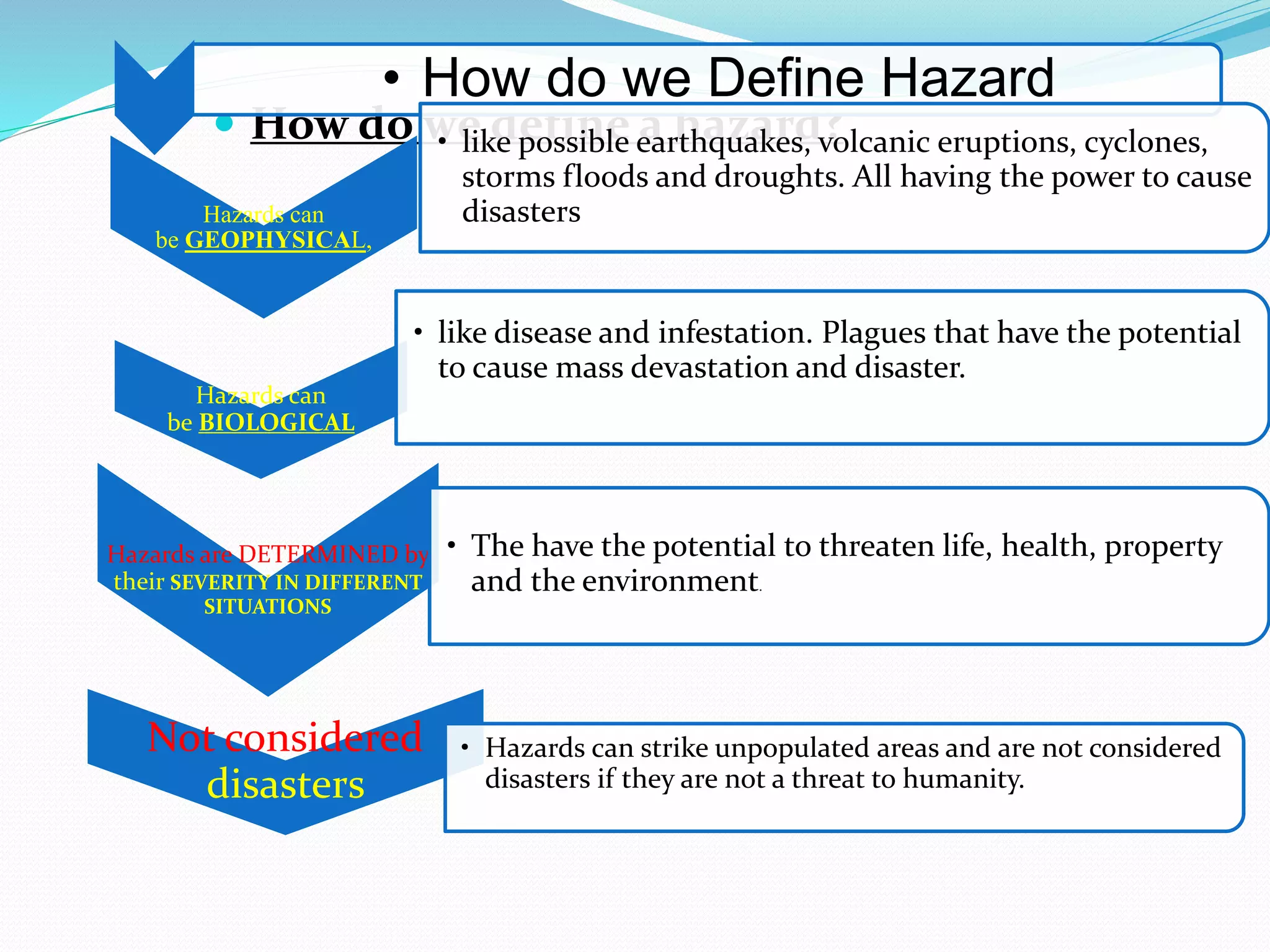
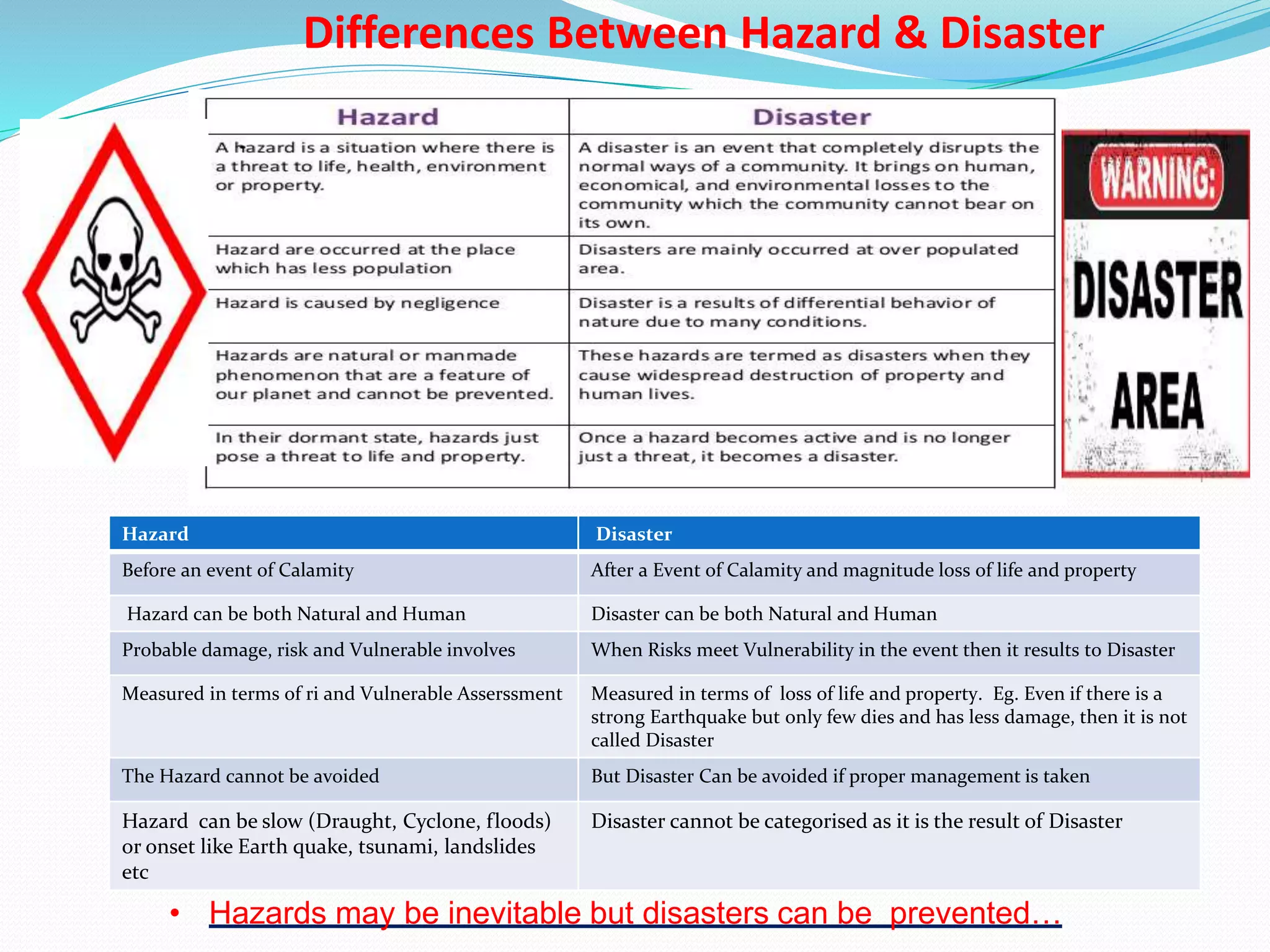
