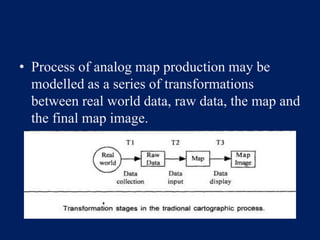
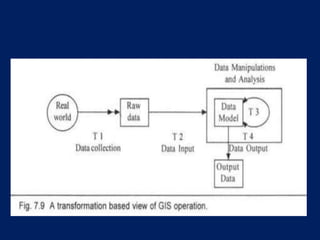
This document outlines the theoretical framework for how data is transformed in a geographic information system (GIS). It discusses four main stages of transformation: (1) data is selected from the real world, (2) input into the GIS, (3) manipulated and stored within the system, and (4) output from the system. Each stage may involve several operations on the data. Understanding how these transformations work forms the theoretical basis for modeling and representing real-world objects and information in a GIS.