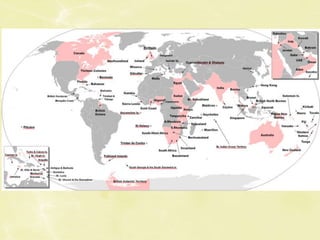
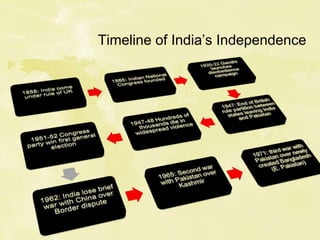
Nationalism has historical roots from the 19th century when industrialization and increased wealth led nations in Europe like Germany and Italy to form based on shared identity. During this time, some nations also built global empires fueled by nationalism. After World War 2, independence movements grew as colonial elites were educated and embraced ideals of self-determination, threatening imperial powers despite resistance. The dominance of the USA and USSR after the war also contributed to independence for colonies that each superpower saw as oppressive or could influence. Decolonization accelerated in the 1960s but resulted in conflicts for some new post-colonial nations in West Africa due to issues like ethnic divisions, wealth disparities, and control of resources.