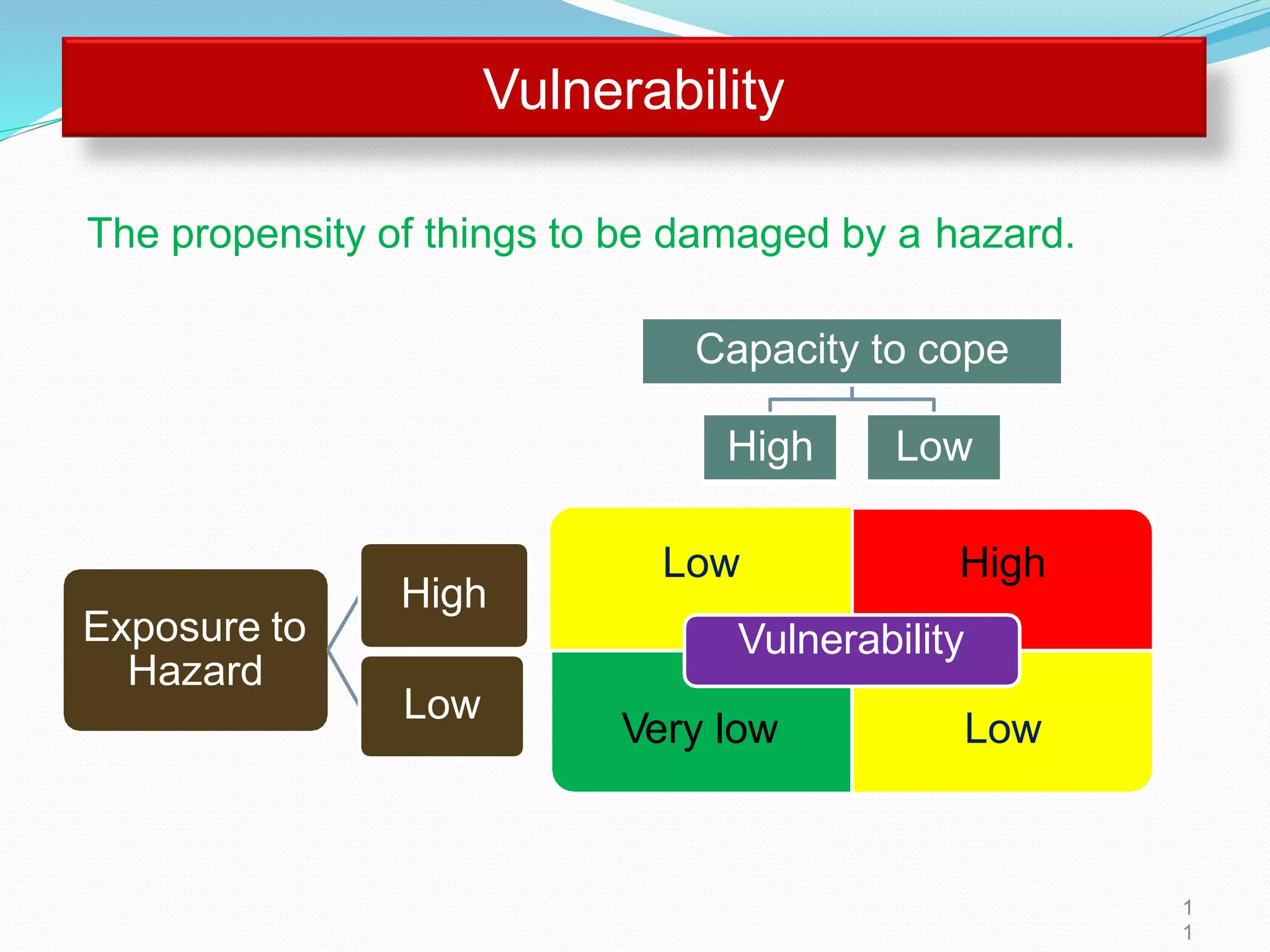
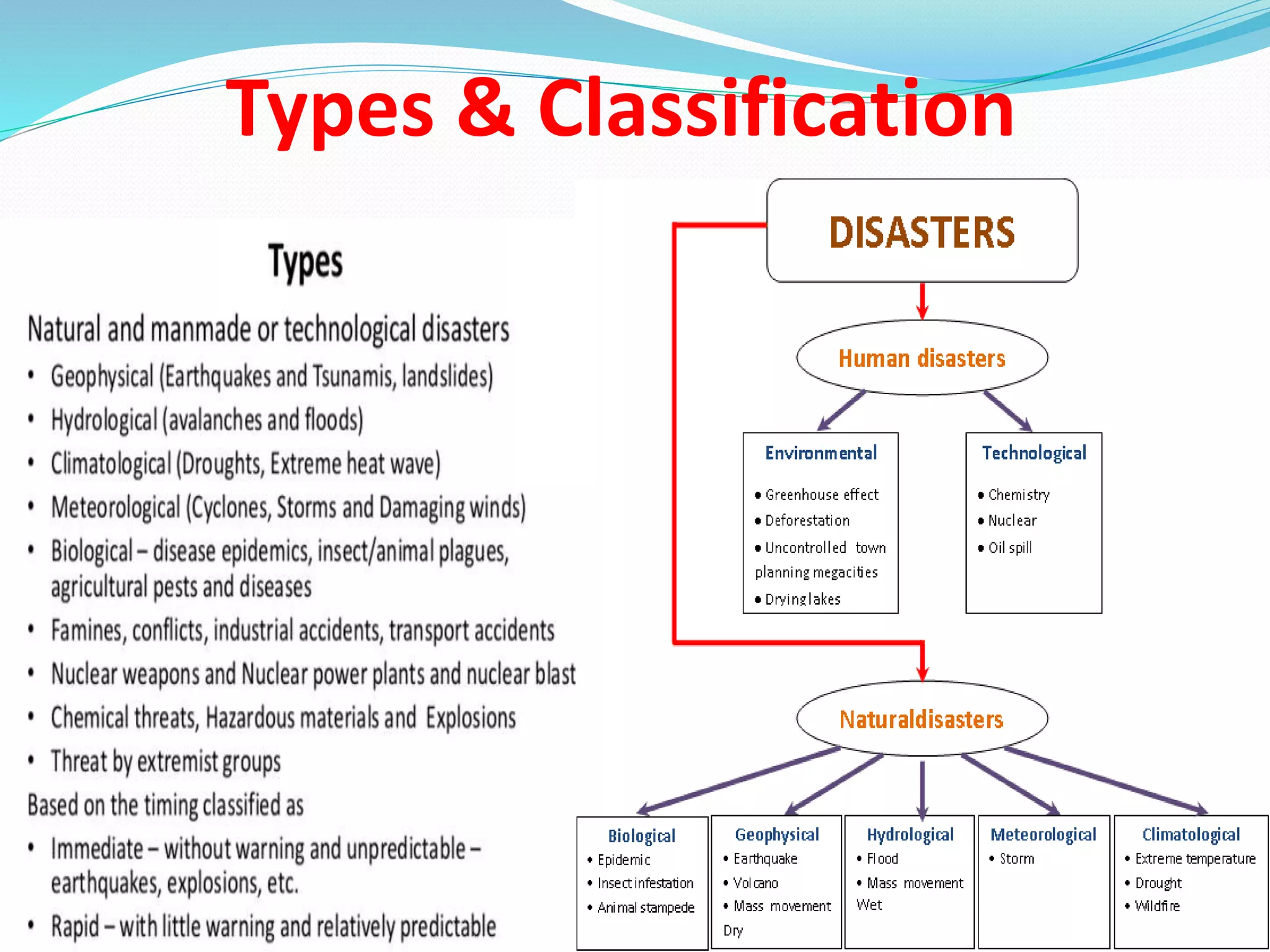
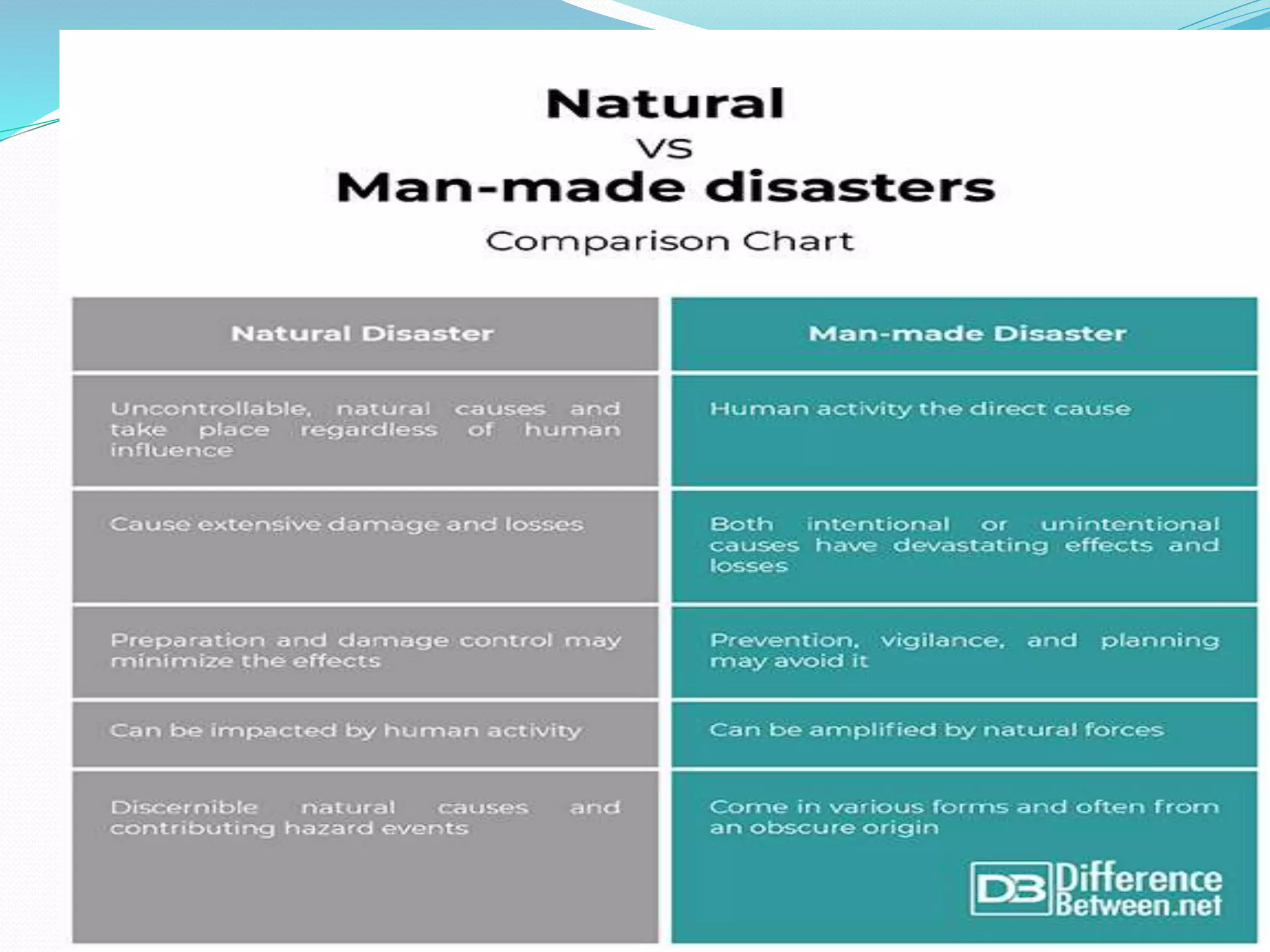
