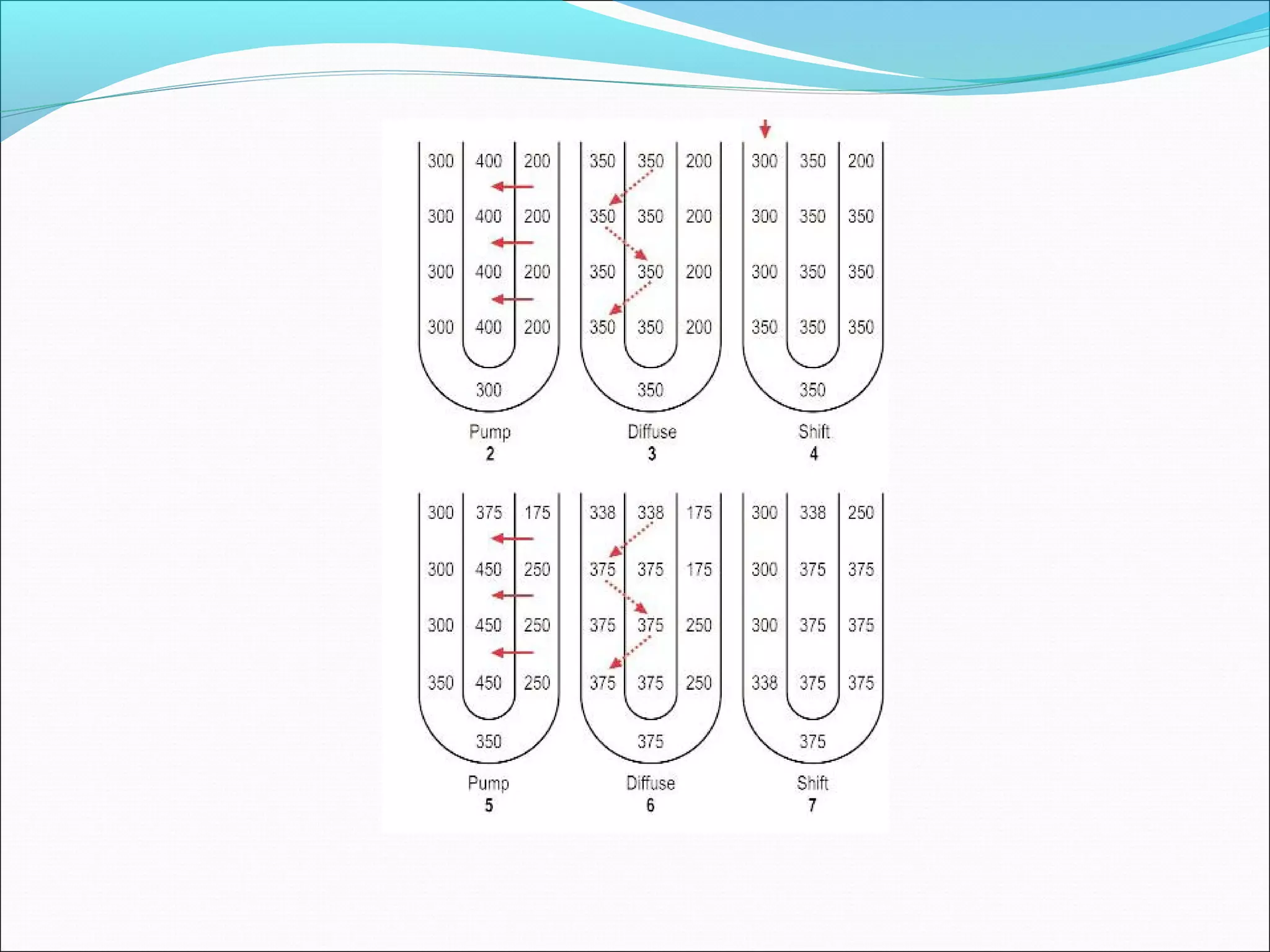
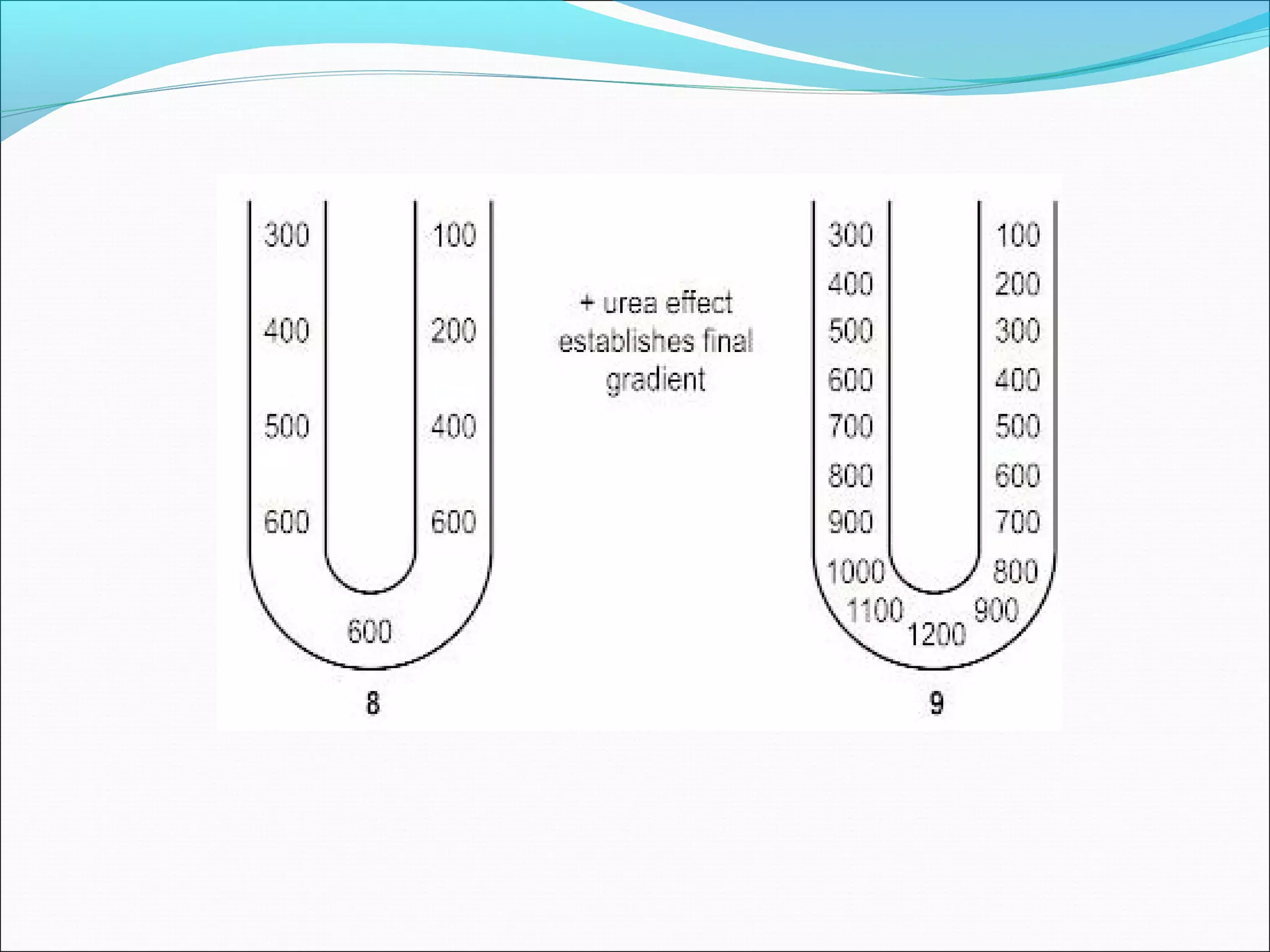
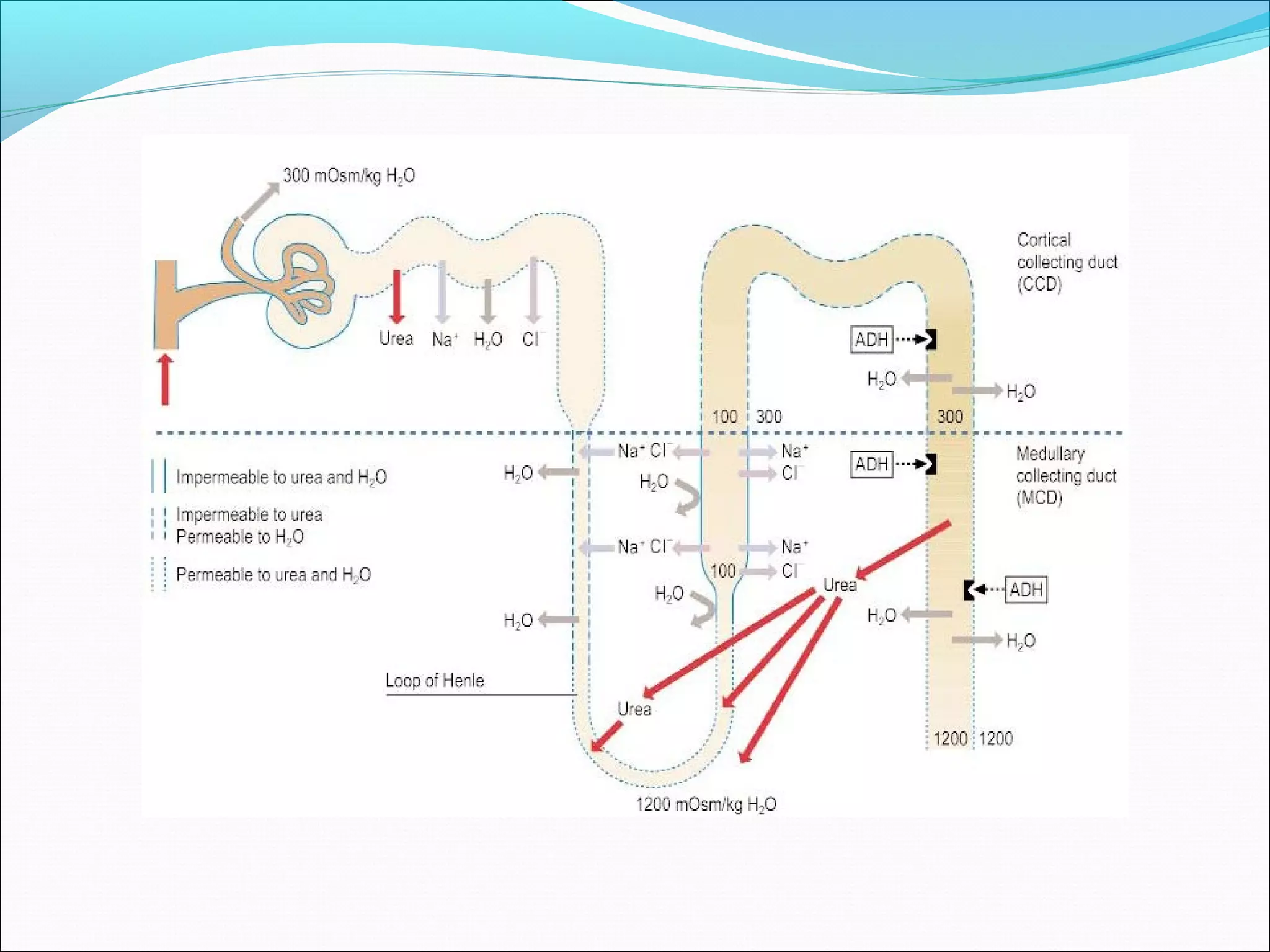
