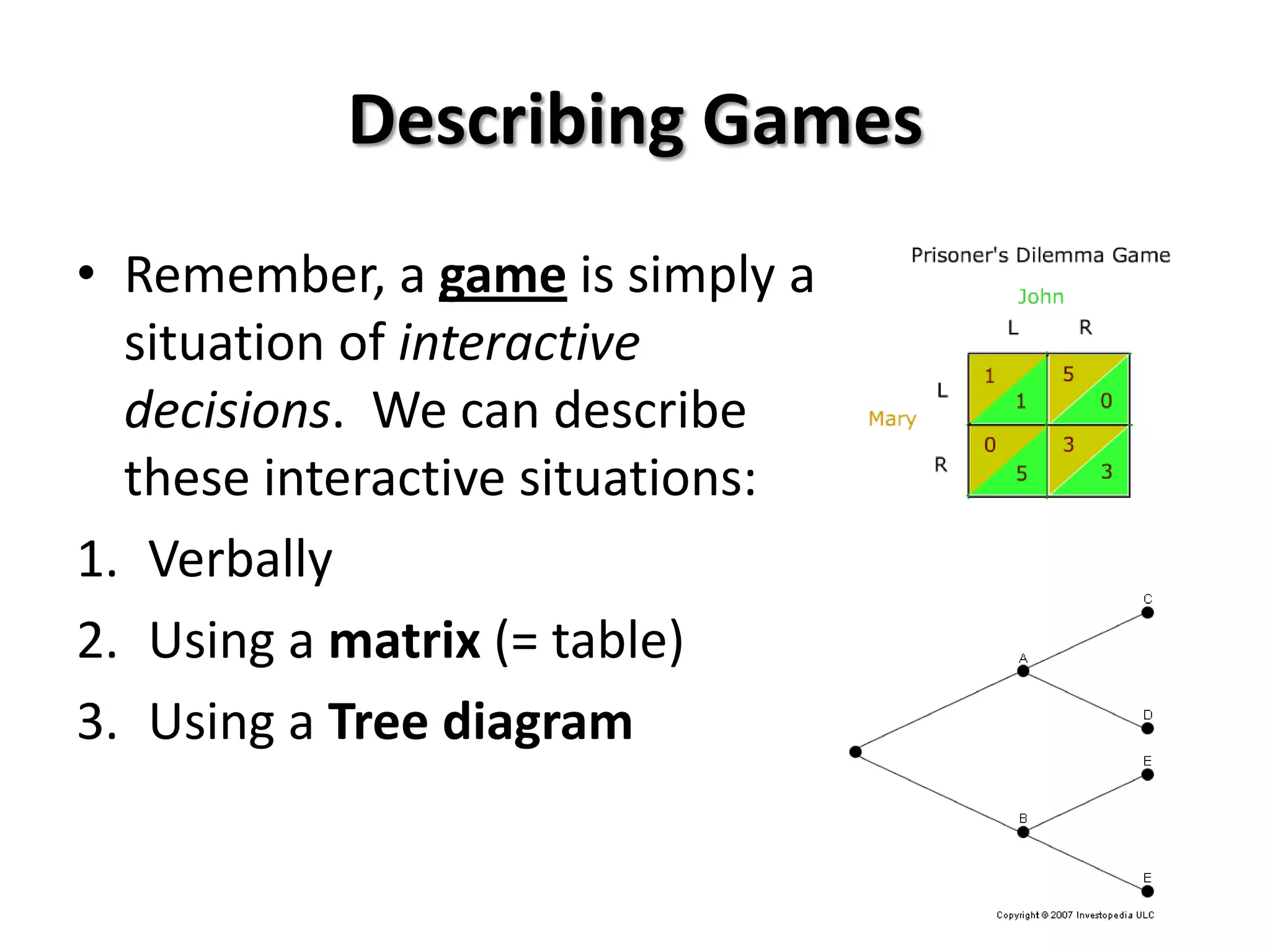
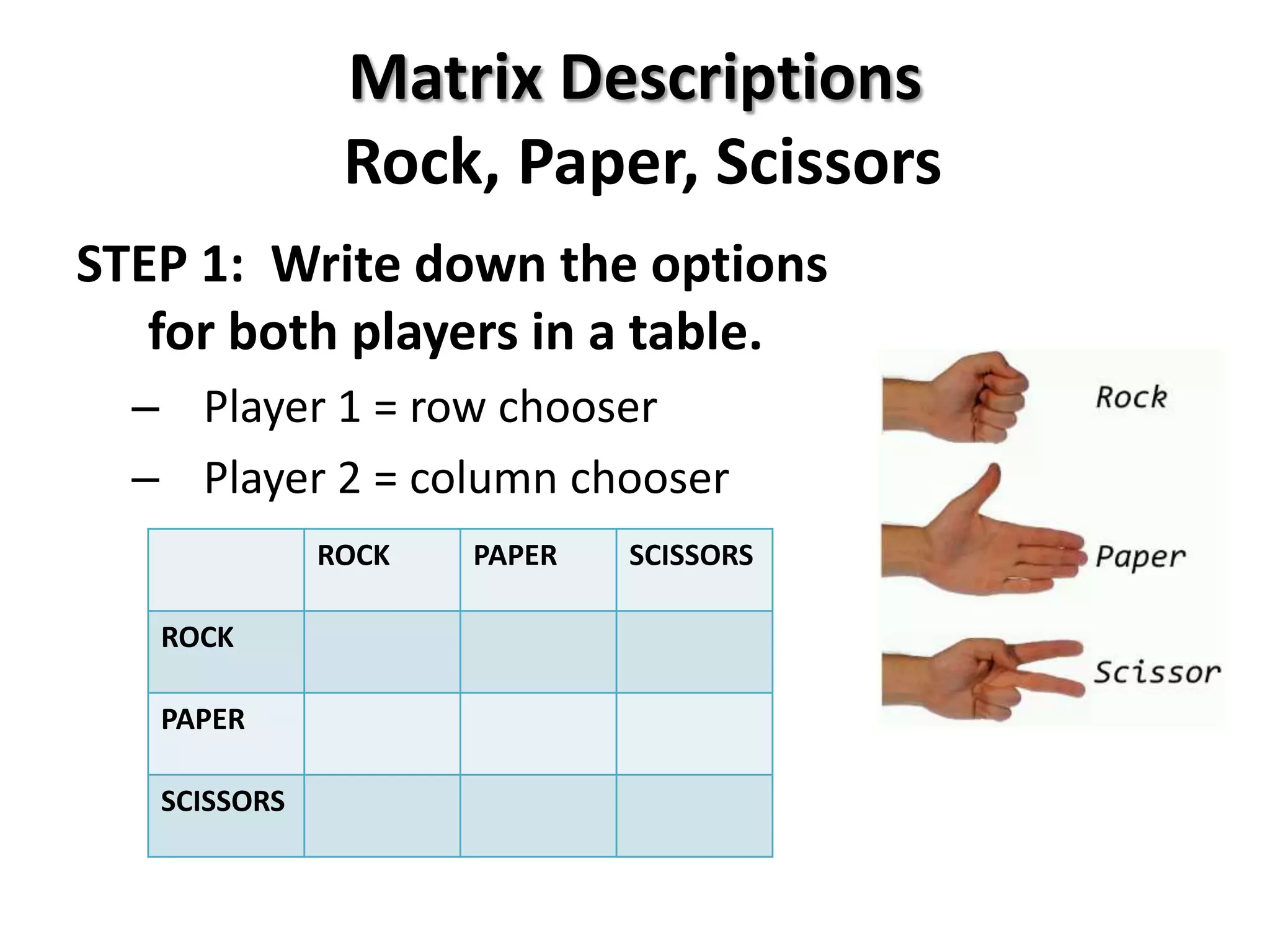
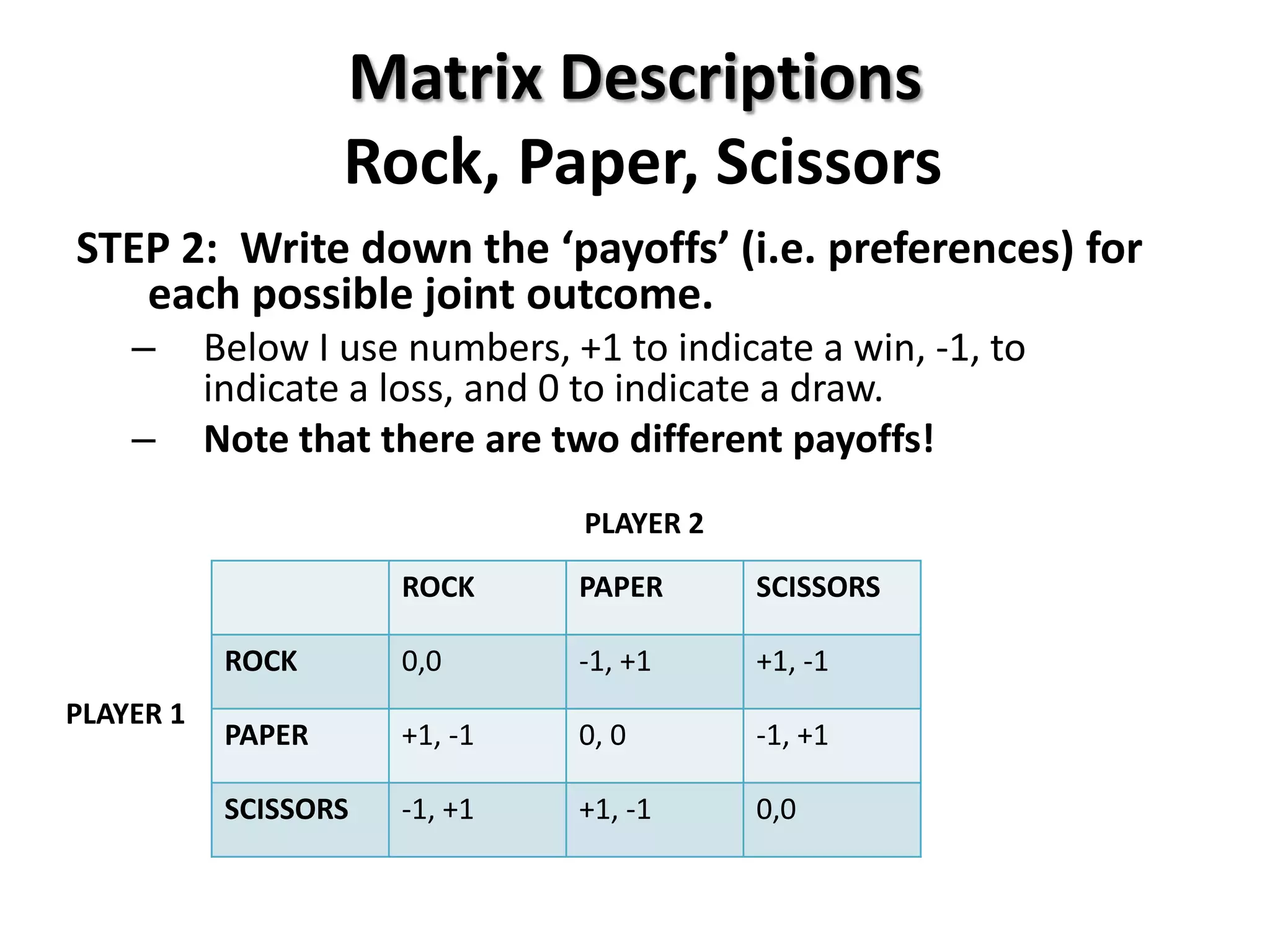
