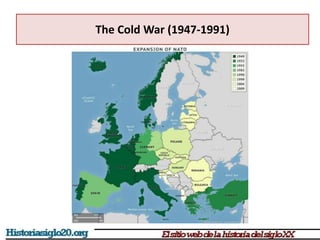
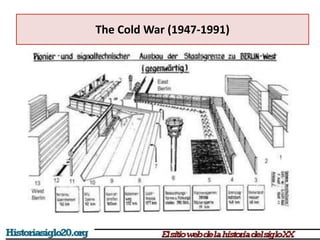
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and Soviet Union from 1947 to 1991. It started with the breakdown of the alliance between the US, Britain, and USSR after WWII and developed into a rivalry between capitalist and communist ideologies. The world divided into two opposing camps led by the two superpowers, and several proxy wars were fought globally without direct conflict between the US and USSR. The Cold War ended with the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 due to economic inefficiencies and internal political pressures.