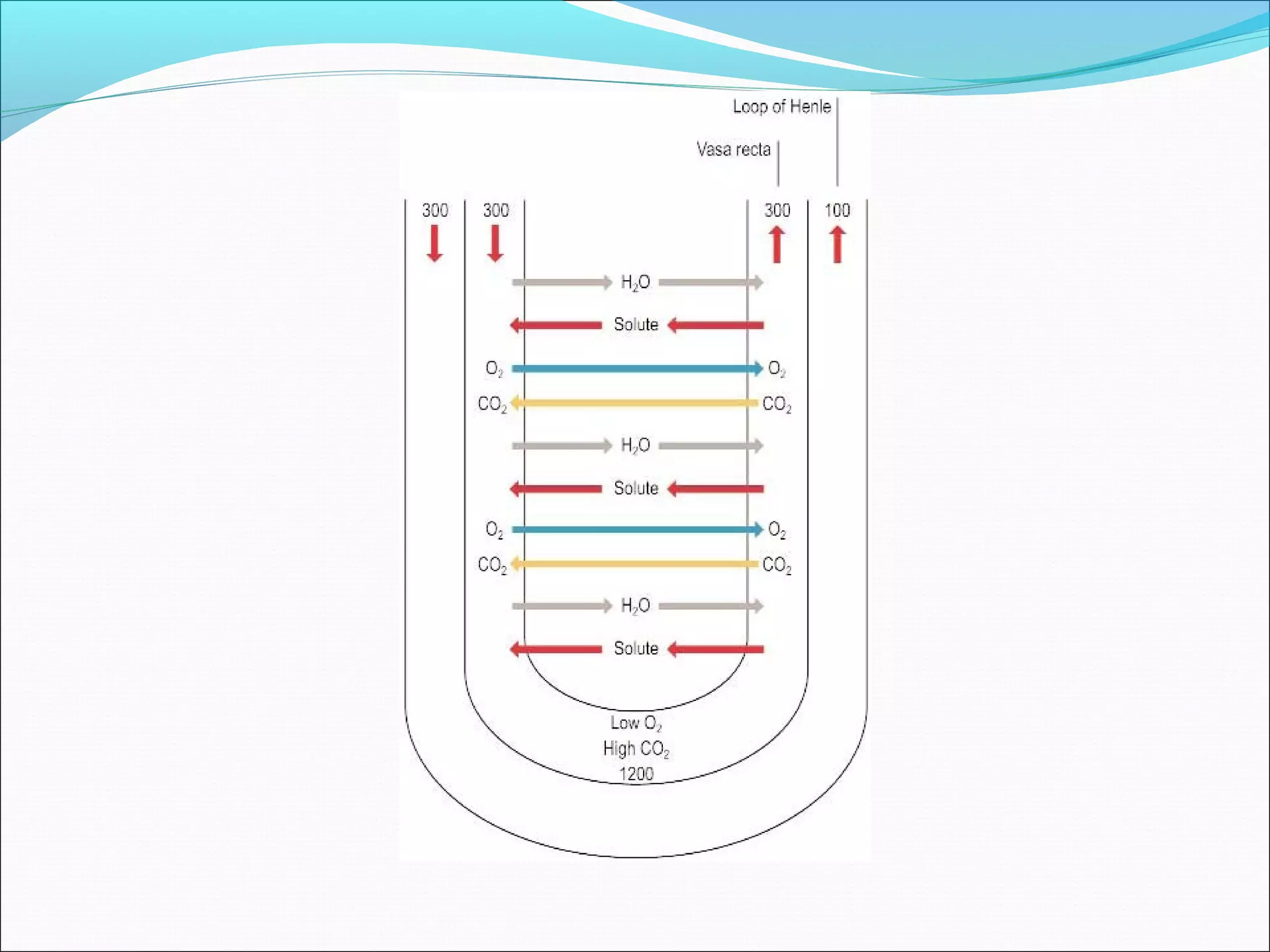
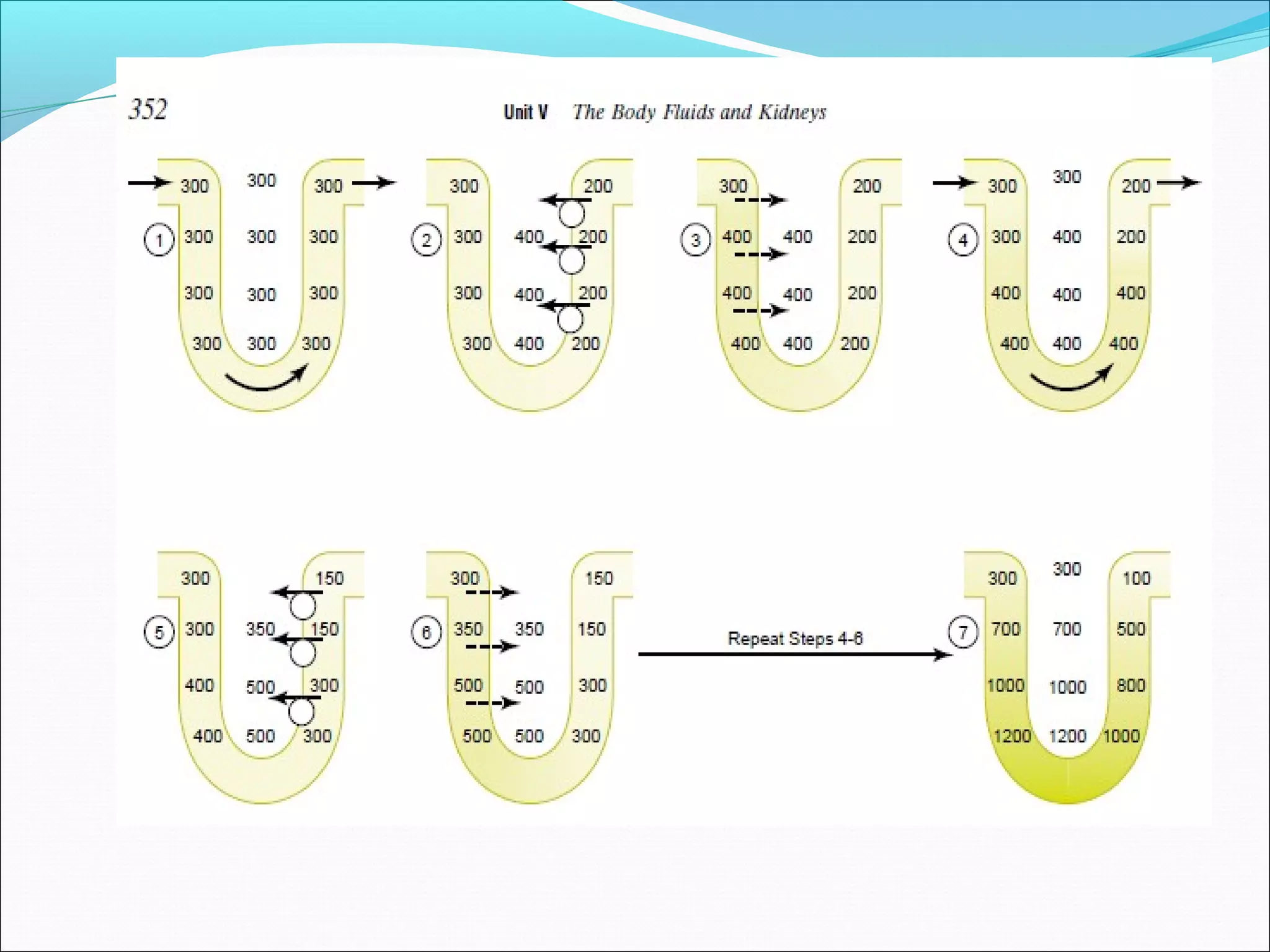
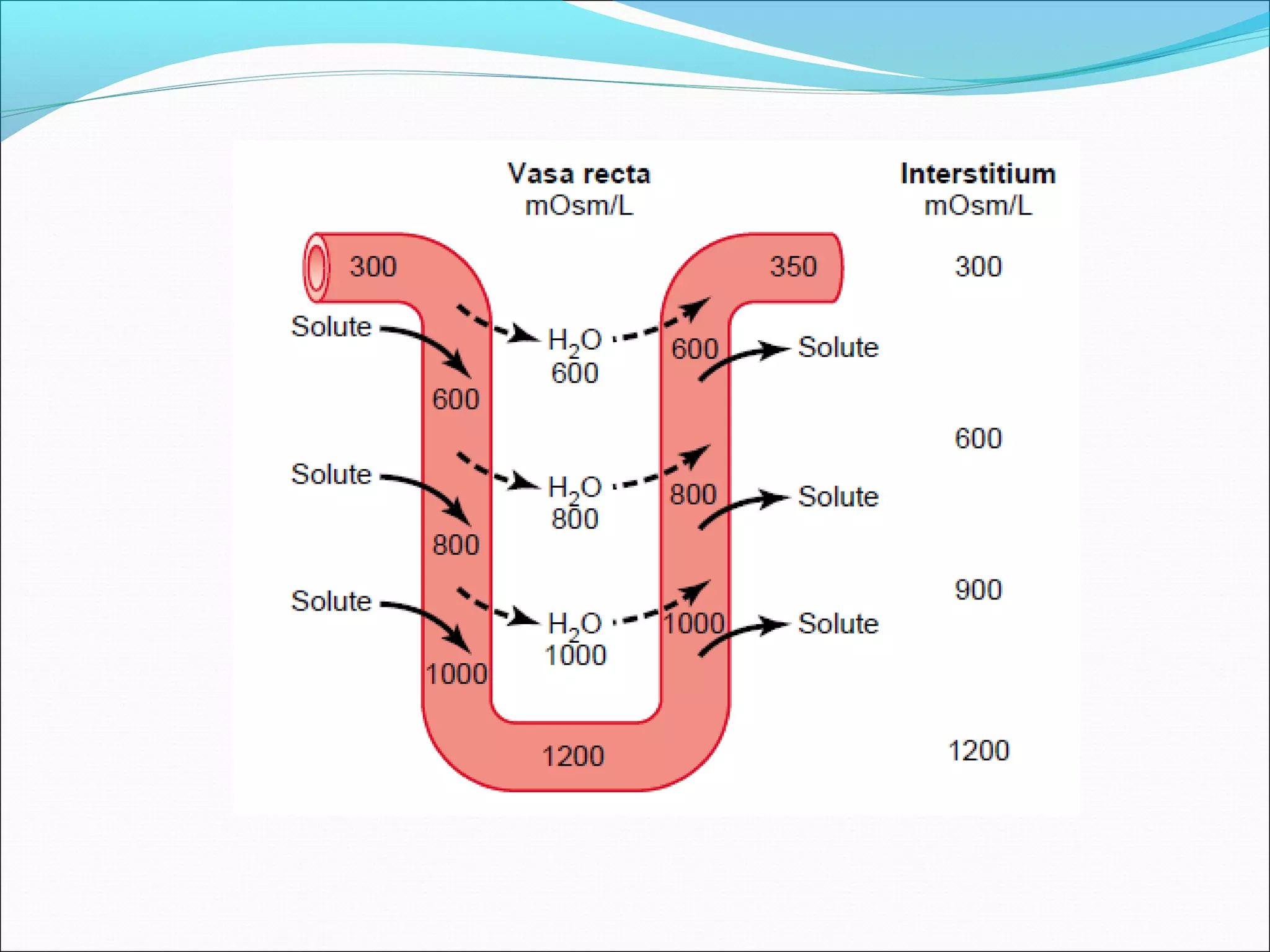
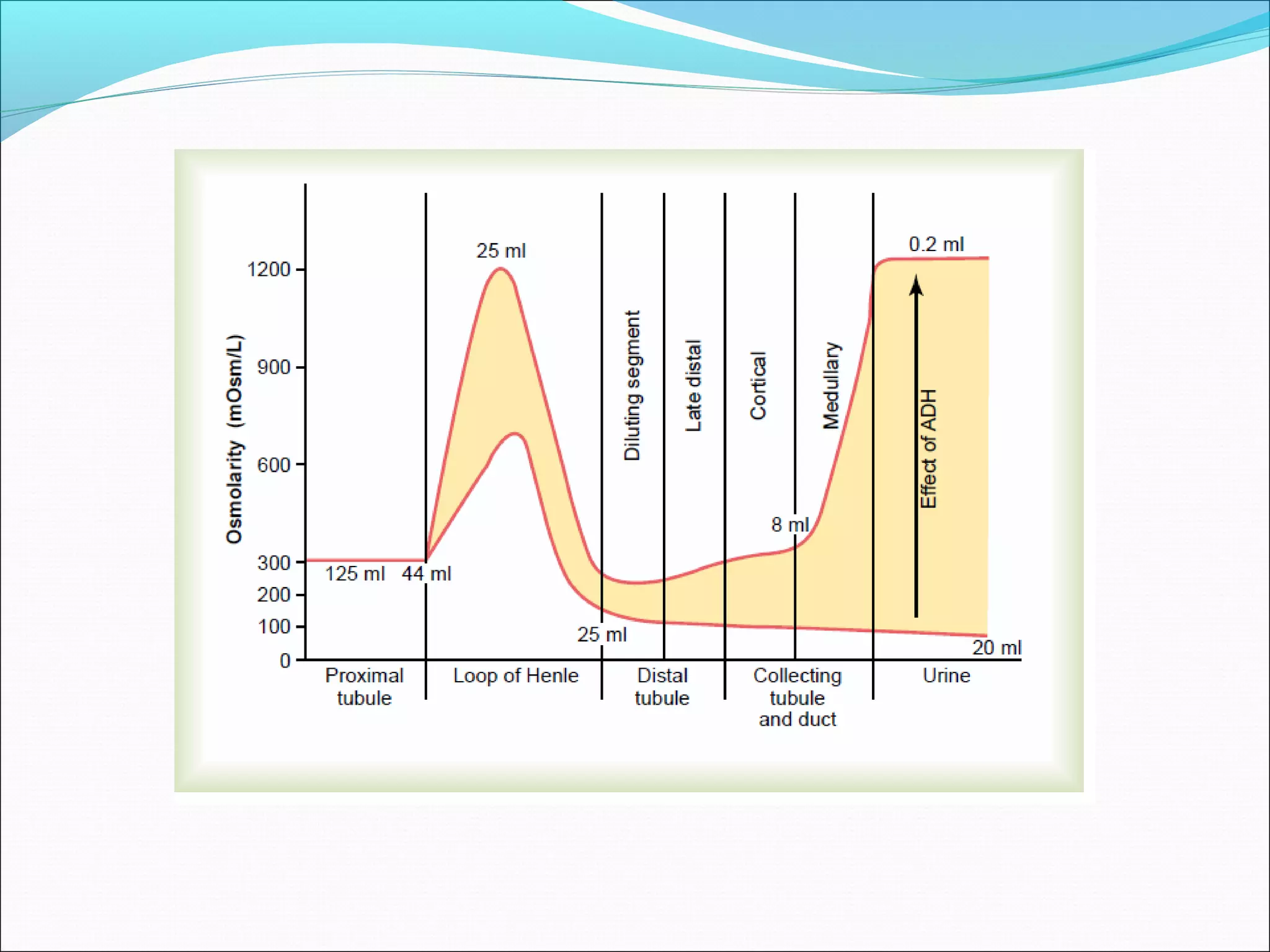
