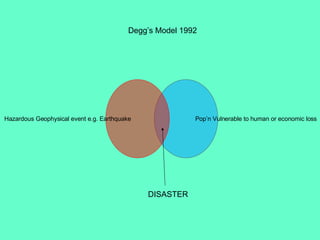
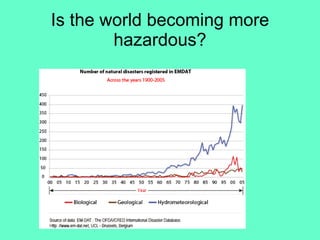
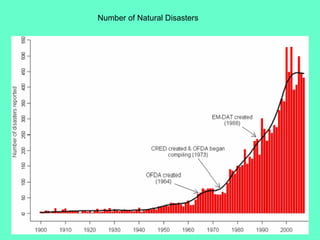
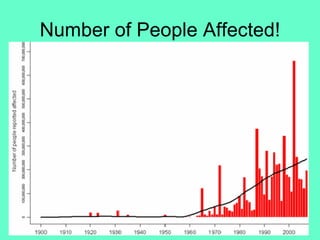
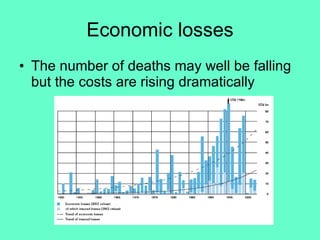
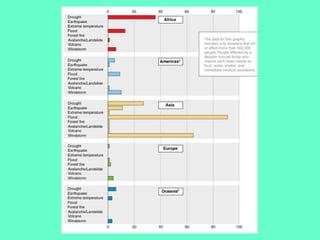
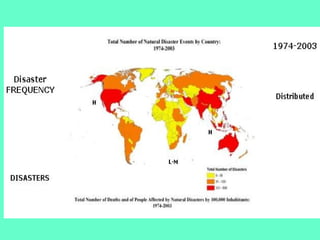
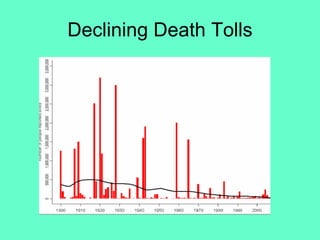
The document discusses natural hazards and disasters. It defines hazards as natural events that involve people, where social and environmental factors can turn an event into a disaster. There are two main classifications of hazards: hydro-meteorological hazards caused by weather patterns like floods and storms, and geophysical hazards caused by earth processes like earthquakes, volcanoes, and landslides. A disaster is defined as a natural event that causes human or economic losses. While the number of deaths from disasters has decreased due to better preparedness, the number of people affected and economic costs have risen due to increasing population in vulnerable areas and climate change impacts.