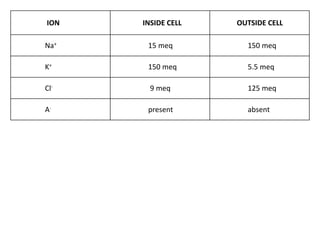
This document discusses the Nernst equation and its role in determining the membrane potential of cells. It introduces concepts like the resting membrane potential, selective permeability of cell membranes to different ions, and the Gibbs-Donnan equilibrium. It then explains the Nernst equation, which calculates the equilibrium potential for each ion based on its concentration gradient across the cell membrane. Finally, it discusses the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation, which integrates the effects of multiple ions, and the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining ion concentration gradients.








![GOLDMANN-HODGKIN-KATZ (GHK) EQUATIONThe Nernst equation helps in calculating the equilibrium potential for each ion individually.However, the magnitude of membrane potential at any given time depends on distribution and permeability of Na+, K+ and Cl- ions.The integrated role of different ions in the generation of membrane potential can be described accurately by the GHK equation.RT ln PK[K+]in + PNa[Na+]in +PCl[Cl-]out F PK[K+]out+ PNa[Na+]out+PCl[Cl-]in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nernstequation-100411060315-phpapp01/85/Nernst-Equation-10-320.jpg)

