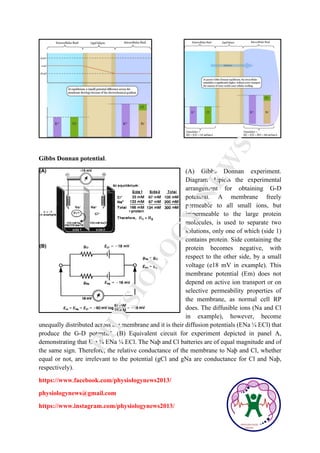
The Gibbs-Donnan effect describes the unequal distribution of permeant ions across a semipermeable membrane due to the presence of impermeant ions, leading to a transmembrane potential difference. At equilibrium, solutions on either side of the membrane remain electrically neutral, and the concentrations of diffusible ions are static. This process is passive, does not involve active transport, and produces a resting membrane potential displayed in the Gibbs-Donnan experiment using electrical potential measurements.