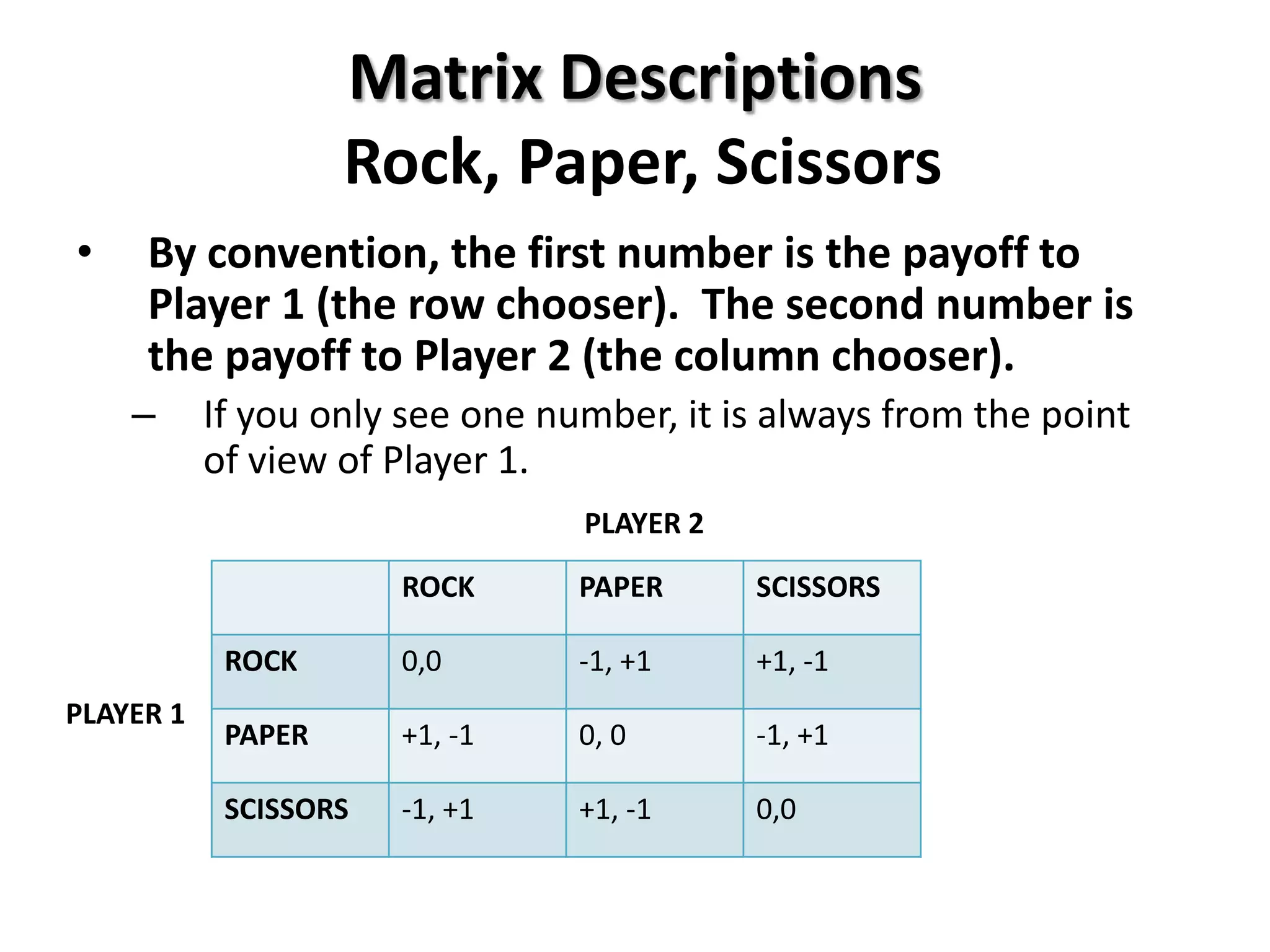
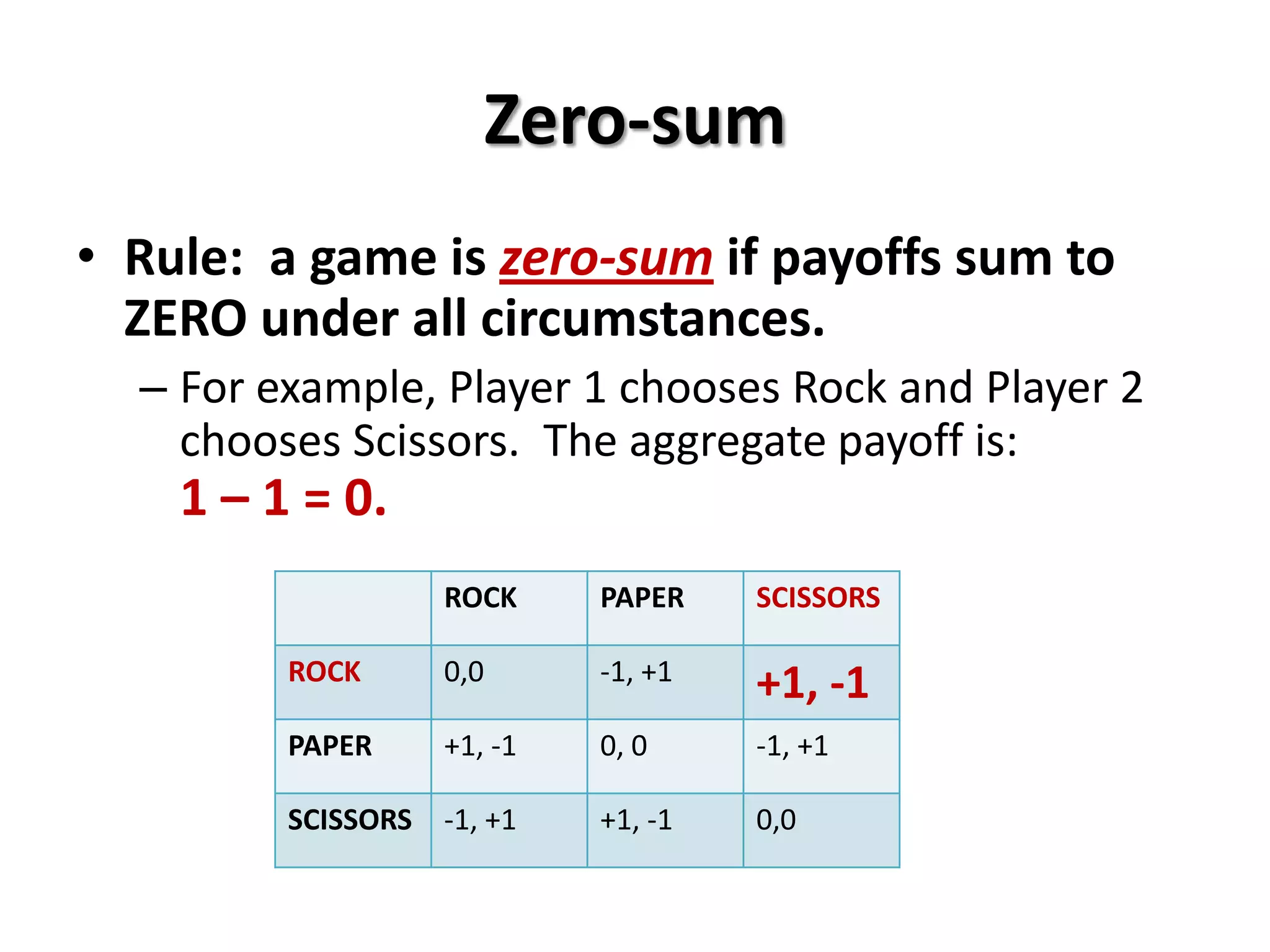
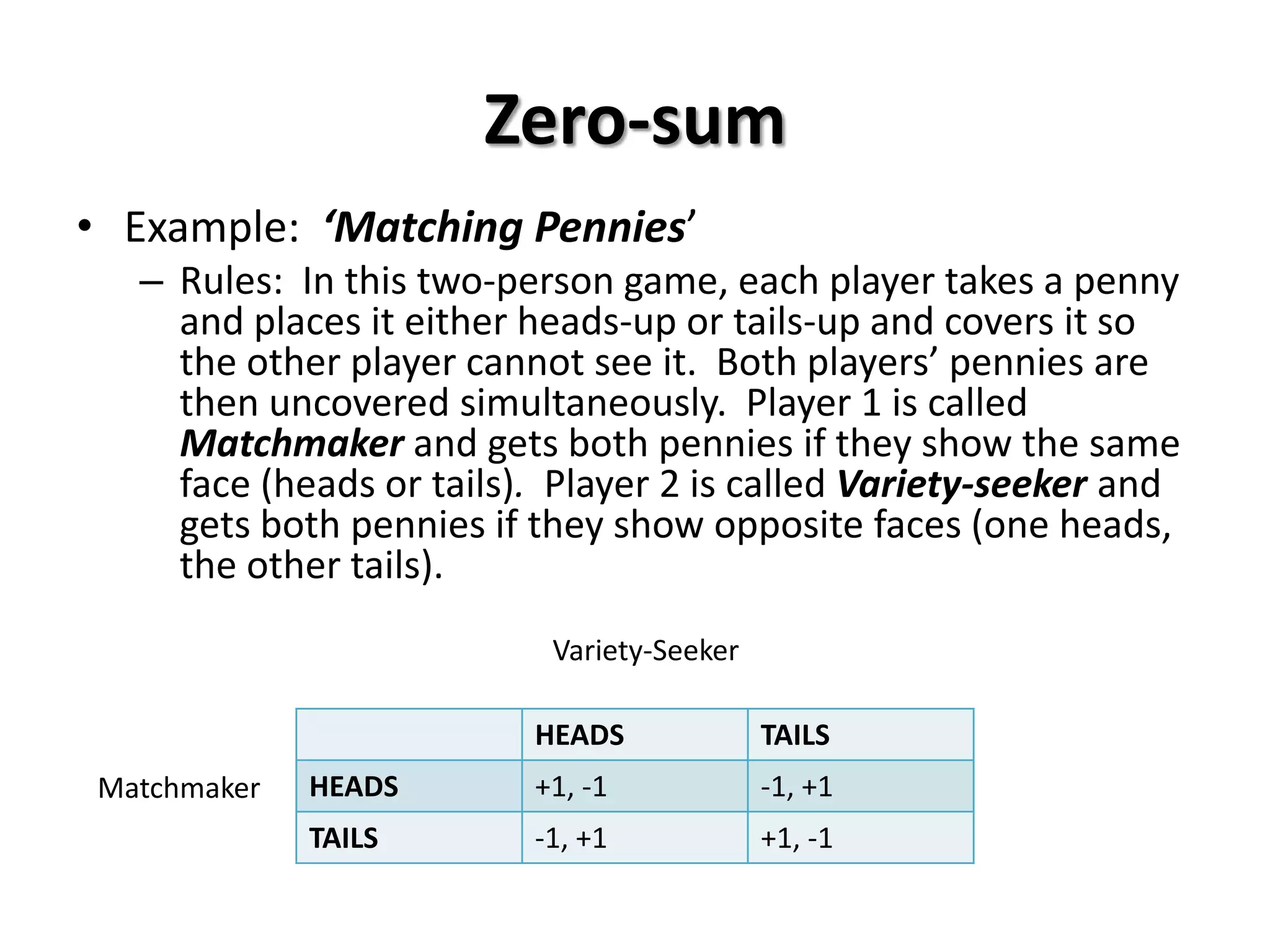