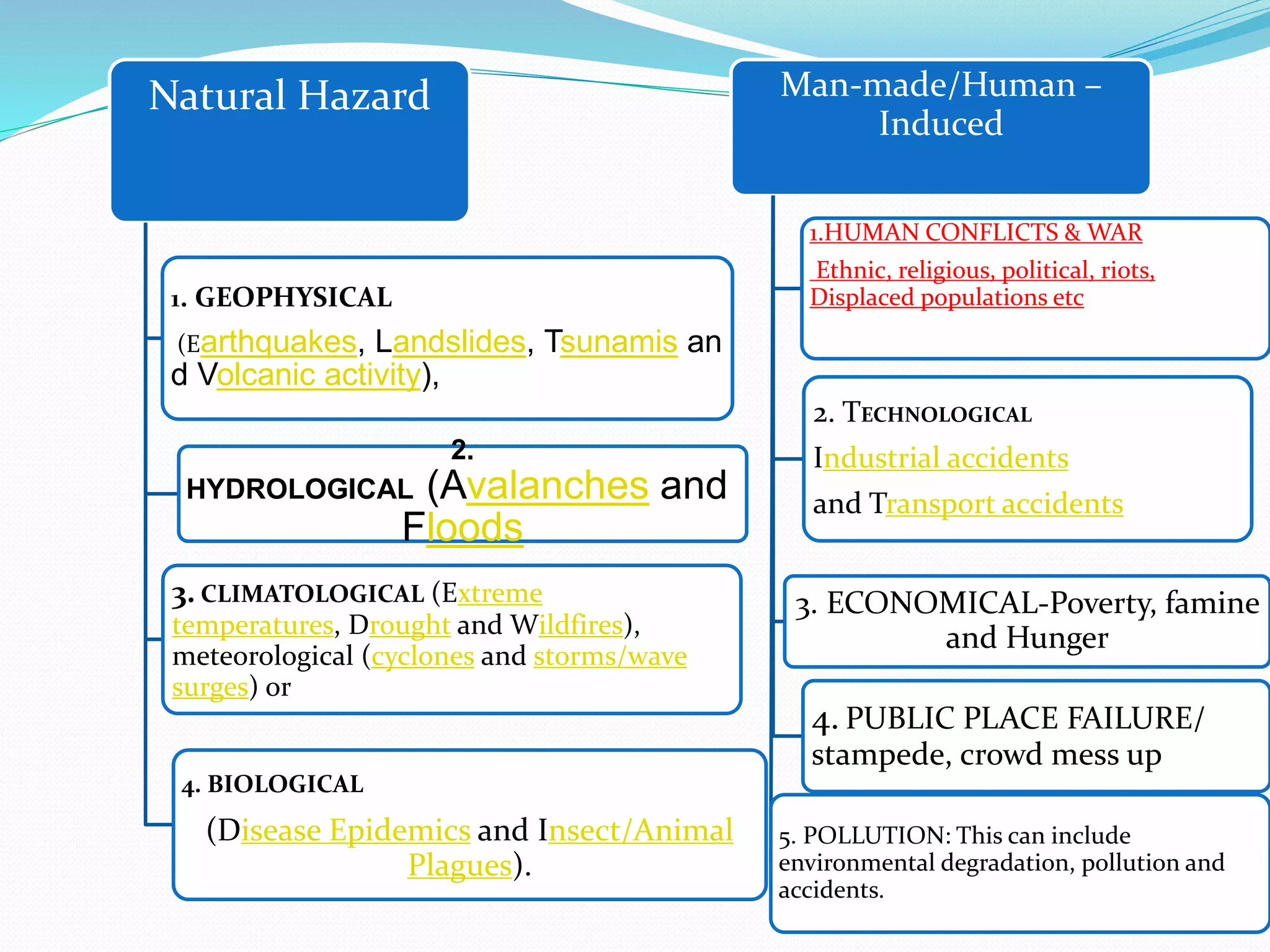
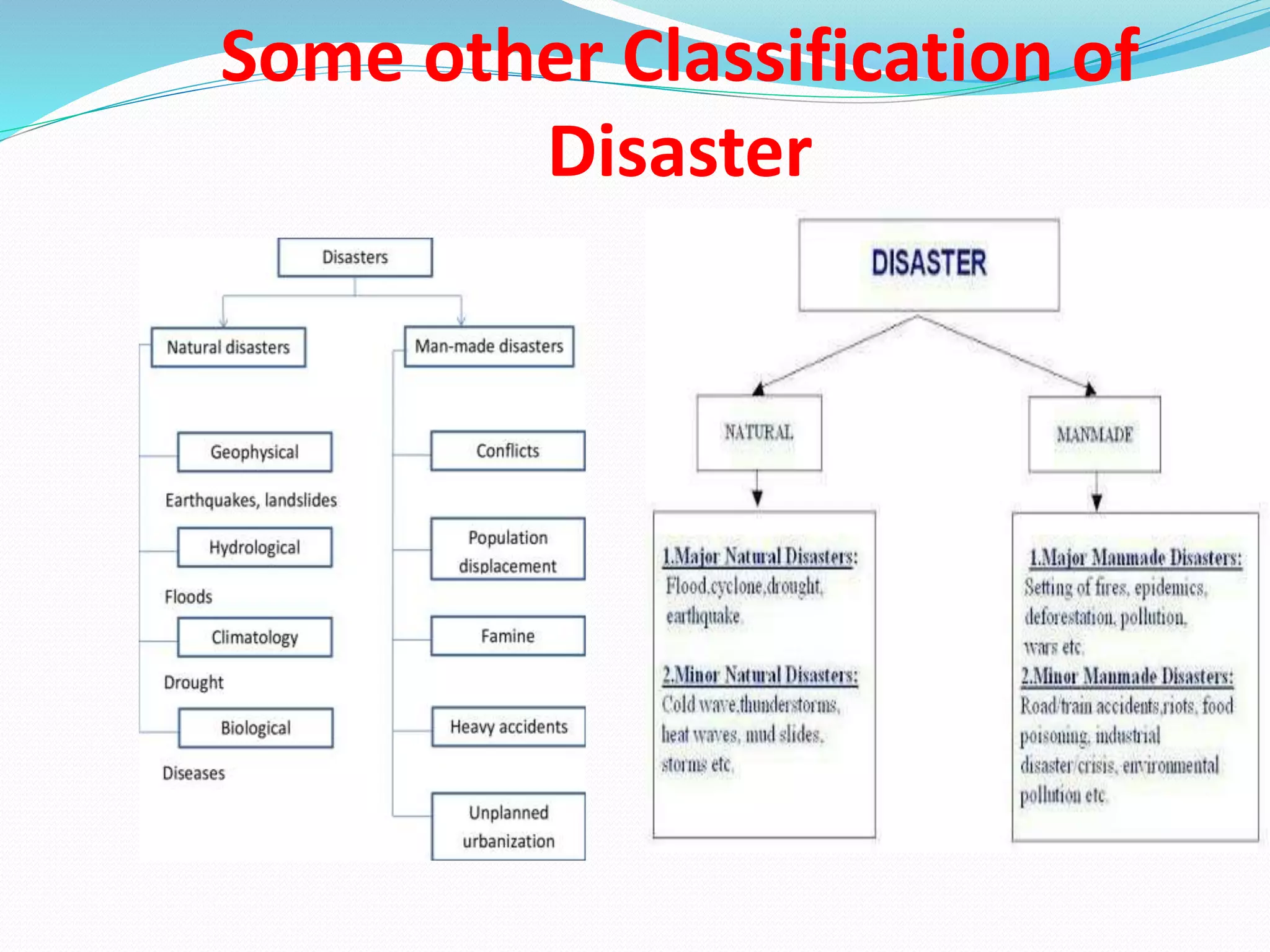
