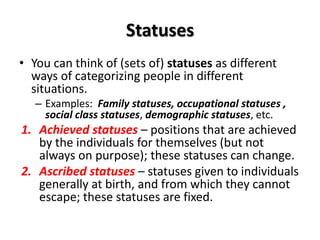
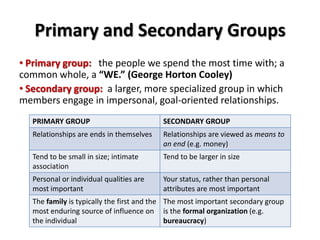
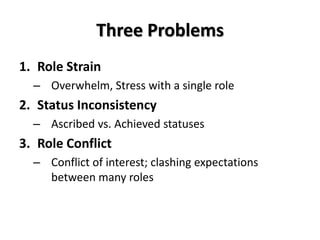
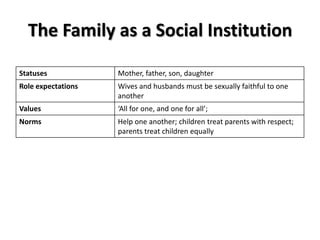
Social structures are organized through statuses and roles. Statuses are positions in society, while roles are expectations for how people in a status should behave. Statuses can be achieved through individual accomplishments or ascribed at birth.
Socialization is the lifelong process through which individuals learn cultural norms and develop a self-identity. It occurs through various social agents like family, schools, peers and the workplace. The self develops through interactions with others and internalizing their perspectives.
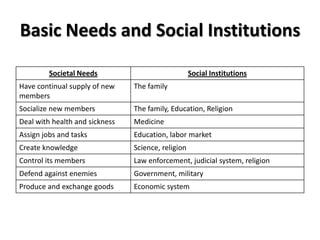
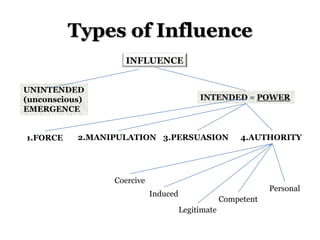
Power and influence take various forms, from force which treats people as objects, to authority which can be based on competence, legitimacy or personal appeal. Manipulation aims to influence without open communication, while persuasion involves evaluating arguments independently. Social institutions like family and