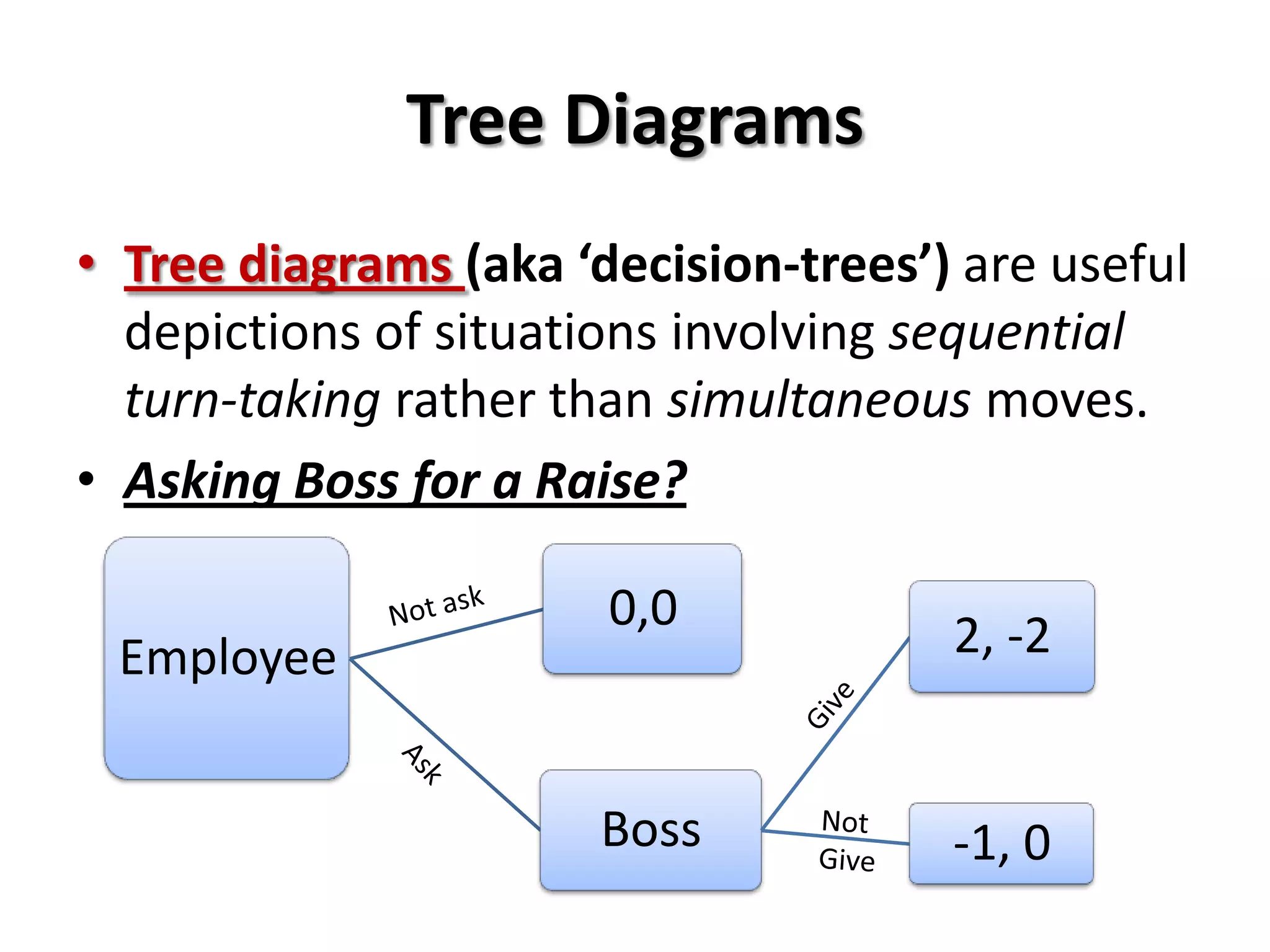
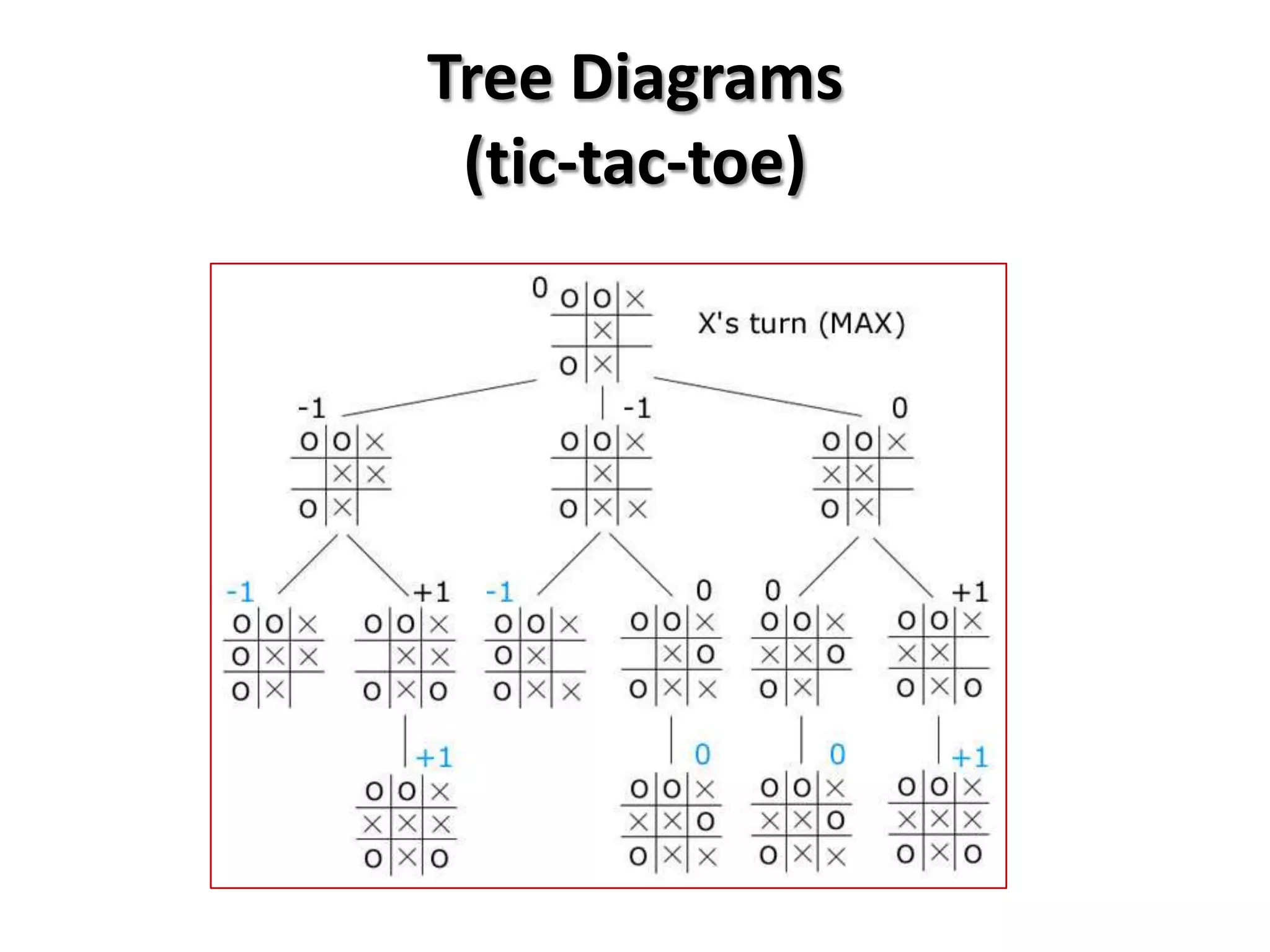
This document provides an introduction to game theory and how to describe games using matrices and tree diagrams. It defines what constitutes a game, including the key elements of players, their options/moves, possible outcomes, and payoffs. Games can be zero-sum, constant-sum, or variable-sum depending on whether the total payoffs equal zero, remain constant, or vary. Matrix tables are used to describe games like Rock-Paper-Scissors and Matching Pennies by listing the options for each player and their payoffs. Tree diagrams depict games involving sequential moves rather than simultaneous choices. The concept of a dominant strategy is also introduced.