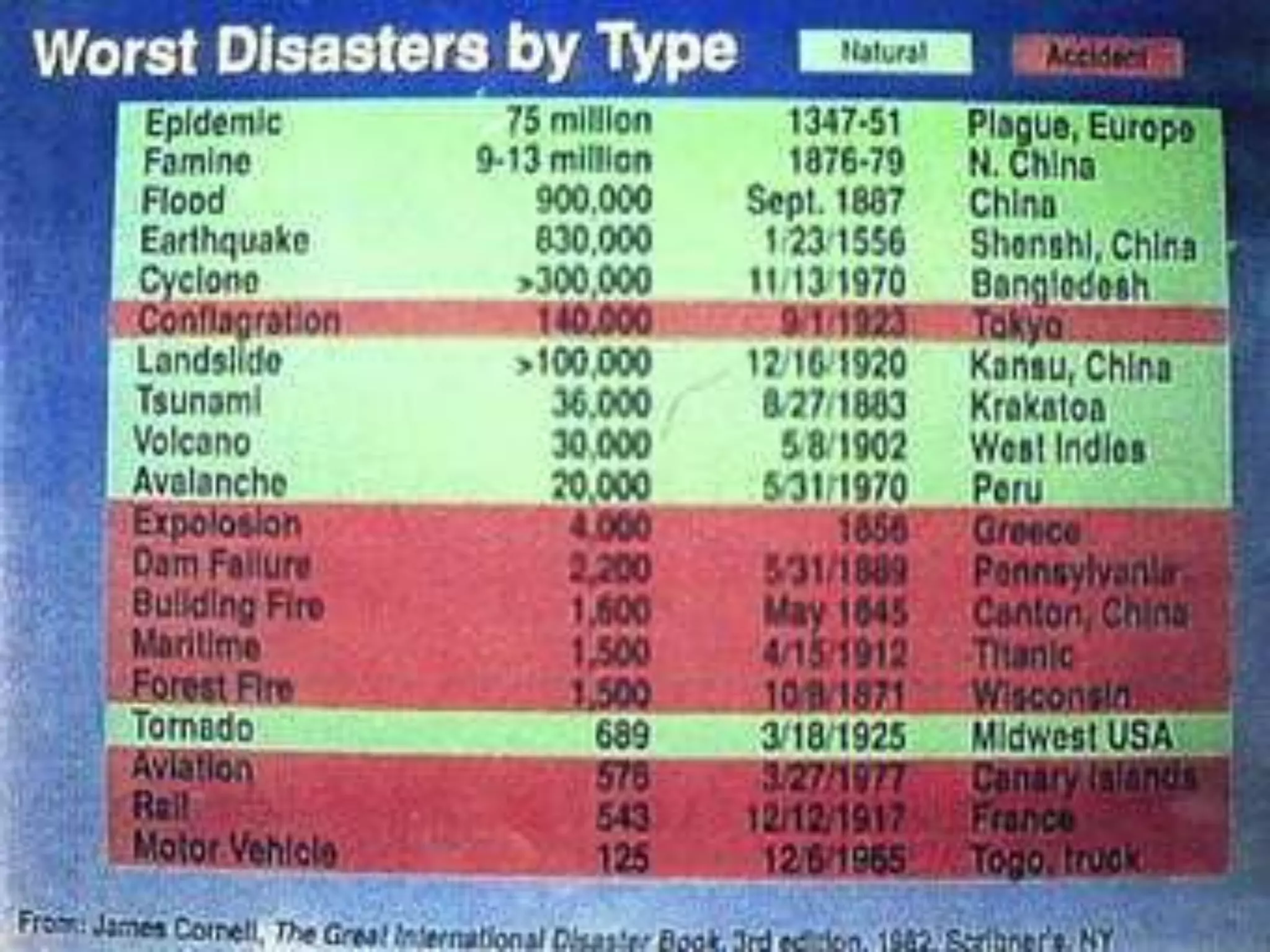
The document presents an overview of disasters, defining them as major hazard events that disrupt communities and require external assistance. It distinguishes between hazards and disasters, outlining types of hazards such as natural, human-induced, and technological incidents, along with factors that contribute to vulnerability and risk. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding these concepts for disaster management and prevention.