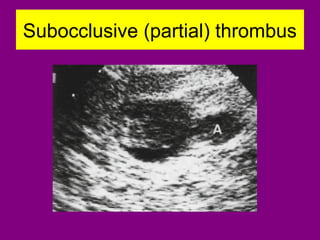
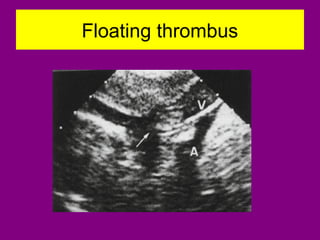
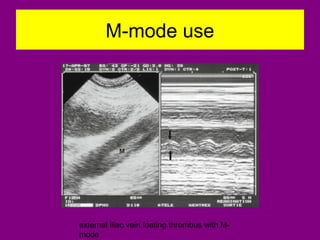
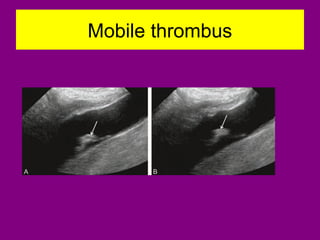
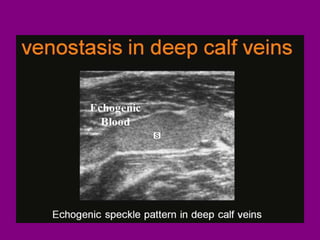
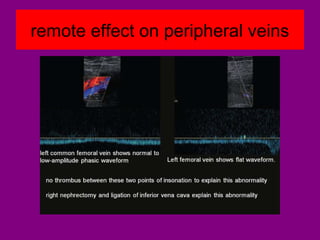
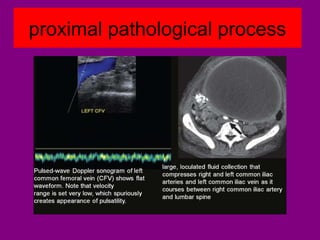
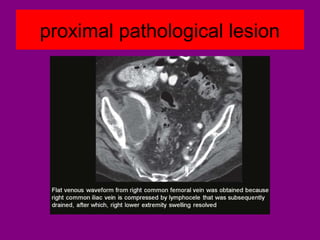
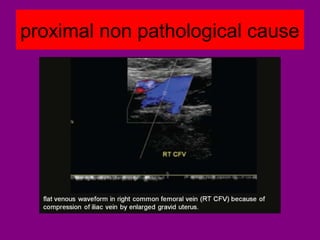
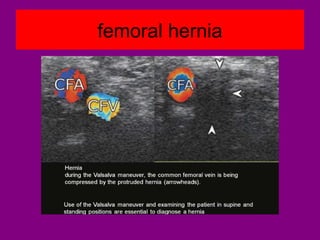
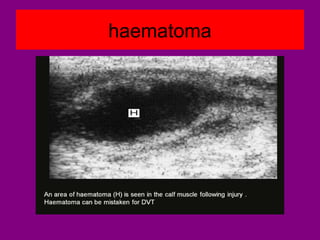
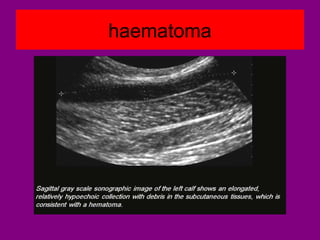
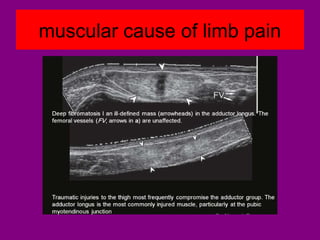
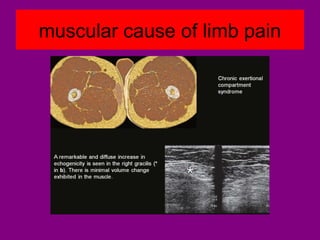
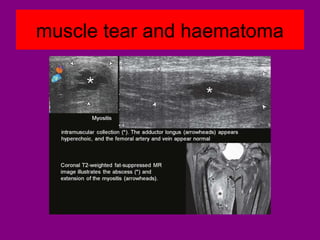
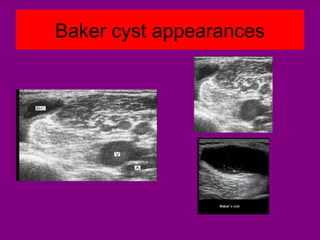
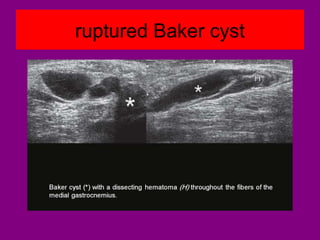
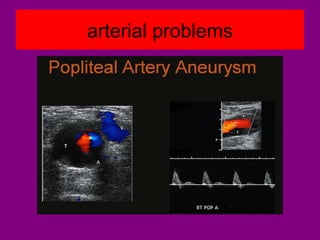
