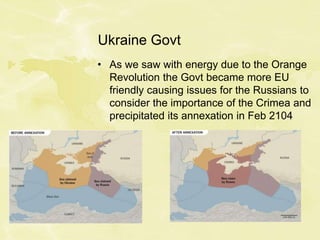
Here is a possible 20 mark evaluation of the effects that contested borders can have on some nations:
Contested borders can have significant political, economic and social effects on nations. Politically, contested borders often lead to instability and tensions as different groups within countries dispute territorial claims. This can undermine the authority and legitimacy of governments as they struggle to unite divided populations. Competing territorial ambitions from neighbouring states can also threaten national sovereignty and security, as seen in the ongoing disputes over Crimea and eastern Ukraine.
Economically, contested borders tend to discourage long term investment and planning due to ongoing uncertainty. Trade and economic cooperation may be limited by political tensions over borders. Infrastructure and transport links are often disrupted if borders change hands through conflict. This instability de