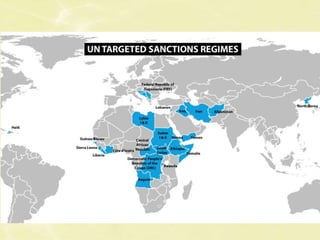
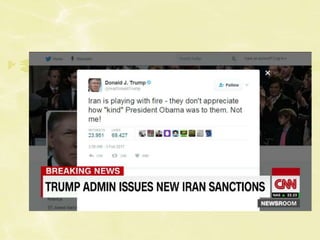
This document discusses global organizations like the United Nations and how they address international issues. It provides details on the UN's evolution over time to take on roles like maintaining peace and security, promoting human rights, and providing humanitarian aid. The UN Security Council can impose sanctions on countries to respond to threats, and examples are given of economic sanctions placed on Iran for its nuclear program and how those sanctions impacted the country. The document also debates whether sanctions are an effective approach for enacting change.