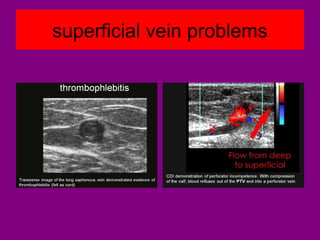
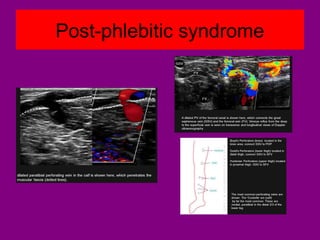
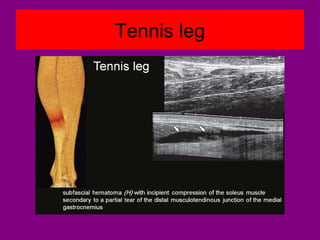
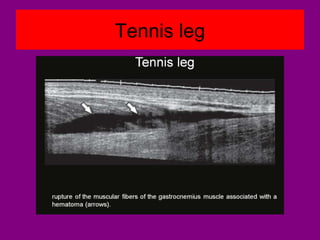
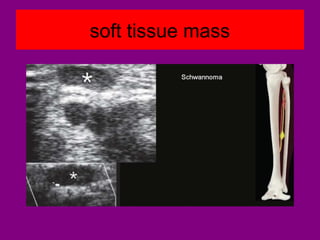
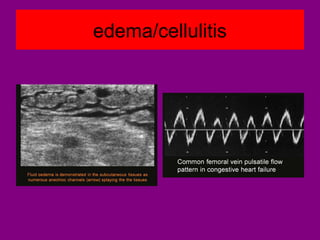
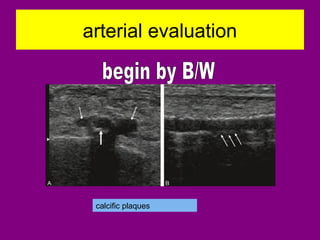
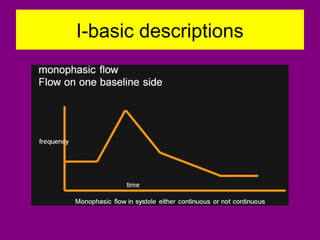
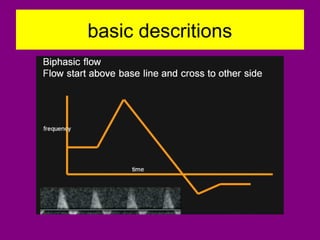
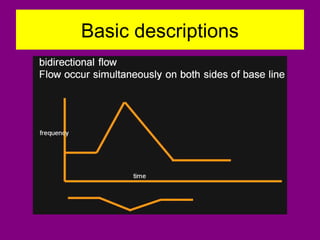
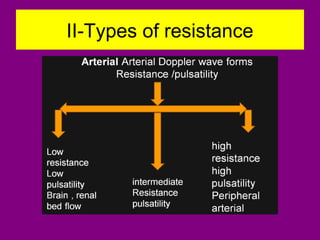
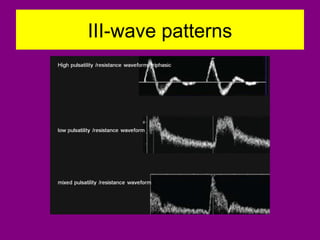
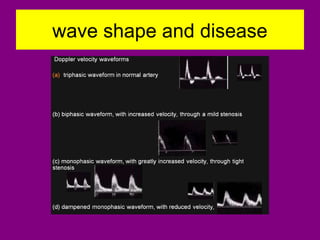
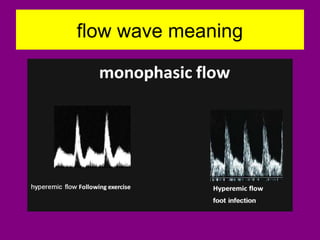
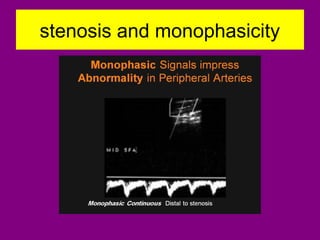
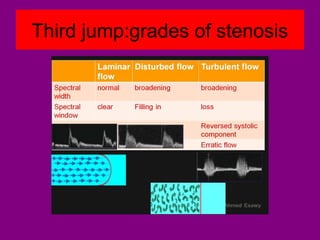
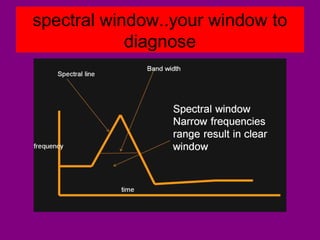
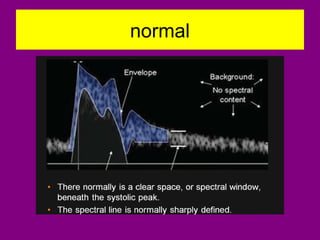
