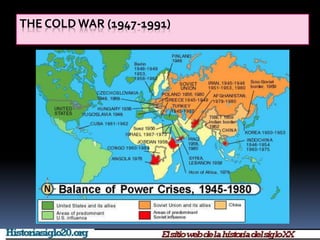
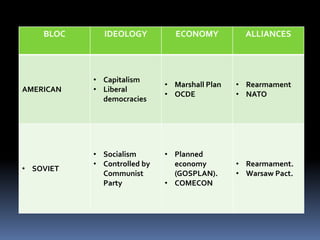
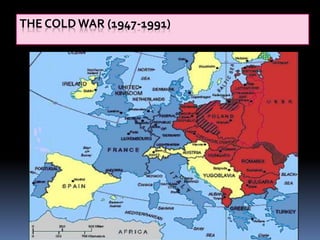
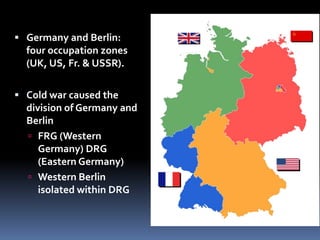
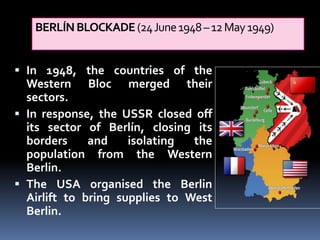
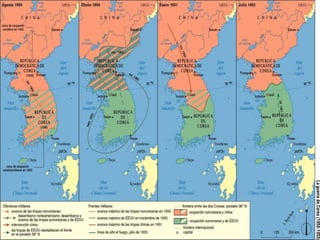
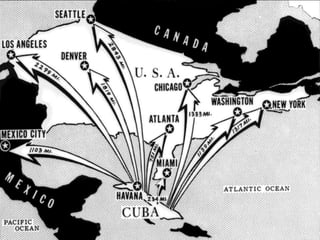
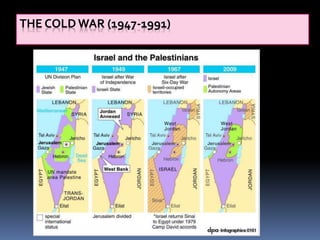
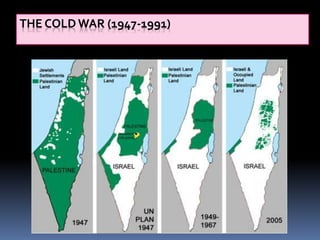
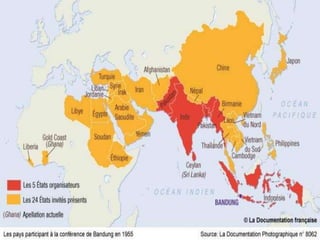
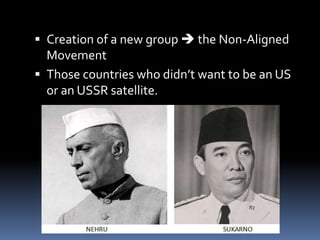
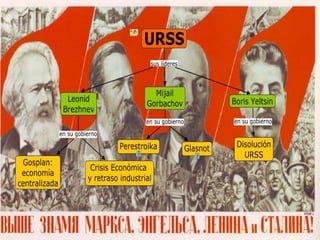
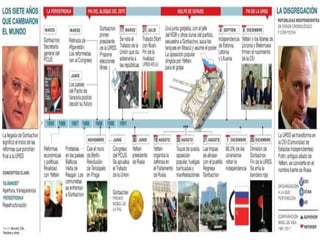
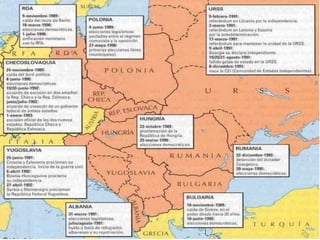
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and Soviet Union from 1947 to 1991. It involved periods of rivalry, conflicts through proxy wars, and efforts at diplomacy. Key events included the division of Germany and Berlin after WWII, the Korean War, Vietnam War, Cuban Missile Crisis, and decolonization movements supported by both superpowers to weaken European colonial powers. While never directly fighting each other, the US and USSR engaged in an arms race, ideological battles, and conflicts by backing opposing sides in regional wars throughout the world.