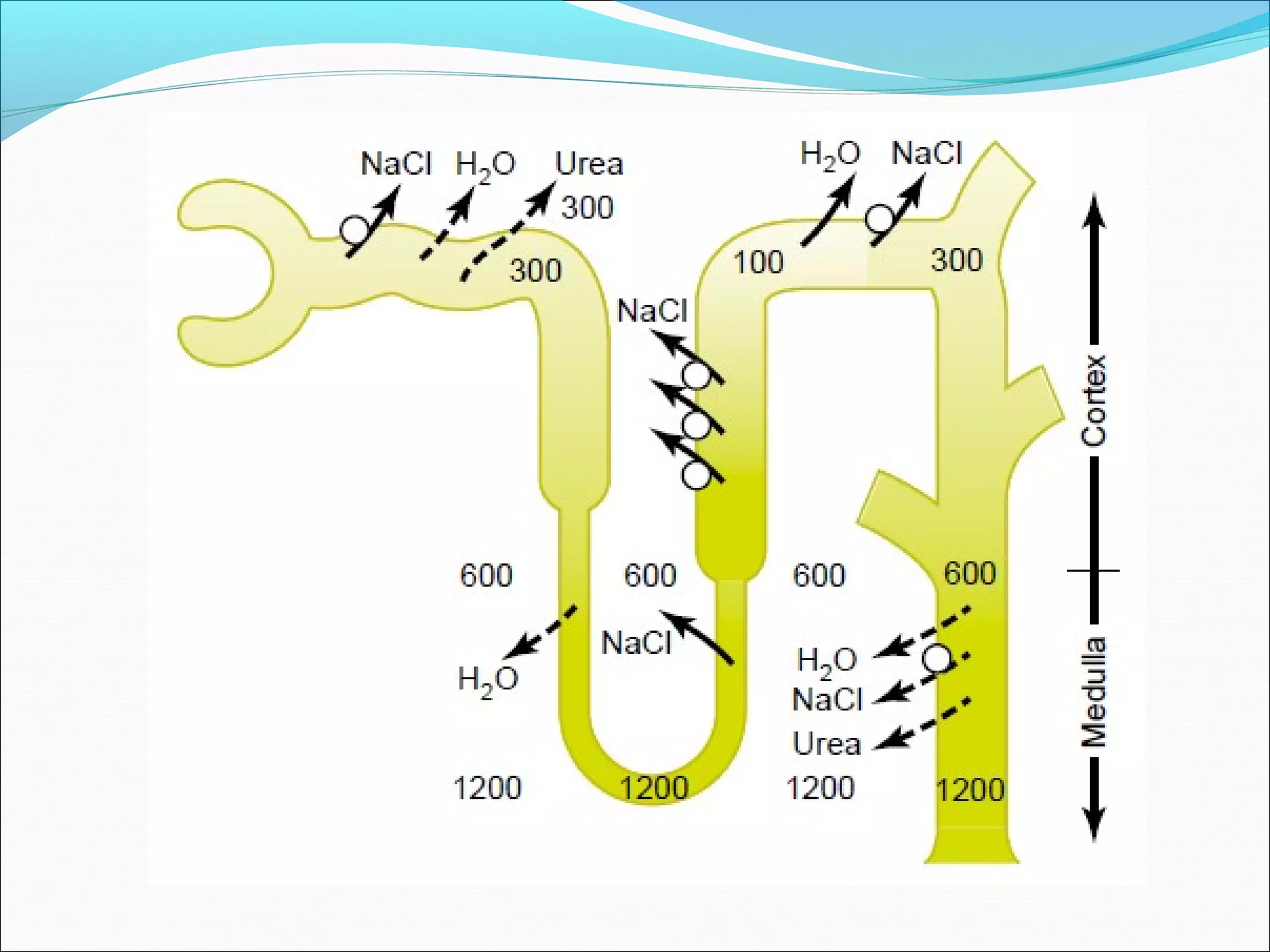
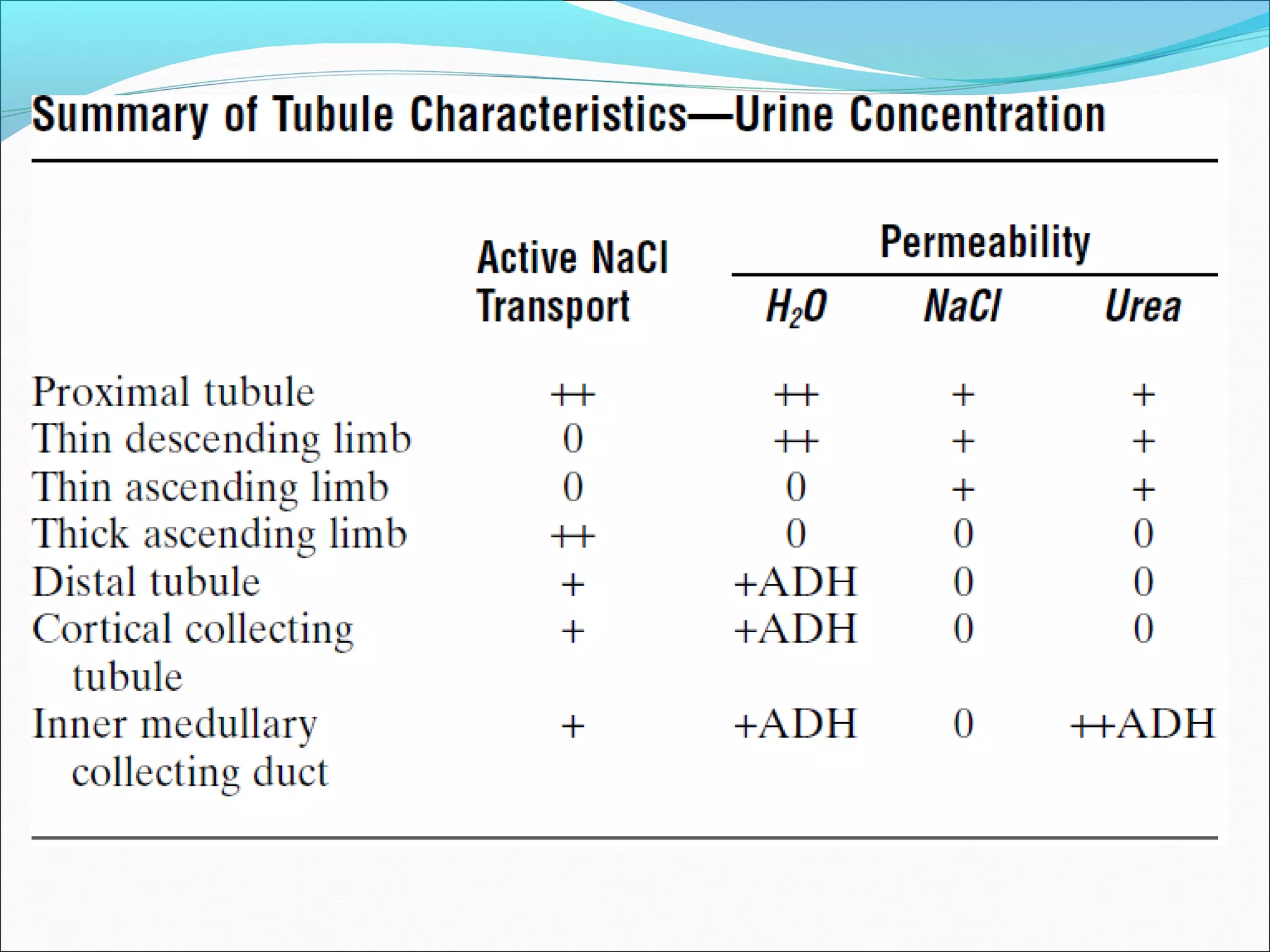
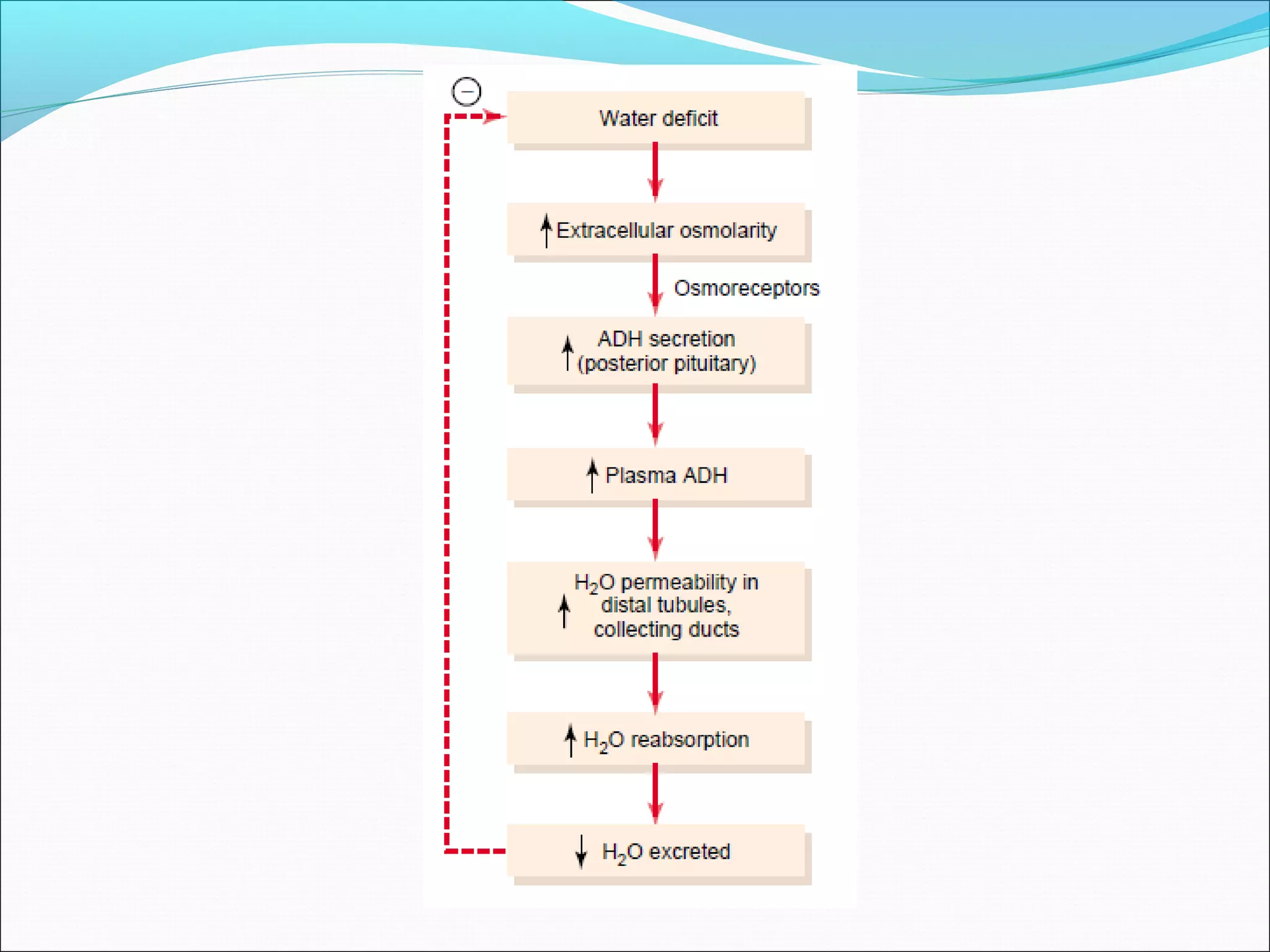