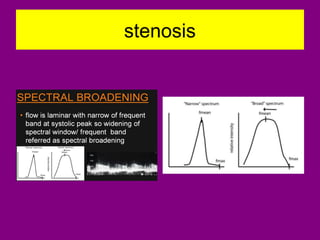
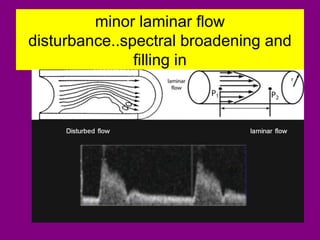
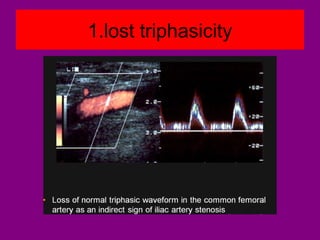
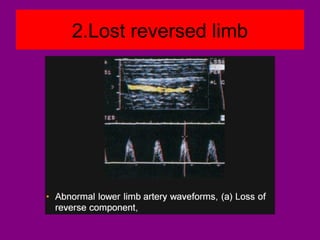
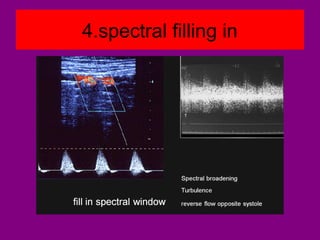
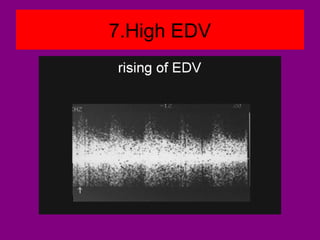
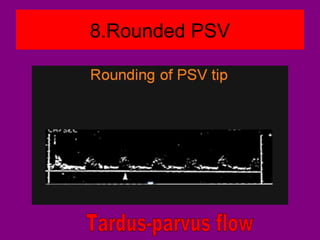
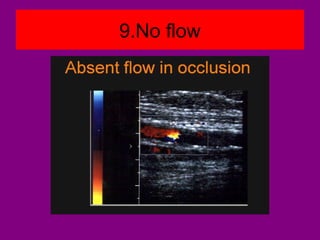
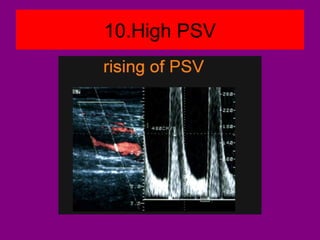
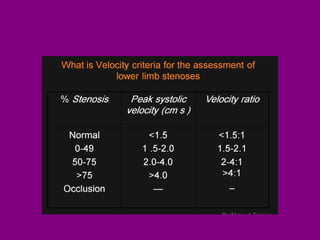
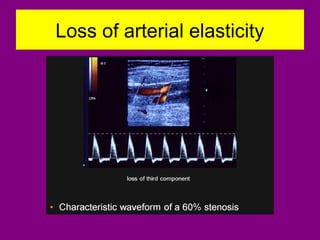
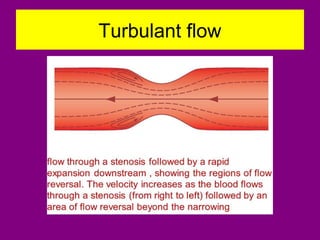
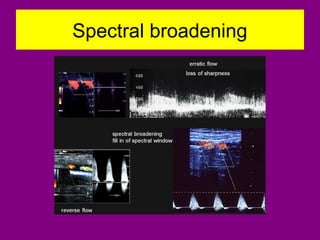
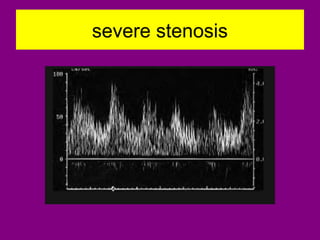
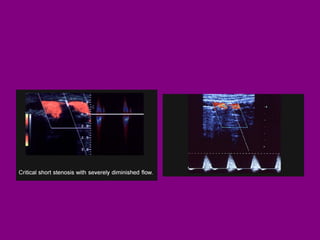
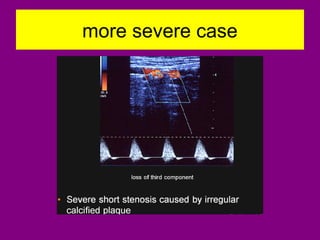
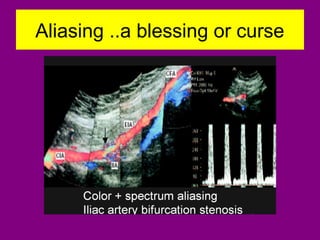
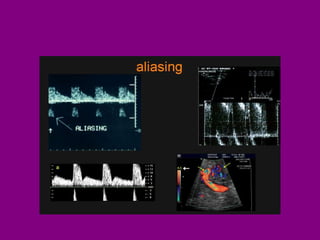
