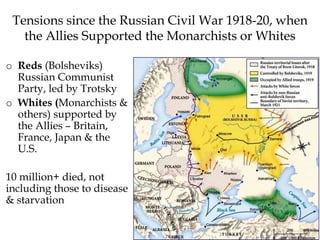
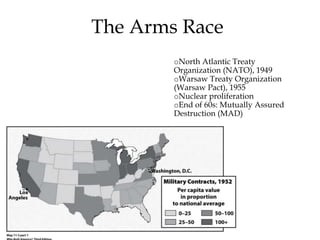
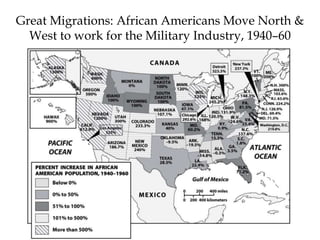
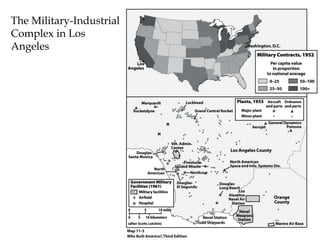
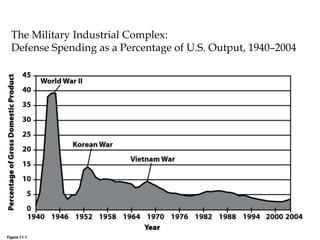
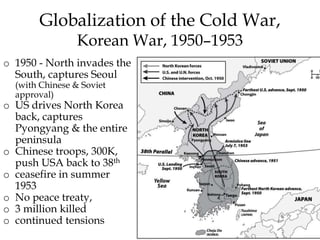
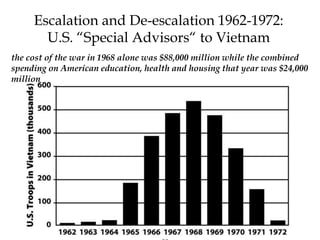
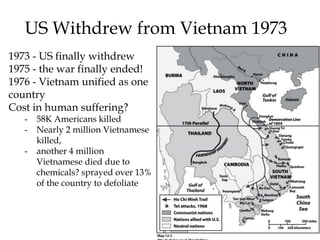
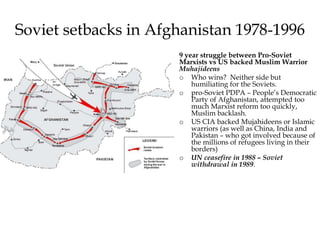
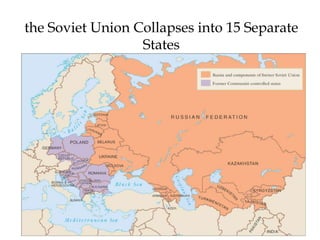
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and Soviet Union from 1947-1991. They were ideological and geopolitical rivals whose relationship polarized the world into capitalist and communist spheres of influence. While direct military conflict was avoided, there were numerous proxy wars fought around the world. Growing nationalist sentiments in Eastern Europe and reforms under Gorbachev led to the collapse of the Soviet Union and end of the Cold War in 1991.