1. Jean Baudrillard was a postmodern philosopher known for his concepts of hyperreality and simulations, where he argued that society has replaced reality with simulations and signs that no longer refer to any deeper reality.
2. Michel Foucault analyzed power relations and argued that knowledge is always produced through power, so what counts as truth depends on social relationships and changes over time and place.
3. Postmodernism more broadly questions universal truths and meta-narratives, emphasizes marginalized groups, and sees history as non-linear rather than progressive. It influenced fields like philosophy, literary criticism, and cultural studies.




![Some tenets of ‘Post-Modernism’Opposition to universals, ‘meta-narratives’, and generality; critical of the Enlightenment.History isn’t progressThere is no ‘Truth’ (or Truth has no ‘foundations’)People (‘subjects’ or ‘subjectivity’) are products of power, and power is everywhere [Foucault]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theorypostmodernism-110926121636-phpapp01/85/Theory-postmodernism-5-320.jpg)





















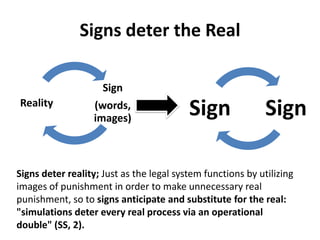




![Hyper-Reality of Disneyland"Disneyland is presented as imaginary in order to make us believe that the rest is real, whereas Los Angeles [is] no longer real, but belongs to the hyperreal order and to the order of simulation."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theorypostmodernism-110926121636-phpapp01/85/Theory-postmodernism-33-320.jpg)