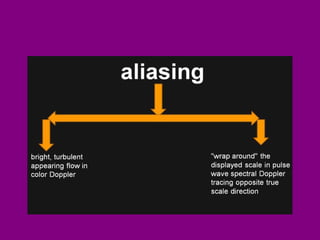
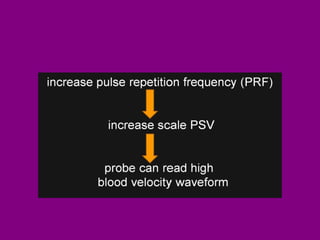
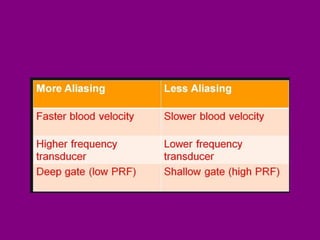
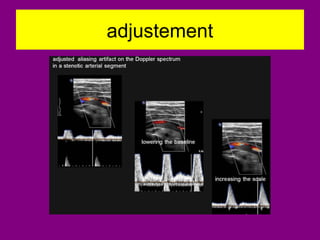
This document provides an overview of performing lower limb doppler examinations to diagnose deep vein thrombosis and other causes of limb pain. It discusses the essential techniques including recognizing the vessels, avoiding pitfalls, applying compression, and following the anatomy. Criteria for diagnosing DVT include vessel expansion, compressibility, presence of thrombus, and absent or reduced blood flow waves. The document also reviews using doppler to diagnose and grade arterial stenosis by analyzing spectral wave patterns and meanings.