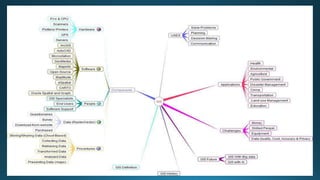
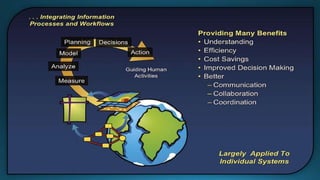
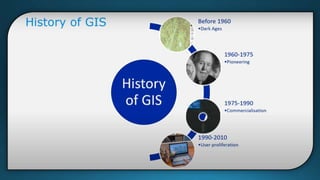
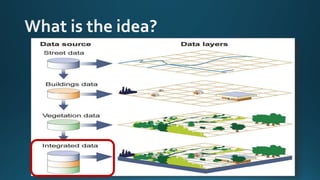
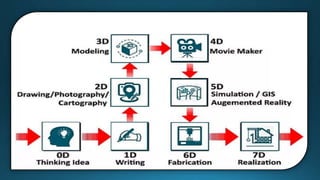
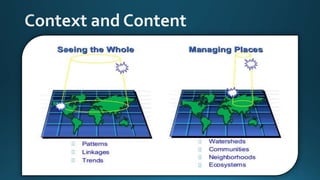
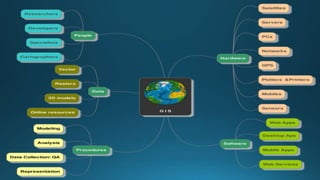
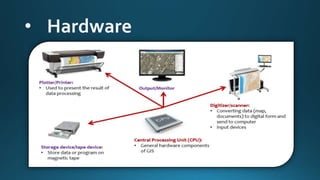
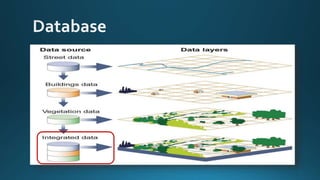
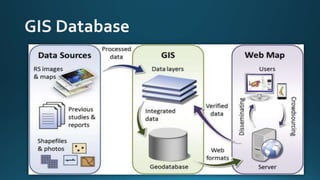
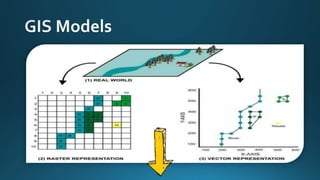
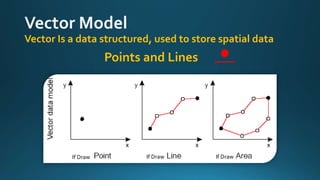
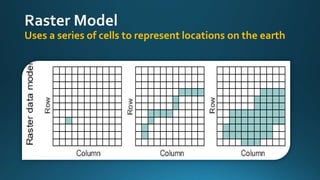
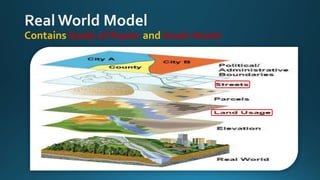
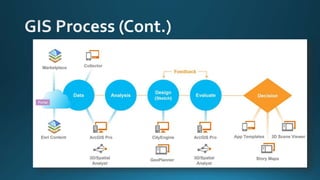
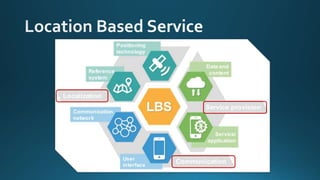
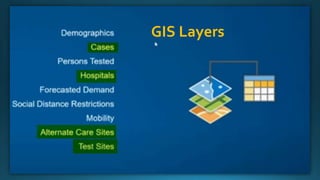
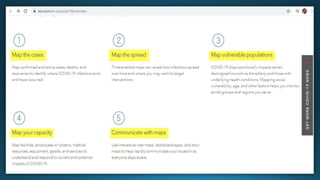
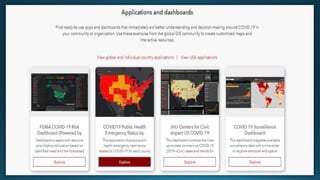
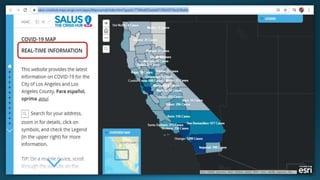
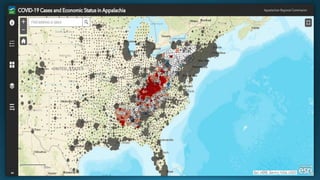
The document provides a comprehensive overview of cartography and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), including their definitions, components, processes, and applications. It highlights the importance of spatial data, data management, and visualization in GIS, as well as various technological tools and challenges associated with its implementation. Case studies involving sectors such as oil and gas, telecommunications, and public health illustrate the practical applications of GIS and emerging technologies like big data and AI.