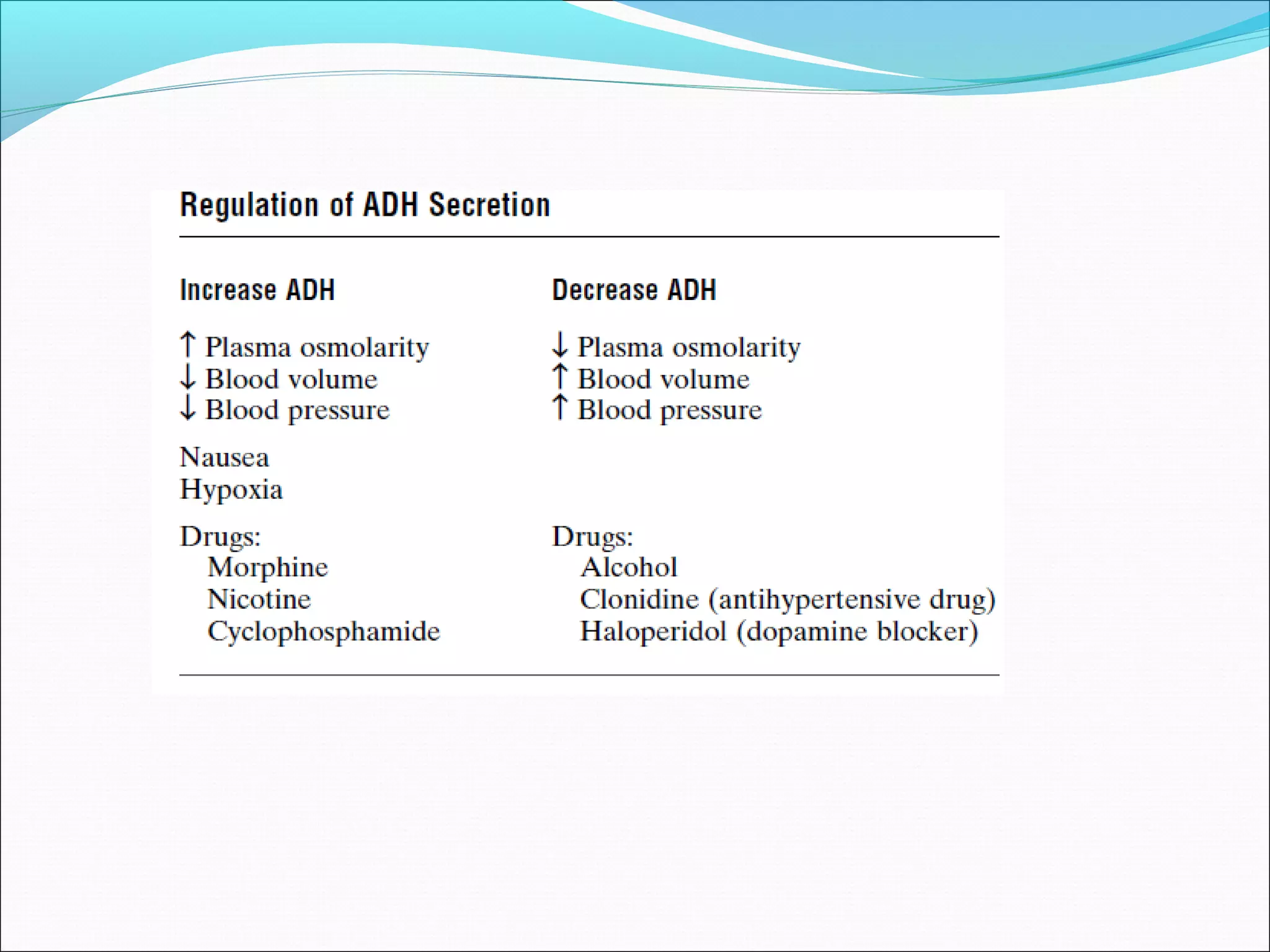
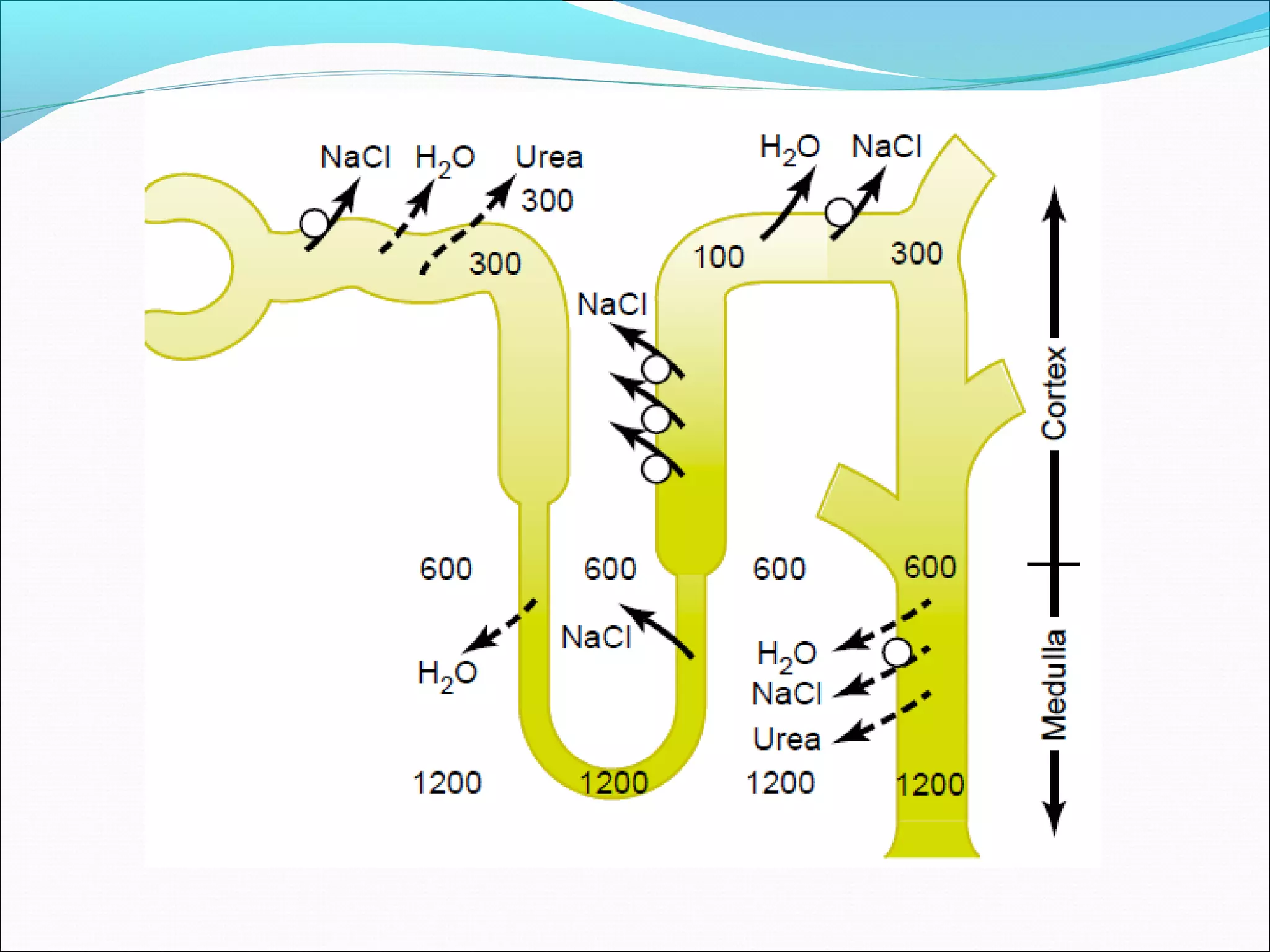
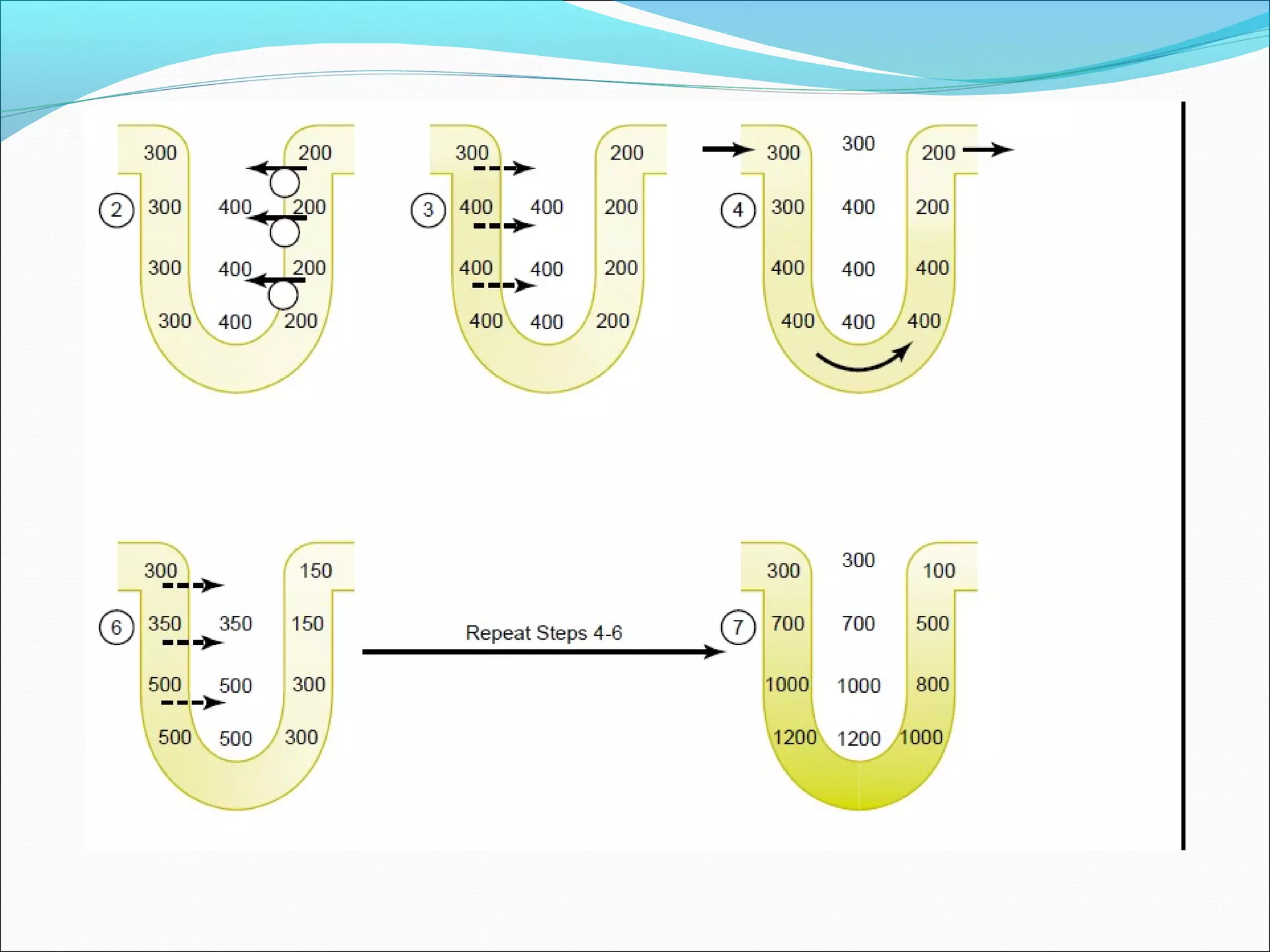
The countercurrent mechanism in the kidney produces a hyperosmotic renal medullary interstitium through three key processes: 1) the countercurrent multiplier effect of the thick ascending loop of Henle which repetitively reabsorbs sodium chloride, 2) active transport of ions from the collecting ducts into the medullary interstitium, and 3) facilitated diffusion of urea from the inner medullary collecting ducts into the medullary interstitium. This hyperosmotic interstitium is maintained by the countercurrent exchange function of the vasa recta blood vessels.