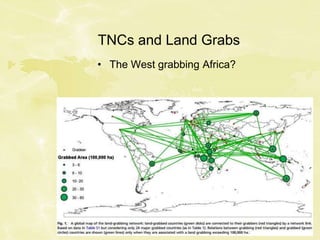
This document discusses national identity and some of the complex issues surrounding it. It defines nationalism and explains how countries often try to reduce strong nationalism by promoting values of democracy, freedom and international cooperation. However, nationalism remains a powerful force that is reinforced through education, sports, politics and national symbols. It also addresses how globalization, migration, terrorism and multinational corporations challenge traditional notions of national identity and ownership.